- Neovim 0.9.5+ - Older versions are not supported, and for best compatibility 0.10.0+ is preferred
- curl - 8.0.0+ is recommended for best compatibility. Should be installed by default on most systems and also shipped with Neovim
- Copilot chat in the IDE setting enabled in GitHub settings
- (Optional) tiktoken_core - Used for more accurate token counting
- For Arch Linux users, you can install
luajit-tiktoken-binorlua51-tiktoken-binfrom aur - Alternatively, install via luarocks:
sudo luarocks install --lua-version 5.1 tiktoken_core - Alternatively, download a pre-built binary from lua-tiktoken releases. You can check your Lua PATH in Neovim by doing
:lua print(package.cpath). Save the binary astiktoken_core.soin any of the given paths.
- For Arch Linux users, you can install
- (Optional) git - Used for fetching git diffs for
gitcontext- For Arch Linux users, you can install
gitfrom the official repositories - For other systems, use your package manager to install
git. For windows use the installer provided from git site
- For Arch Linux users, you can install
- (Optional) lynx - Used for improved fetching of URLs for
urlcontext- For Arch Linux users, you can install
lynxfrom the official repositories - For other systems, use your package manager to install
lynx. For windows use the installer provided from lynx site
- For Arch Linux users, you can install
Warning
If you are on neovim < 0.11.0, you also might want to add noinsert and popup to your completeopt to make the chat completion behave well.
return {
{
"CopilotC-Nvim/CopilotChat.nvim",
dependencies = {
{ "github/copilot.vim" }, -- or zbirenbaum/copilot.lua
{ "nvim-lua/plenary.nvim", branch = "master" }, -- for curl, log and async functions
},
build = "make tiktoken", -- Only on MacOS or Linux
opts = {
-- See Configuration section for options
},
-- See Commands section for default commands if you want to lazy load on them
},
}See @jellydn for configuration
Similar to the lazy setup, you can use the following configuration:
call plug#begin()
Plug 'github/copilot.vim'
Plug 'nvim-lua/plenary.nvim'
Plug 'CopilotC-Nvim/CopilotChat.nvim'
call plug#end()
lua << EOF
require("CopilotChat").setup {
-- See Configuration section for options
}
EOF- Put the files in the right place
mkdir -p ~/.config/nvim/pack/copilotchat/start
cd ~/.config/nvim/pack/copilotchat/start
git clone https://github.com/github/copilot.vim
git clone https://github.com/nvim-lua/plenary.nvim
git clone https://github.com/CopilotC-Nvim/CopilotChat.nvim
- Add to your configuration (e.g.
~/.config/nvim/init.lua)
require("CopilotChat").setup {
-- See Configuration section for options
}See @deathbeam for configuration
:CopilotChat <input>?- Open chat window with optional input:CopilotChatOpen- Open chat window:CopilotChatClose- Close chat window:CopilotChatToggle- Toggle chat window:CopilotChatStop- Stop current copilot output:CopilotChatReset- Reset chat window:CopilotChatSave <name>?- Save chat history to file:CopilotChatLoad <name>?- Load chat history from file:CopilotChatDebugInfo- Show debug information:CopilotChatModels- View and select available models. This is reset when a new instance is made. Please set your model ininit.luafor persistence.:CopilotChatAgents- View and select available agents. This is reset when a new instance is made. Please set your agent ininit.luafor persistence.:CopilotChat<PromptName>- Ask a question with a specific prompt. For example,:CopilotChatExplainwill ask a question with theExplainprompt. See Prompts for more information.
<Tab>- Trigger completion menu for special tokens or accept current completion (see help)q/<C-c>- Close the chat window<C-l>- Reset and clear the chat window<CR>/<C-s>- Submit the current promptgr- Toggle sticky prompt for the line under cursor<C-y>- Accept nearest diff (works best withCOPILOT_GENERATEprompt)gj- Jump to section of nearest diff. If in different buffer, jumps there; creates buffer if needed (works best withCOPILOT_GENERATEprompt)gq- Add all diffs from chat to quickfix listgy- Yank nearest diff to register (defaults to")gd- Show diff between source and nearest diffgi- Show info about current chat (model, agent, system prompt)gc- Show current chat contextgh- Show help message
The mappings can be customized by setting the mappings table in your configuration. Each mapping can have:
normal: Key for normal modeinsert: Key for insert modedetail: Description of what the mapping does
For example, to change the submit prompt mapping:
{
mappings = {
submit_prompt = {
normal = '<Leader>s',
insert = '<C-s>'
}
}
}You can ask Copilot to do various tasks with prompts. You can reference prompts with /PromptName in chat or call with command :CopilotChat<PromptName>.
Default prompts are:
Explain- Write an explanation for the selected code as paragraphs of textReview- Review the selected codeFix- There is a problem in this code. Rewrite the code to show it with the bug fixedOptimize- Optimize the selected code to improve performance and readabilityDocs- Please add documentation comments to the selected codeTests- Please generate tests for my codeCommit- Write commit message for the change with commitizen convention
You can define custom prompts like this (only prompt is required):
{
prompts = {
MyCustomPrompt = {
prompt = 'Explain how it works.',
system_prompt = 'You are very good at explaining stuff',
mapping = '<leader>ccmc',
description = 'My custom prompt description',
}
}
}System prompts specify the behavior of the AI model. You can reference system prompts with /PROMPT_NAME in chat.
Default system prompts are:
COPILOT_INSTRUCTIONS- Base GitHub Copilot instructionsCOPILOT_EXPLAIN- On top of the base instructions adds coding tutor behaviorCOPILOT_REVIEW- On top of the base instructions adds code review behavior with instructions on how to generate diagnosticsCOPILOT_GENERATE- On top of the base instructions adds code generation behavior, with predefined formatting and generation rules
You can define custom system prompts like this (works same as prompts so you can combine prompt and system prompt definitions):
{
prompts = {
Yarrr = {
system_prompt = 'You are fascinated by pirates, so please respond in pirate speak.',
}
}
}You can set sticky prompt in chat by prefixing the text with > using markdown blockquote syntax.
The sticky prompt will be copied at start of every new prompt in chat window. You can freely edit the sticky prompt, only rule is > prefix at beginning of line.
This is useful for preserving stuff like context and agent selection (see below).
Example usage:
> #files
List all files in the workspace> @models Using Mistral-small
What is 1 + 11You can list available models with :CopilotChatModels command. Model determines the AI model used for the chat.
You can set the model in the prompt by using $ followed by the model name or default model via config using model key.
Default models are:
gpt-4o- This is the default Copilot Chat model. It is a versatile, multimodal model that excels in both text and image processing and is designed to provide fast, reliable responses. It also has superior performance in non-English languages. Gpt-4o is hosted on Azure.claude-3.5-sonnet- This model excels at coding tasks across the entire software development lifecycle, from initial design to bug fixes, maintenance to optimizations. GitHub Copilot uses Claude 3.5 Sonnet hosted on Amazon Web Services. Claude is not available everywhere so if you do not see it, try github codespaces or VPN.o1-preview- This model is focused on advanced reasoning and solving complex problems, in particular in math and science. It responds more slowly than the gpt-4o model. You can make 10 requests to this model per day. o1-preview is hosted on Azure.o1-mini- This is the faster version of the o1-preview model, balancing the use of complex reasoning with the need for faster responses. It is best suited for code generation and small context operations. You can make 50 requests to this model per day. o1-mini is hosted on Azure.
For more information about models, see here
You can use more models from here by using @models agent from here (example: @models Using Mistral-small, what is 1 + 11)
Agents are used to determine the AI agent used for the chat. You can list available agents with :CopilotChatAgents command.
You can set the agent in the prompt by using @ followed by the agent name or default agent via config using agent key.
Default "noop" agent is copilot.
For more information about extension agents, see here
You can install more agents from here
Contexts are used to determine the context of the chat.
You can add context to the prompt by using # followed by the context name or default context via config using context (can be single or array) key.
Any amount of context can be added to the prompt.
If context supports input, you can set the input in the prompt by using : followed by the input (or pressing complete key after :).
Default contexts are:
buffer- Includes specified buffer in chat context. Supports input (default current).buffers- Includes all buffers in chat context. Supports input (default listed).file- Includes content of provided file in chat context. Supports input.files- Includes all non-hidden files in the current workspace in chat context. Supports input (default list).files:list- Only lists file names.files:full- Includes file content for each file found. Can be slow on large workspaces, use with care.
git- Requiresgit. Includes current git diff in chat context. Supports input (default unstaged).git:unstaged- Includes unstaged changes in chat context.git:staged- Includes staged changes in chat context.
url- Includes content of provided URL in chat context. Supports input.register- Includes contents of register in chat context. Supports input (default +, e.g clipboard).
You can define custom contexts like this:
{
contexts = {
birthday = {
input = function(callback)
vim.ui.select({ 'user', 'napoleon' }, {
prompt = 'Select birthday> ',
}, callback)
end,
resolve = function(input)
input = input or 'user'
local birthday = input
if input == 'user' then
birthday = birthday .. ' birthday is April 1, 1990'
elseif input == 'napoleon' then
birthday = birthday .. ' birthday is August 15, 1769'
end
return {
{
content = birthday,
filename = input .. '_birthday',
filetype = 'text',
}
}
end
}
}
}> #birthday:user
What is my birthdaySelections are used to determine the source of the chat (so basically what to chat about).
Selections are configurable either by default or by prompt.
Default selection is visual or buffer (if no visual selection).
Selection includes content, start and end position, buffer info and diagnostic info (if available).
Supported selections that live in local select = require("CopilotChat.select") are:
select.visual- Current visual selection.select.buffer- Current buffer content.select.line- Current line content.select.unnamed- Unnamed register content. This register contains last deleted, changed or yanked content.
You can chain multiple selections like this:
{
selection = function(source)
return select.visual(source) or select.buffer(source)
end
}local chat = require("CopilotChat")
-- Open chat window
chat.open()
-- Open chat window with custom options
chat.open({
window = {
layout = 'float',
title = 'My Title',
},
})
-- Close chat window
chat.close()
-- Toggle chat window
chat.toggle()
-- Toggle chat window with custom options
chat.toggle({
window = {
layout = 'float',
title = 'My Title',
},
})
-- Reset chat window
chat.reset()
-- Ask a question
chat.ask("Explain how it works.")
-- Ask a question with custom options
chat.ask("Explain how it works.", {
selection = require("CopilotChat.select").buffer,
})
-- Ask a question and provide custom contexts
chat.ask("Explain how it works.", {
context = { 'buffers', 'files', 'register:+' },
})
-- Ask a question and do something with the response
chat.ask("Show me something interesting", {
callback = function(response)
print("Response:", response)
end,
})
-- Get all available prompts (can be used for integrations like fzf/telescope)
local prompts = chat.prompts()
-- Get last copilot response (also can be used for integrations and custom keymaps)
local response = chat.response()
-- Retrieve current chat config
local config = chat.config
print(config.model)
-- Pick a prompt using vim.ui.select
local actions = require("CopilotChat.actions")
-- Pick prompt actions
actions.pick(actions.prompt_actions({
selection = require("CopilotChat.select").visual,
}))
-- Programmatically set log level
chat.log_level("debug")Also see here:
{
-- Shared config starts here (can be passed to functions at runtime and configured via setup function)
system_prompt = prompts.COPILOT_INSTRUCTIONS, -- System prompt to use (can be specified manually in prompt via /).
model = 'gpt-4o', -- Default model to use, see ':CopilotChatModels' for available models (can be specified manually in prompt via $).
agent = 'copilot', -- Default agent to use, see ':CopilotChatAgents' for available agents (can be specified manually in prompt via @).
context = nil, -- Default context or array of contexts to use (can be specified manually in prompt via #).
temperature = 0.1, -- GPT result temperature
headless = false, -- Do not write to chat buffer and use history(useful for using callback for custom processing)
callback = nil, -- Callback to use when ask response is received
-- default selection
selection = function(source)
return select.visual(source) or select.buffer(source)
end,
-- default window options
window = {
layout = 'vertical', -- 'vertical', 'horizontal', 'float', 'replace'
width = 0.5, -- fractional width of parent, or absolute width in columns when > 1
height = 0.5, -- fractional height of parent, or absolute height in rows when > 1
-- Options below only apply to floating windows
relative = 'editor', -- 'editor', 'win', 'cursor', 'mouse'
border = 'single', -- 'none', single', 'double', 'rounded', 'solid', 'shadow'
row = nil, -- row position of the window, default is centered
col = nil, -- column position of the window, default is centered
title = 'Copilot Chat', -- title of chat window
footer = nil, -- footer of chat window
zindex = 1, -- determines if window is on top or below other floating windows
},
show_help = true, -- Shows help message as virtual lines when waiting for user input
show_folds = true, -- Shows folds for sections in chat
highlight_selection = true, -- Highlight selection
highlight_headers = true, -- Highlight headers in chat, disable if using markdown renderers (like render-markdown.nvim)
auto_follow_cursor = true, -- Auto-follow cursor in chat
auto_insert_mode = false, -- Automatically enter insert mode when opening window and on new prompt
insert_at_end = false, -- Move cursor to end of buffer when inserting text
clear_chat_on_new_prompt = false, -- Clears chat on every new prompt
-- Static config starts here (can be configured only via setup function)
debug = false, -- Enable debug logging (same as 'log_level = 'debug')
log_level = 'info', -- Log level to use, 'trace', 'debug', 'info', 'warn', 'error', 'fatal'
proxy = nil, -- [protocol://]host[:port] Use this proxy
allow_insecure = false, -- Allow insecure server connections
chat_autocomplete = true, -- Enable chat autocompletion (when disabled, requires manual `mappings.complete` trigger)
history_path = vim.fn.stdpath('data') .. '/copilotchat_history', -- Default path to stored history
question_header = '# User ', -- Header to use for user questions
answer_header = '# Copilot ', -- Header to use for AI answers
error_header = '# Error ', -- Header to use for errors
separator = '───', -- Separator to use in chat
-- default contexts
contexts = {
buffer = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
buffers = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
file = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
files = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
git = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
url = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
register = {
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
},
-- default prompts
prompts = {
Explain = {
prompt = '> /COPILOT_EXPLAIN\n\nWrite an explanation for the selected code as paragraphs of text.',
},
Review = {
prompt = '> /COPILOT_REVIEW\n\nReview the selected code.',
-- see config.lua for implementation
},
Fix = {
prompt = '> /COPILOT_GENERATE\n\nThere is a problem in this code. Rewrite the code to show it with the bug fixed.',
},
Optimize = {
prompt = '> /COPILOT_GENERATE\n\nOptimize the selected code to improve performance and readability.',
},
Docs = {
prompt = '> /COPILOT_GENERATE\n\nPlease add documentation comments to the selected code.',
},
Tests = {
prompt = '> /COPILOT_GENERATE\n\nPlease generate tests for my code.',
},
Commit = {
prompt = '> #git:staged\n\nWrite commit message for the change with commitizen convention. Make sure the title has maximum 50 characters and message is wrapped at 72 characters. Wrap the whole message in code block with language gitcommit.',
},
},
-- default mappings
mappings = {
complete = {
insert = '<Tab>',
},
close = {
normal = 'q',
insert = '<C-c>',
},
reset = {
normal = '<C-l>',
insert = '<C-l>',
},
submit_prompt = {
normal = '<CR>',
insert = '<C-s>',
},
toggle_sticky = {
detail = 'Makes line under cursor sticky or deletes sticky line.',
normal = 'gr',
},
accept_diff = {
normal = '<C-y>',
insert = '<C-y>',
},
jump_to_diff = {
normal = 'gj',
},
quickfix_diffs = {
normal = 'gq',
},
yank_diff = {
normal = 'gy',
register = '"',
},
show_diff = {
normal = 'gd',
},
show_info = {
normal = 'gi',
},
show_context = {
normal = 'gc',
},
show_help = {
normal = 'gh',
},
},
}You can set local options for the buffers that are created by this plugin, copilot-chat, copilot-diff, copilot-overlay:
vim.api.nvim_create_autocmd('BufEnter', {
pattern = 'copilot-*',
callback = function()
vim.opt_local.relativenumber = true
-- C-p to print last response
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-p>', function()
print(require("CopilotChat").response())
end, { buffer = true, remap = true })
end
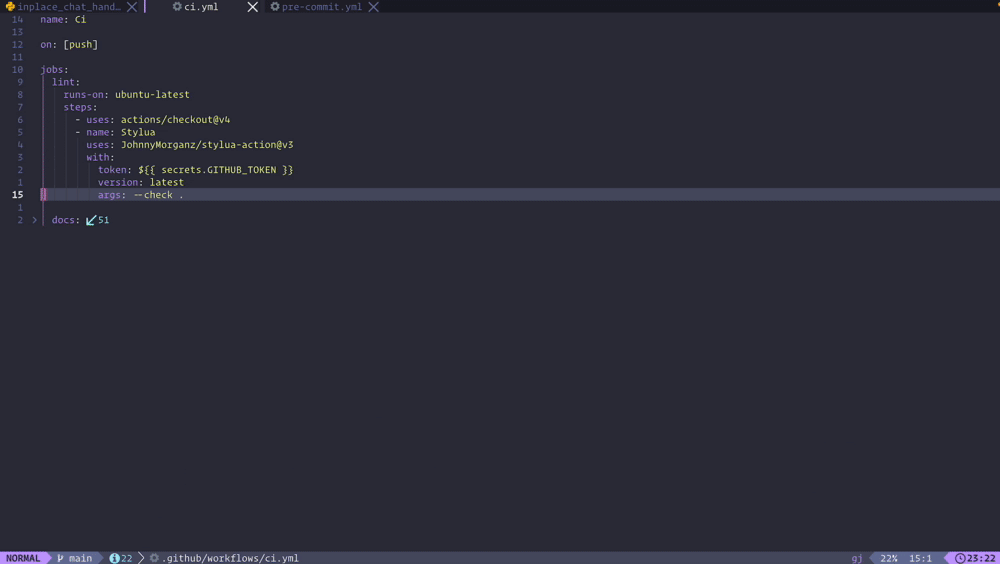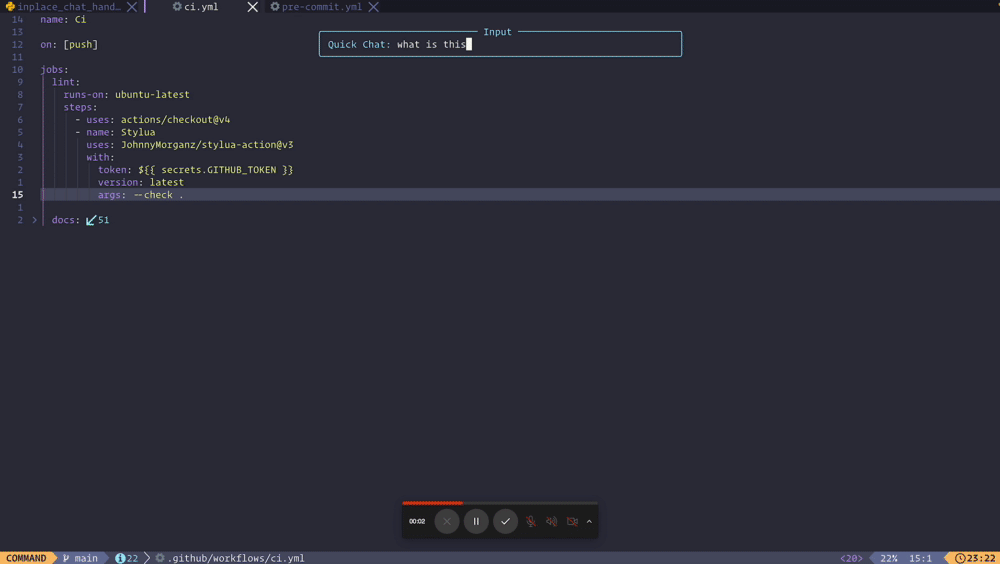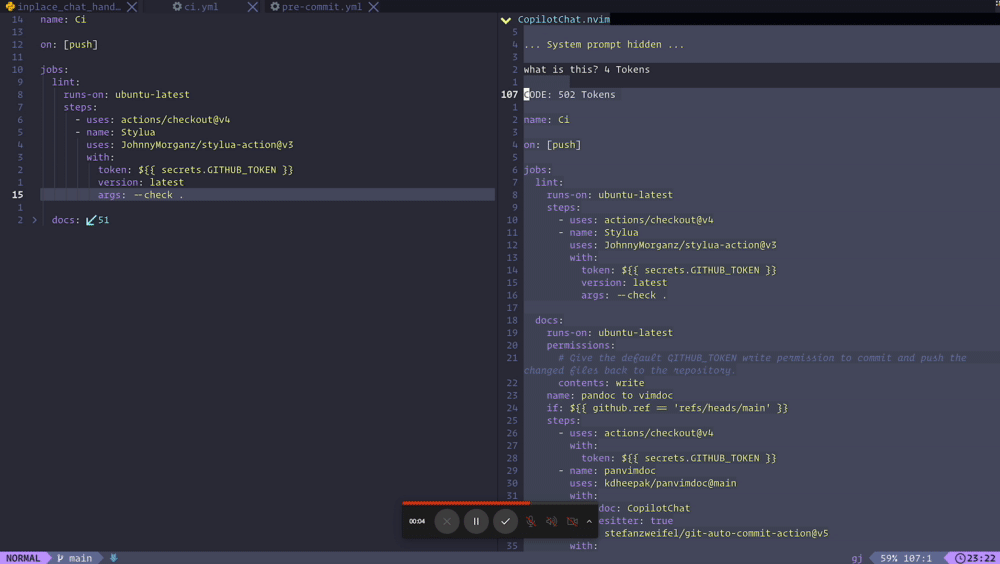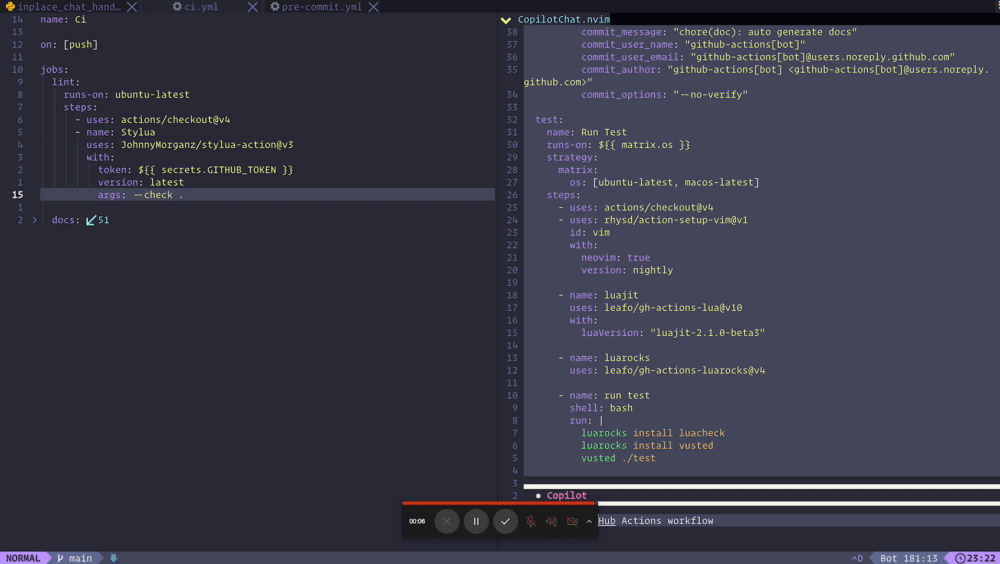
})Quick chat with your buffer
To chat with Copilot using the entire content of the buffer, you can add the following configuration to your keymap:
-- lazy.nvim keys
-- Quick chat with Copilot
{
"<leader>ccq",
function()
local input = vim.fn.input("Quick Chat: ")
if input ~= "" then
require("CopilotChat").ask(input, { selection = require("CopilotChat.select").buffer })
end
end,
desc = "CopilotChat - Quick chat",
}Inline chat
Change the window layout to float and position relative to cursor to make the window look like inline chat.
This will allow you to chat with Copilot without opening a new window.
-- lazy.nvim opts
{
window = {
layout = 'float',
relative = 'cursor',
width = 1,
height = 0.4,
row = 1
}
}Telescope integration
Requires telescope.nvim plugin to be installed.
-- lazy.nvim keys
-- Show prompts actions with telescope
{
"<leader>ccp",
function()
local actions = require("CopilotChat.actions")
require("CopilotChat.integrations.telescope").pick(actions.prompt_actions())
end,
desc = "CopilotChat - Prompt actions",
},fzf-lua integration
Requires fzf-lua plugin to be installed.
-- lazy.nvim keys
-- Show prompts actions with fzf-lua
{
"<leader>ccp",
function()
local actions = require("CopilotChat.actions")
require("CopilotChat.integrations.fzflua").pick(actions.prompt_actions())
end,
desc = "CopilotChat - Prompt actions",
},render-markdown integration
Requires render-markdown plugin to be installed.
-- Registers copilot-chat filetype for markdown rendering
require('render-markdown').setup({
file_types = { 'markdown', 'copilot-chat' },
})
-- You might also want to disable default header highlighting for copilot chat when doing this and set error header style and separator
require('CopilotChat').setup({
highlight_headers = false,
separator = '---',
error_header = '> [!ERROR] Error',
-- rest of your config
})- Improved caching for context (persistence through restarts/smarter caching)
- General QOL improvements
For development, you can use the provided Makefile command to install the pre-commit tool:
make install-pre-commitThis will install the pre-commit tool and the pre-commit hooks.
If you want to contribute to this project, please read the CONTRIBUTING.md file.
Thanks goes to these wonderful people (emoji key):
This project follows the all-contributors specification. Contributions of any kind are welcome!