-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
[树 🌲] #2
Comments
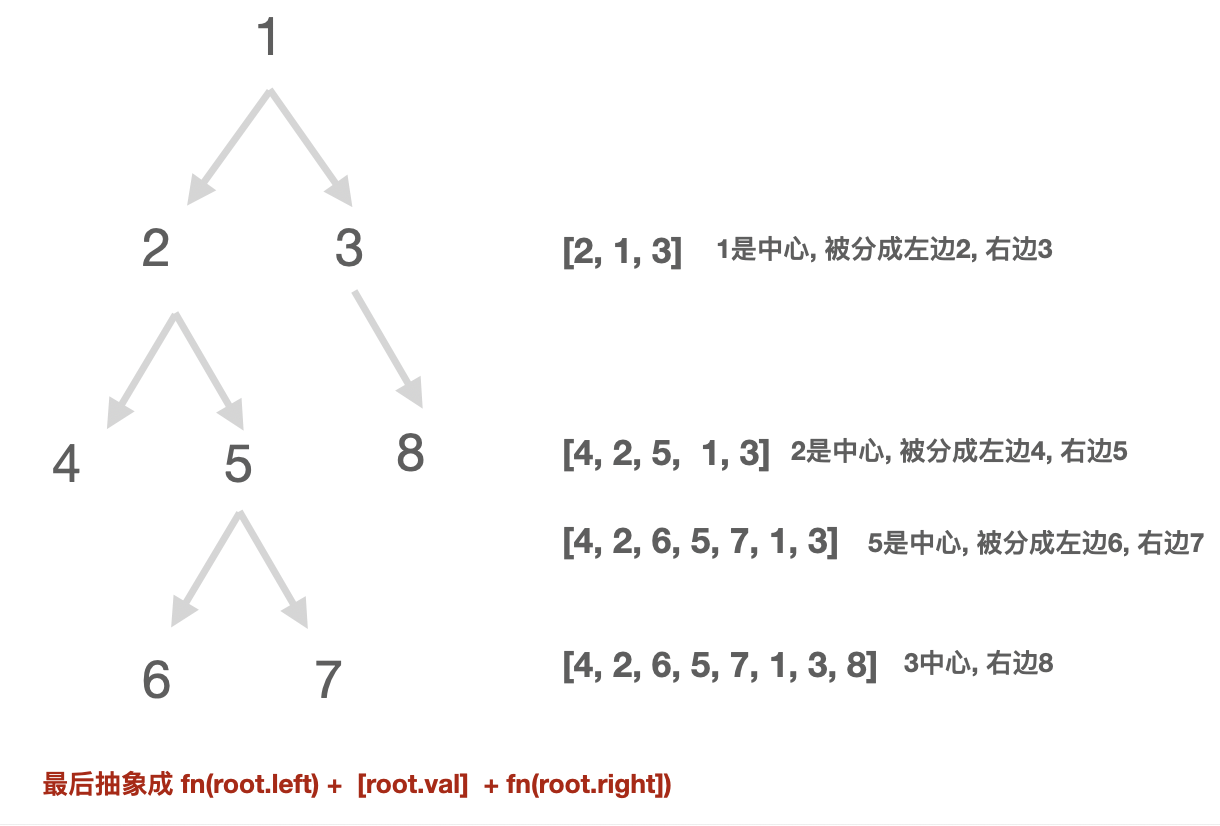
1 - 先序遍历144. 二叉树的前序遍历589. N叉树的前序遍历114. 二叉树展开为链表 给定一个二叉树,原地将它展开为一个单链表方法1 - 迭代 入栈root 先入栈执行, 虽然是left 优先级大于right, 但因为是入栈 pop出去的是栈顶内容, 所以先right 入栈, 后left 入栈, 再left出栈, right出栈。 # 迭代
class Solution(object):
def preorderTraversal(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
stack, result = [root], []
while stack: # 栈一直有值
root = stack.pop()
# root优先级最高
if root is not None:
result.append(root.val)
# 第二优先级应该是left, 但因为是数组, 最先pop的是优先级高的, 所以是right先入栈
if root.right is not None: stack.append(root.right)
if root.left is not None: stack.append(root.left)
return resultvar preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) {
return [];
}
var result = [];
var stack = [root];
while (stack.length > 0) {
var node = stack.pop();
result.push(node.val);
if (node) {
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return result;
};方法2 - 递归 分裂class Solution:
def preorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
def traverse(root):
if root is None: return [] # 必须给这个结束标识
return [root.val] + traverse(root.left) + traverse(root.right)
return traverse(root)// JS 递归
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
var result = [];
function traverse (node, result) {
if (node) {
result.push(node.val);
traverse(node.left, result);
traverse(node.right, result);
}
}
traverse(root, result);
return result;
};# 114. 二叉树展开为链表
class Solution:
def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
"""
# 深度优先搜索 前序遍历 中左右
if root is None: return None
stack = [(root, 'light')]
result = TreeNode(None)
tmp = result
while stack:
(node, flag) = stack.pop()
if node:
if flag == 'light':
if node.right: stack.append((node.right, 'light'))
if node.left: stack.append((node.left, 'light'))
node.left = None # 把自己变成叶子节点
node.right = None
stack.append((node, 'grey'))
else:
tmp.right = node
tmp = tmp.right
return result.right |
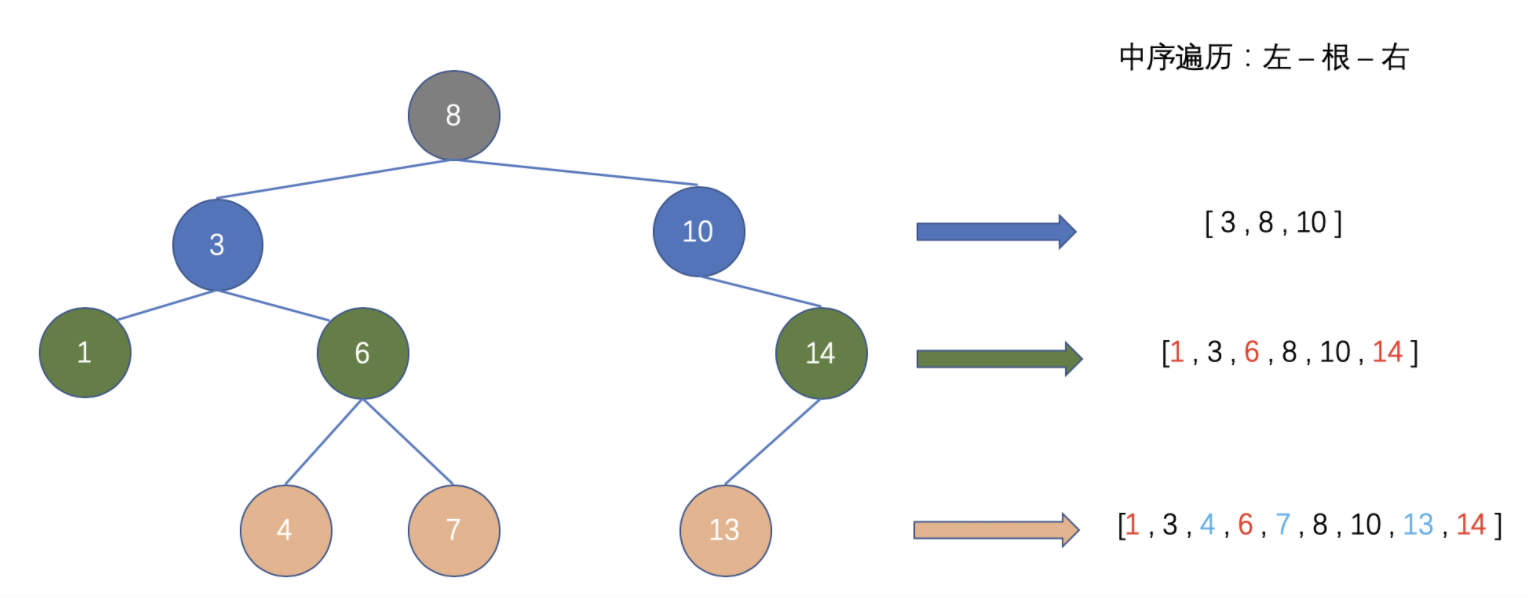
2 - 中序遍历94. 二叉树的中序遍历173. 二叉搜索树迭代器迭代 1# 迭代
class Solution:
def inorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if root is None: return []
stack, result = [(root, 'active')], []
while stack:
(node, status) = stack.pop()
if status == 'active':
node.right and stack.append((node.right, 'active')) # right后执行, 先入栈
stack.append((node, 'grey'))
node.left and stack.append((node.left, 'active')) # left最先执行, 后入栈
else:
result.append(node.val) # 置灰状态直接返回值, 说明已经遍历完左子树了。
return result// 这个写法并不是非常的好
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
var result = [];
var stack = [{ node: root, isTraversed: false }];
while (stack.length > 0) {
var { node, isTraversed } = stack.pop();
if (node) {
if (isTraversed === true) {
result.push(node.val);
} else {
node.right && stack.push({ node: node.right, isTraversed: false });
stack.push({ node, isTraversed: true });
node.left && stack.push({ node: node.left, isTraversed: false });
}
}
}
return result;
};迭代 2
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
var result = [];
var stack = [];
while (root || stack.length > 0) {
// 左侧子树, 全部放进栈中
while (root) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
var node = stack.pop();
result.push(node.val);
// 遇到右侧子树,作为新节点,再次左侧子树处理
root = node.right;
}
return result;
};递归# 递归
class Solution(object):
def inorderTraversal(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# left => root => right
def traverse(node):
if node is None: return []
return traverse(node.left) + [node.val] + traverse(node.right)
return traverse(root)var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
var result = [];
function traverse (node, result) {
if (node) {
traverse(node.left, result);
result.push(node.val);
traverse(node.right, result);
}
}
traverse(root, result);
return result;
}; |
3 - 后序遍历145. 二叉树的后序遍历# 迭代 同上面一样, 取色 取状态判断
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def postorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
# 迭代
if root is None: return []
stack, result = [(root, 'active')], []
while stack:
(node, status) = stack.pop()
if status == 'active':
stack.append((node, 'grey'))
node.right and stack.append((node.right, 'active'))
node.left and stack.append((node.left, 'active'))
else:
result.append(node.val)
return resultvar postorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
var stack = [{ node: root, flag: false }];
var result = [];
while (stack.length > 0) {
var { node, flag } = stack.pop();
if (flag === true) {
result.push(node.val);
} else {
// [中, 右, 左]
node && stack.push({ node, flag: true });
node.right && stack.push({ node: node.right, flag: false });
node.left && stack.push({ node: node.left, flag: false });
}
}
return result;
};# 递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def postorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
# 递归
if root is None: return []
return self.postorderTraversal(root.left) + self.postorderTraversal(root.right) + [root.val]var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
var result = [];
function traverse (node, result) {
if (node) {
traverse(node.left, result);
traverse(node.right, result);
result.push(node.val);
}
}
traverse(root, result);
return result;
};剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点通过遍历树来解决, 优先级为 右 中 左 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def kthLargest(self, root: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:
# right root left遍历
if root is None: return root
stack = [(root, 'light')]
x = 1
while stack:
(node, flag) = stack.pop() # pop最后一个
if node:
if flag == 'light':
# 右中左, 后执行后入栈
if node.left: stack.append((node.left, 'light'))
stack.append((node, 'grey'))
if node.right: stack.append((node.right, 'light'))
else:
if x != k: x += 1
else: return node.val |
4 - 广度优先搜索102. 二叉树的层序遍历116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II# 迭代
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
"""
current = [当前执行节点]
child = [当前执行节点.left, 当前执行节点.right]
遍历current, 当current遍历结束, 则current = child, child = []
直到current为空, 结束
"""
if root is None: return []
current = [root]
result = []
while current:
tmp, child = [], []
for node in current:
tmp.append(node.val)
if node.left: child.append(node.left)
if node.right: child.append(node.right)
result.append(tmp)
current = child
return result// 层次遍历 递归
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return []
var result = []
var traverse = (node, i) => {
if (!node) return
if (!result[i] || result[i] && result[i].length === 0) {
result[i] = [node.val]
} else {
result[i].push(node.val)
}
return traverse(node.left, i + 1) || traverse(node.right, i + 1)
}
traverse(root, 0)
return result
}// 递归
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
var result = [];
function traverse (node, layer = 0) {
if (node) {
if (result[layer]) {
result[layer].push(node.val);
} else {
result.push([node.val]);
}
}
node.left && traverse(node.left, layer + 1);
node.right && traverse(node.right, layer + 1);
}
traverse(root, 0);
return result;
};// 迭代
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
var result = [];
var cur_layer = [root];
var child_layer = [];
while (cur_layer.length > 0) {
var tmp_result = [];
for (i = 0; i < cur_layer.length; i++) {
var node = cur_layer[i];
if (node) {
tmp_result.push(node.val);
node.left && child_layer.push(node.left);
node.right && child_layer.push(node.right);
}
}
cur_layer = child_layer;
child_layer = [];
result.push(tmp_result);
}
return result;
}; |
5 - 最大深度104. 二叉树的最大深度559. N叉树的最大深度
# 递归
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None: return 0
return max(self.maxDepth(root.left), self.maxDepth(root.right)) + 1# 迭代
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# 先序遍历, 每层深度保存, 并和暂存区最大对比
if root is None: return 0
stack = [(root, 1)] # 此时root是一个节点, 深度为1
_max = 1
while stack:
(node, depth) = stack.pop()
_max = max(_max, depth) # 当前深度和最大比较
if node.right: stack.append((node.right, depth + 1)) # 先将右子树入栈, 并深度 +1
if node.left: stack.append((node.left, depth + 1)) # 先将左子树入栈, 并深度 +1
return _max |
6 - * 对称二叉树 * 未独立思考出来 TODO 迭代101. 对称二叉树镜子原理, 整出来两棵树, p1 和 p2 进行对比 对比逻辑是 # 递归
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
# 镜子
def mirror(p1, p2):
if p1 is None and p2 is None: # 都是空, 则返回True
return True
if p1 and p2 and p1.val == p2.val: # 当前结点 值 相同, 则去比较子树内容。
return mirror(p1.left, p2.right) and mirror(p1.right, p2.left)
return False
return mirror(root, root)# 递归 在一棵树上的递归遍历
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if root is None: return True
def compare(p1, p2):
if p1 is None and p2 is None: return True # 叶子节点
if p1 and p2 and p1.val == p2.val: # 那就继续走下去
return compare(p1.left, p2.right) and compare(p1.right, p2.left)
return False
return compare(root.left, root.right) |
7 - 路径总和112. 路径总和
# 递归
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if root is None:
return False
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return root.val == sum # 是个叶子节点, 且值匹配
sum -= root.val
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum)# 迭代
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
# 深度优先搜索, 中序遍历
# 广度优先搜索
if root is None: return False
current = [root]
while current:
child = []
for i in current:
# 如果到头了 是个叶子节点, 就比较值 有的话就直接返回
if i.val == sum and i.left is None and i.right is None:
return True
if i.left:
i.left.val += i.val
child.append(i.left)
if i.right:
i.right.val += i.val
child.append(i.right)
current = child
return False剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径 进阶🔥同 113. 路径总和 II# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if root is None: return []
if root and root.left is None and root.right is None:
return [[root.val]] if root.val == sum else []
result = []
def traverse (node, _sum, tmpList):
if node:
val = node.val
# 叶子节点 且 值为0
if _sum - val == 0 and node.left is None and node.right is None:
result.append(tmpList + [val])
traverse(node.left, _sum - val, tmpList + [val])
traverse(node.right, _sum - val, tmpList + [val])
traverse(root.left, sum - root.val, [root.val])
traverse(root.right, sum - root.val, [root.val])
return result |
8 - 二叉树镜像面试题27. 二叉树的镜像同 226. 翻转二叉树# 递归
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if root is None: return None
def swap(node):
if node:
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left # 交换
swap(node.left) # 继续处理左子树
swap(node.right) # 继续处理右子树
swap(root)
return root# 迭代
class Solution(object):
def invertTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# 迭代 广度优先遍历, 将节点遍历交换
if root is None: return None
stack = [root]
while stack:
child = [] # 将节点放到child里面
for node in stack:
if node:
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left # 将节点left, right 交换
child.append(node.left)
child.append(node.right)
stack = child
return root |
9 - 树的子结构面试题26. 树的子结构# 广度优先迭代 + isSubTree 子节点判断递归
class Solution:
def isSubTree(self, A, B):
if A is None and B: return False # A都遍历完了, B还有
if B is None: return True # B反正遍历完了, 返回True
# 是否是子树结构
if A.val == B.val:
return self.isSubTree(A.left, B.left) and self.isSubTree(A.right, B.right)
def isSubStructure(self, A: TreeNode, B: TreeNode) -> bool:
# 广度优先遍历
if A is None or B is None: return False
stack = [A]
while stack:
child = []
for node in stack:
if node:
if node.val == B.val: # 如果节点相同,就去找
if self.isSubTree(node, B) == True: return True # 判断当前结点是否是子节点
child.append(node.left) # 继续找
child.append(node.right)
stack = child
return False |
10 - 重建二叉树105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树同 剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if len(preorder) == 0: return None
if len(preorder) == 1: return TreeNode(preorder[0])
root_val = preorder.pop(0) # 先序遍历第一个肯定是 root
root = TreeNode(root_val) # 创建root
# i = 0
# while i < len(inorder):
# if inorder[i] == root_val:
# break
# i+= 1
i = inorder.index(root_val) # 找位置
root.left = self.buildTree(preorder[0: i], inorder[0: i])
root.right = self.buildTree(preorder[i: ], inorder[i+1: ])
return root106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树# 跟上面一样的类型,思路要整理清晰
class Solution(object):
def buildTree(self, inorder, postorder):
if len(inorder) == 0: return None
if len(inorder) == 1: return TreeNode(inorder[0])
# postorder[-1] 最后一个肯定是 root
root_val = postorder[-1]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
index = inorder.index(root_val) # 找值, 返回 index
root.left = self.buildTree(inorder[0: index], postorder[0: index])
root.right = self.buildTree(inorder[index + 1: ], postorder[index: len(postorder) - 1])
return root |
11 - 二叉树🌲 公共祖先 / 二叉搜索树🌲 公共祖先236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先同 剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先二叉树🌲 公共祖先class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if root is None: return None
# 有一个是root点, 就返回root
if root == p or root == q: return root
# 左右子树在同一层上, 就返回root
if root.left == p and root.right == q or root.right == p and root.left == q: return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if left is None or right is None: return right or left
else: return root二叉搜索树🌲 公共祖先剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先同 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if root is None: return None
if root == p or root == q: return root
if (root.left == p and root.right == q) or (root.left == q and root.right == p): return root
# 都在左侧
if p.val < root.val and q.val < root.val: return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
# 都在右侧
if p.val > root.val and q.val > root.val: return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
# 在左右侧都有, 则返回root
return root |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment












No description provided.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: