This package was designed as part of an academic project at the Université Lumière Lyon 2. The objective was to develop an R package following the R6 standard which implements a naive Bayesian classification.
The naive Bayesian classifier is a probabilistic classification method based on Bayes' theorem. The model assumes conditional independence between features, which simplifies calculations and allows rapid classification. Despite its simplicity, the naive Bayesian classifier is powerful and efficient.
Here are some different features of our package that we will present to you below.
- Model training
The package allow users to train the model by providing a training dataset with corresponding features and class labels. - Prediction Once the model is trained, users will be able to make predictions on new data by providing the features, and the package will return the associated class predictions or probability of each class.
- Categorical data handling
The package supports data mixing and provides tools for encoding categorical variables. - Performance evaluation
The package provide tools to evaluate the performance of the model, including accuracy, precision, recall and F1-measure. - Documentation
Detailed documentation, including usage examples and explanations of settings, is be available to help users get the most out of the package.
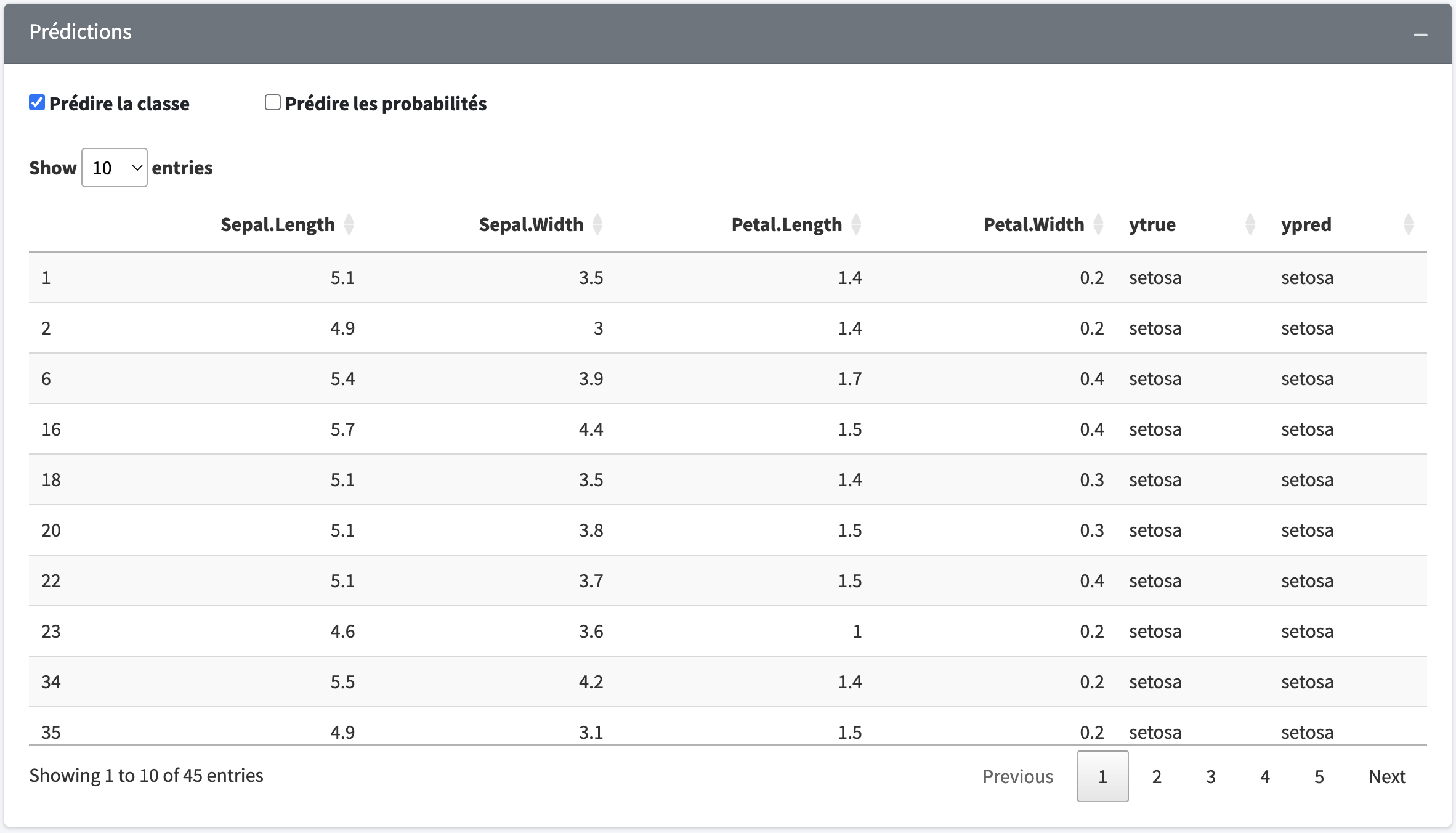
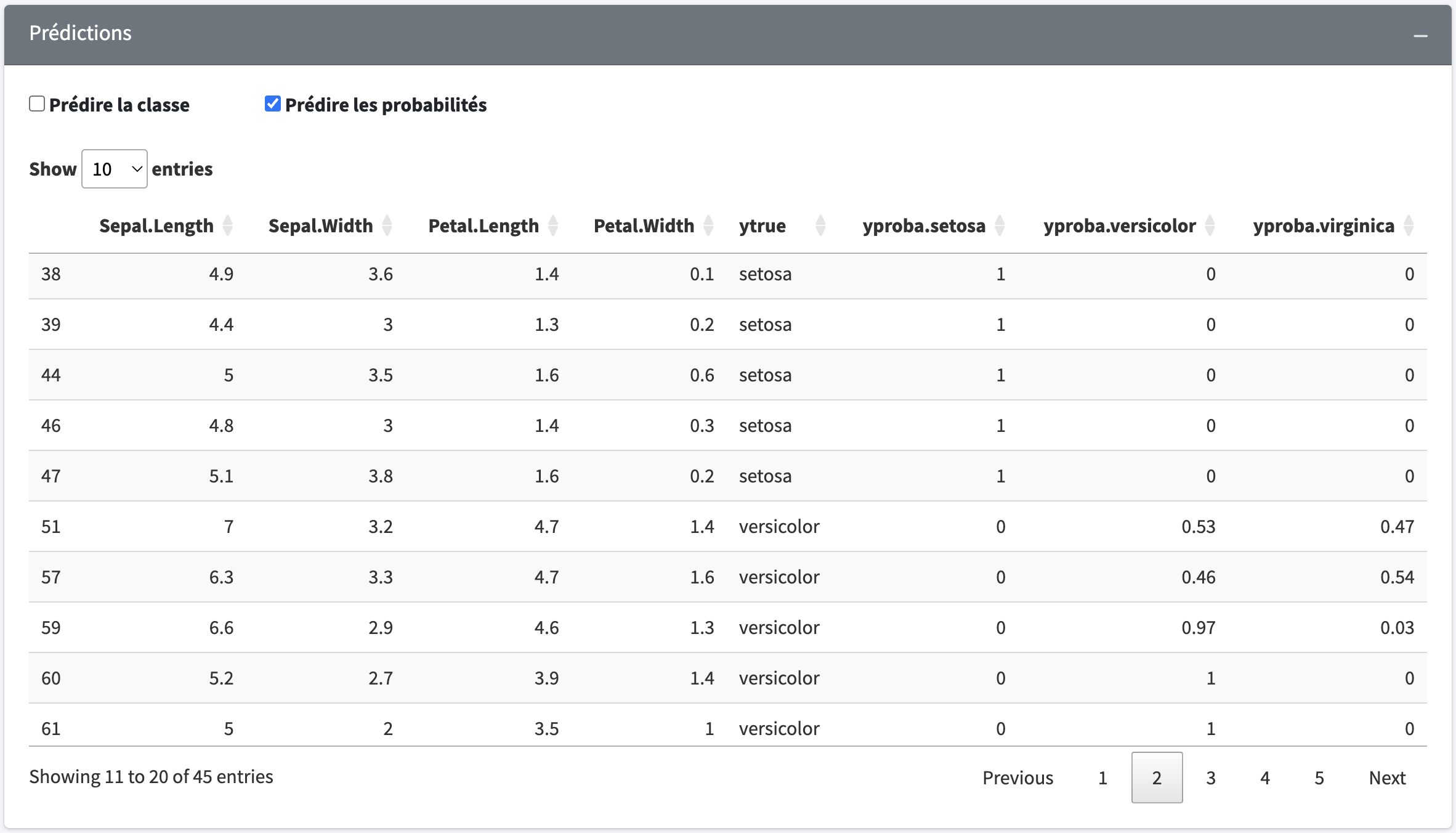
We have developed an r-shiny application which allows you to test the different functionalities of the package.
In order to use our package, you should install it from Github.
1.1 Install and load devtools
install.packages("devtools")library(devtools)1.2 Install an load our package NaiveBayes
install_github("Naghan1132/naive_bayes_R")library(NaiveBayes)To access the complete documentation for this package, use the help functions built into R.
You can get help on any class or function in the package by using the help() function in the R console. For example:
help("naive_bayes")Another way to get help is to use the ? symbol followed by the function name. For example:
?naive_bayesBelow is a use of the NaiveBayes package with the iris dataset (150 observations, 4 explanatory variables and 1 target variable)
# load iris dataset
data("iris")The train_test_split function takes a data frame as input and returns two datasets (a training dataset and a test dataset). As a parameter you can enter:
- The proportional size of the training dataset
train_size. - The name of the variable to use to
stratifythe split (the target variable). This ensures that the distribution of classes of this given variable in the training set is similar to that in the testing set. - The
seedthat ensures that the split results will be consistent each time the code runs.
sets <- train_test_split(iris, train_size = 0.7, stratify = 'Species', seed <- 123)- The train set
# 5 is the index of target variable Species
Xtrain <- sets$train_set[-5]
ytrain <- sets$train_set[[5]]- The test set
Xtest <- sets$test_set[-5]
ytest <- sets$test_set[[5]]To use the classifier you must instantiate the naive_bayes class.
model <- naive_bayes$new()You can use also use the classifier in parallel mode by specifying multi_thread and the number of CPU to use n_cluster.
model <- naive_bayes$new(multi_thread = TRUE, n_cluster=2)To train the model on the training game you must use the fit method of the naive_bayes class.
model$fit(Xtrain, ytrain)You can then perform a prediction on the test set
ypred <- model$predict(Xtest)You can also get the probabilities associated with each class
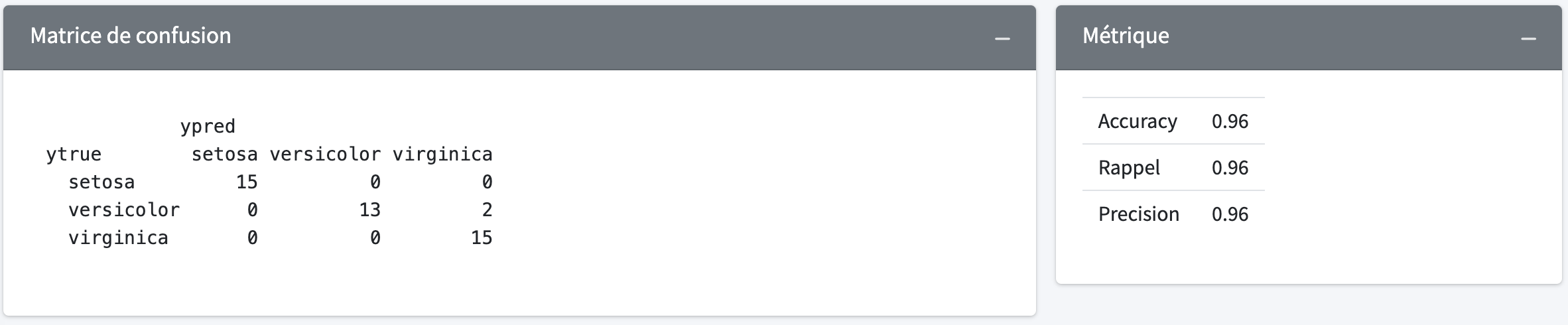
probas <- model$predict_proba(Xtest)There is a set of functions available in the metrics class to evaluate the performance of your model.
metrics$confusion_matrix(ytest, ypred)metrics$accuracy_score(ytest, ypred)metrics$recall_score(ytest, ypred)metrics$precision_score(ytest, ypred)The package also includes the encoder class one_hot_encode which allows you to perform an one-hot of encoding
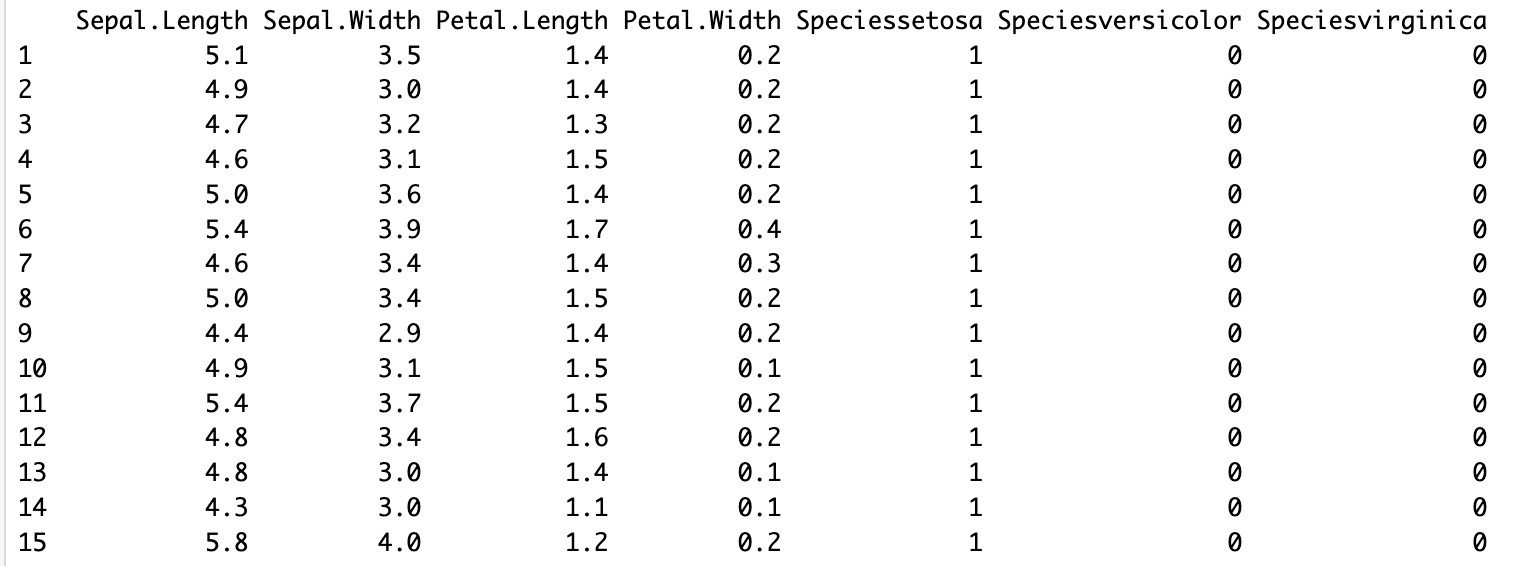
Create an instance of the One-Hot Encoder
encoder_ <- one_hot_encoder$new()Fit the encoder to your data
encoder_$fit(iris)Transform your data using the fitted encoder.
encoder_$transform(iris)The transform method will return a modified version of your data with one-hot encoded categorical variables.
We have developed an r-shiny application which allows you to test the different functionalities of ours package. This application allows users, whether novice or expert in R programming, to easily explore the capabilities of the Naive Bayesian classifier without requiring any prior knowledge in-depth programming. It allows, among other things, to train and save a model for later use.
It is available at the following address: https://moiseberthe.shinyapps.io/naive-bayes-r-shiny/