Unsupervised image representations have significantly reduced the gap with supervised pretraining, notably with the recent achievements of contrastive learning methods. These contrastive methods typically work online and rely on a large number of explicit pairwise feature comparisons, which is computationally challenging. In this paper, we propose an online algorithm, SwAV, that takes advantage of contrastive methods without requiring to compute pairwise comparisons. Specifically, our method simultaneously clusters the data while enforcing consistency between cluster assignments produced for different augmentations (or views) of the same image, instead of comparing features directly as in contrastive learning. Simply put, we use a swapped prediction mechanism where we predict the cluster assignment of a view from the representation of another view. Our method can be trained with large and small batches and can scale to unlimited amounts of data. Compared to previous contrastive methods, our method is more memory efficient since it does not require a large memory bank or a special momentum network. In addition, we also propose a new data augmentation strategy, multi-crop, that uses a mix of views with different resolutions in place of two full-resolution views, without increasing the memory or compute requirements much. We validate our findings by achieving 75.3% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet with ResNet-50, as well as surpassing supervised pretraining on all the considered transfer tasks.
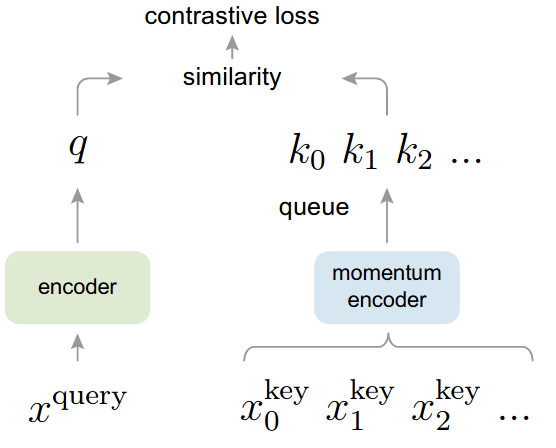
We present Momentum Contrast (MoCo) for unsupervised visual representation learning. From a perspective on contrastive learning as dictionary look-up, we build a dynamic dictionary with a queue and a moving-averaged encoder. This enables building a large and consistent dictionary on-the-fly that facilitates contrastive unsupervised learning. MoCo provides competitive results under the common linear protocol on ImageNet classification. More importantly, the representations learned by MoCo transfer well to downstream tasks. MoCo can outperform its supervised pre-training counterpart in 7 detection/segmentation tasks on PASCAL VOC, COCO, and other datasets, sometimes surpassing it by large margins. This suggests that the gap between unsupervised and supervised representation learning has been largely closed in many vision tasks.
To use a self-supervisely pretrained backbone, there are two steps to do:
- Download and convert the model to PyTorch-style supported by MMDetection
- Modify the config and change the training setting accordingly
For more general usage, we also provide script selfsup2mmdet.py in the tools directory to convert the key of models pretrained by different self-supervised methods to PyTorch-style checkpoints used in MMDetection.
python -u tools/model_converters/selfsup2mmdet.py ${PRETRAIN_PATH} ${STORE_PATH} --selfsup ${method}This script convert model from PRETRAIN_PATH and store the converted model in STORE_PATH.
For example, to use a ResNet-50 backbone released by MoCo, you can download it from here and use the following command
python -u tools/model_converters/selfsup2mmdet.py ./moco_v2_800ep_pretrain.pth.tar mocov2_r50_800ep_pretrain.pth --selfsup mocoTo use the ResNet-50 backbone released by SwAV, you can download it from here
The backbone requires SyncBN and the frozen_stages need to be changed. A config that use the moco backbone is as below
_base_ = [
'../_base_/models/mask_rcnn_r50_fpn.py',
'../_base_/datasets/coco_instance.py',
'../_base_/schedules/schedule_1x.py', '../_base_/default_runtime.py'
]
model = dict(
pretrained='./mocov2_r50_800ep_pretrain.pth',
backbone=dict(
frozen_stages=0,
norm_cfg=dict(type='SyncBN', requires_grad=True),
norm_eval=False))| Method | Backbone | Style | Lr schd | Mem (GB) | Inf time (fps) | box AP | mask AP | Config | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask RCNN | R50 by MoCo v2 | pytorch | 1x | 38.0 | 34.3 | config | model | log | ||
| Mask RCNN | R50 by MoCo v2 | pytorch | multi-scale 2x | 40.8 | 36.8 | config | model | log | ||
| Mask RCNN | R50 by SwAV | pytorch | 1x | 39.1 | 35.7 | config | model | log | ||
| Mask RCNN | R50 by SwAV | pytorch | multi-scale 2x | 41.3 | 37.3 | config | model | log |
- We only provide single-scale 1x and multi-scale 2x configs as examples to show how to use backbones trained by self-supervised algorithms. We will try to reproduce the results in their corresponding paper using the released backbone in the future. Please stay tuned.
We support to apply the backbone models pre-trained by different self-supervised methods in detection systems and provide their results on Mask R-CNN.
The pre-trained models are converted from MoCo and downloaded from SwAV.
For SwAV, please cite
@article{caron2020unsupervised,
title={Unsupervised Learning of Visual Features by Contrasting Cluster Assignments},
author={Caron, Mathilde and Misra, Ishan and Mairal, Julien and Goyal, Priya and Bojanowski, Piotr and Joulin, Armand},
booktitle={Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)},
year={2020}
}For MoCo, please cite
@Article{he2019moco,
author = {Kaiming He and Haoqi Fan and Yuxin Wu and Saining Xie and Ross Girshick},
title = {Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.05722},
year = {2019},
}
@Article{chen2020mocov2,
author = {Xinlei Chen and Haoqi Fan and Ross Girshick and Kaiming He},
title = {Improved Baselines with Momentum Contrastive Learning},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04297},
year = {2020},
}