A CLI tool and Go library for generating a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) from container images and filesystems. Exceptional for vulnerability detection when used with a scanner like Grype.
- Calendar: https://calendar.google.com/calendar/u/0/r?cid=Y182OTM4dGt0MjRtajI0NnNzOThiaGtnM29qNEBncm91cC5jYWxlbmRhci5nb29nbGUuY29t
- Agenda: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1ZtSAa6fj2a6KRWviTn3WoJm09edvrNUp4Iz_dOjjyY8/edit?usp=sharing (join this group for write access)
- All are welcome!
- Generates SBOMs for container images, filesystems, archives, and more to discover packages and libraries
- Supports OCI and Docker image formats
- Linux distribution identification
- Works seamlessly with Grype (a fast, modern vulnerability scanner)
- Able to create signed SBOM attestations using the in-toto specification
- Alpine (apk)
- Dart (pubs)
- Debian (dpkg)
- Go (go.mod, Go binaries)
- Java (jar, ear, war, par, sar)
- JavaScript (npm, yarn)
- Jenkins Plugins (jpi, hpi)
- PHP (composer)
- Python (wheel, egg, poetry, requirements.txt)
- Red Hat (rpm)
- Ruby (gem)
- Rust (cargo.lock)
Note: Currently, Syft is built only for Linux, macOS and Windows.
curl -sSfL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anchore/syft/main/install.sh | sh -s -- -b /usr/local/bin... or, you can specify a release version and destination directory for the installation:
curl -sSfL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/anchore/syft/main/install.sh | sh -s -- -b <DESTINATION_DIR> <RELEASE_VERSION>
brew tap anchore/syft
brew install syftNote: Nix packaging of Syft is community maintained. Syft is currently only in the unstable channel awaiting the 22.05 release
nix-env -i syft... or, just try it out in an ephemeral nix shell:
nix-shell -p syftTo generate an SBOM for a container image:
syft <image>
The above output includes only software that is visible in the container (i.e., the squashed representation of the image). To include software from all image layers in the SBOM, regardless of its presence in the final image, provide --scope all-layers:
syft <image> --scope all-layers
To generate an SBOM attestation for a container image:
syft attest --output [FORMAT] --key [KEY] [SOURCE] [flags]
The above output is in the form of the DSSE envelope.
The payload is a base64 encoded in-toto statement with the generated SBOM as the predicate. For details on workflows using this command see here.
Syft can generate a SBOM from a variety of sources:
# catalog a container image archive (from the result of `docker image save ...`, `podman save ...`, or `skopeo copy` commands)
syft path/to/image.tar
# catalog a directory
syft path/to/dir
Sources can be explicitly provided with a scheme:
docker:yourrepo/yourimage:tag use images from the Docker daemon
podman:yourrepo/yourimage:tag use images from the Podman daemon
docker-archive:path/to/yourimage.tar use a tarball from disk for archives created from "docker save"
oci-archive:path/to/yourimage.tar use a tarball from disk for OCI archives (from Skopeo or otherwise)
oci-dir:path/to/yourimage read directly from a path on disk for OCI layout directories (from Skopeo or otherwise)
dir:path/to/yourproject read directly from a path on disk (any directory)
file:path/to/yourproject/file read directly from a path on disk (any single file)
registry:yourrepo/yourimage:tag pull image directly from a registry (no container runtime required)
Syft can exclude files and paths from being scanned within a source by using glob expressions
with one or more --exclude parameters:
syft <source> --exclude './out/**/*.json' --exclude /etc
Note: in the case of image scanning, since the entire filesystem is scanned it is
possible to use absolute paths like /etc or /usr/**/*.txt whereas directory scans
exclude files relative to the specified directory. For example: scanning /usr/foo with
--exclude ./package.json would exclude /usr/foo/package.json and --exclude '**/package.json'
would exclude all package.json files under /usr/foo. For directory scans,
it is required to begin path expressions with ./, */, or **/, all of which
will be resolved relative to the specified scan directory. Keep in mind, your shell
may attempt to expand wildcards, so put those parameters in single quotes, like:
'**/*.json'.
The output format for Syft is configurable as well using the
-o (or --output) option:
syft <image> -o <format>
Where the formats available are:
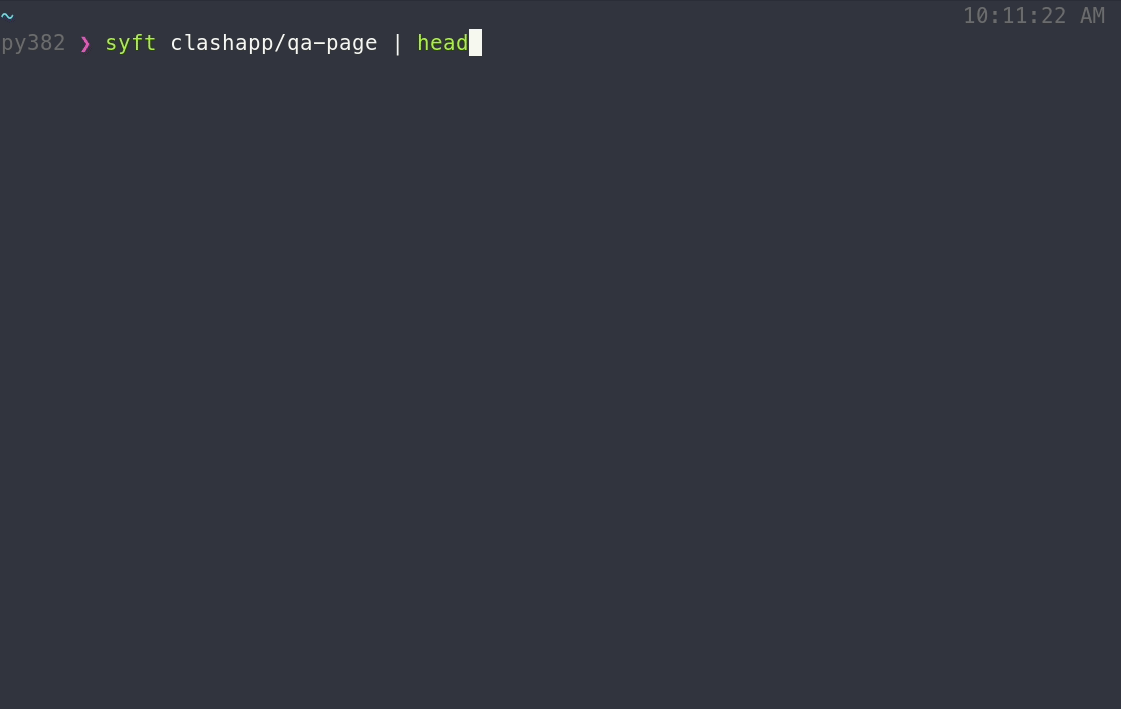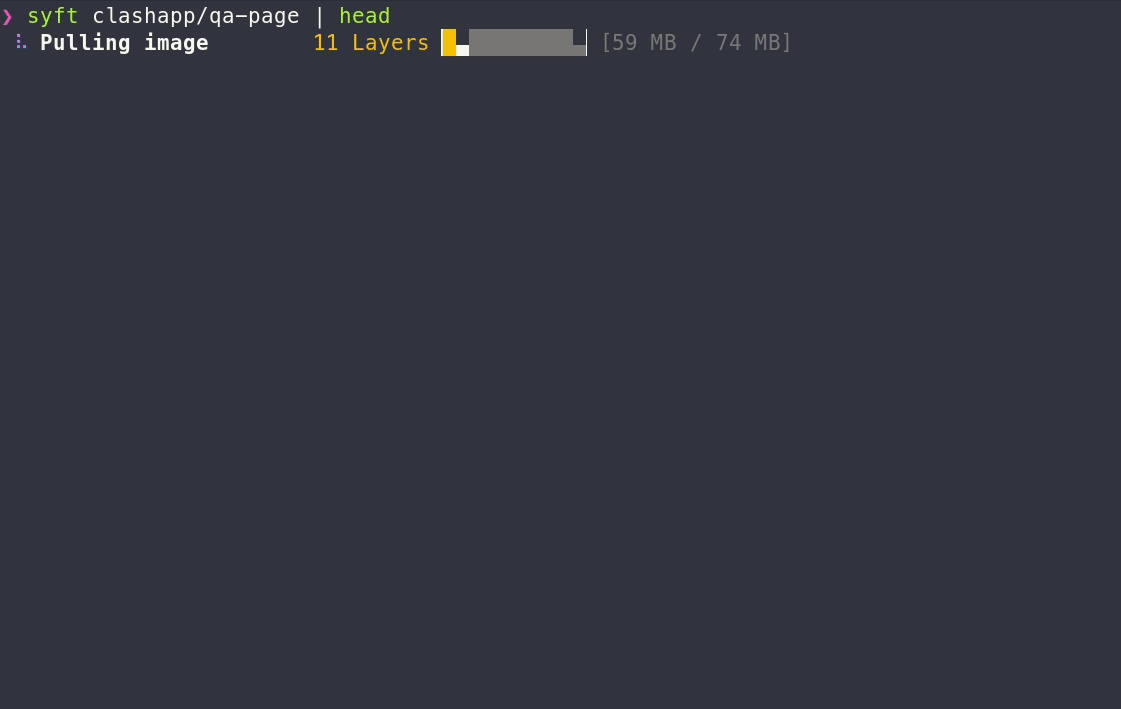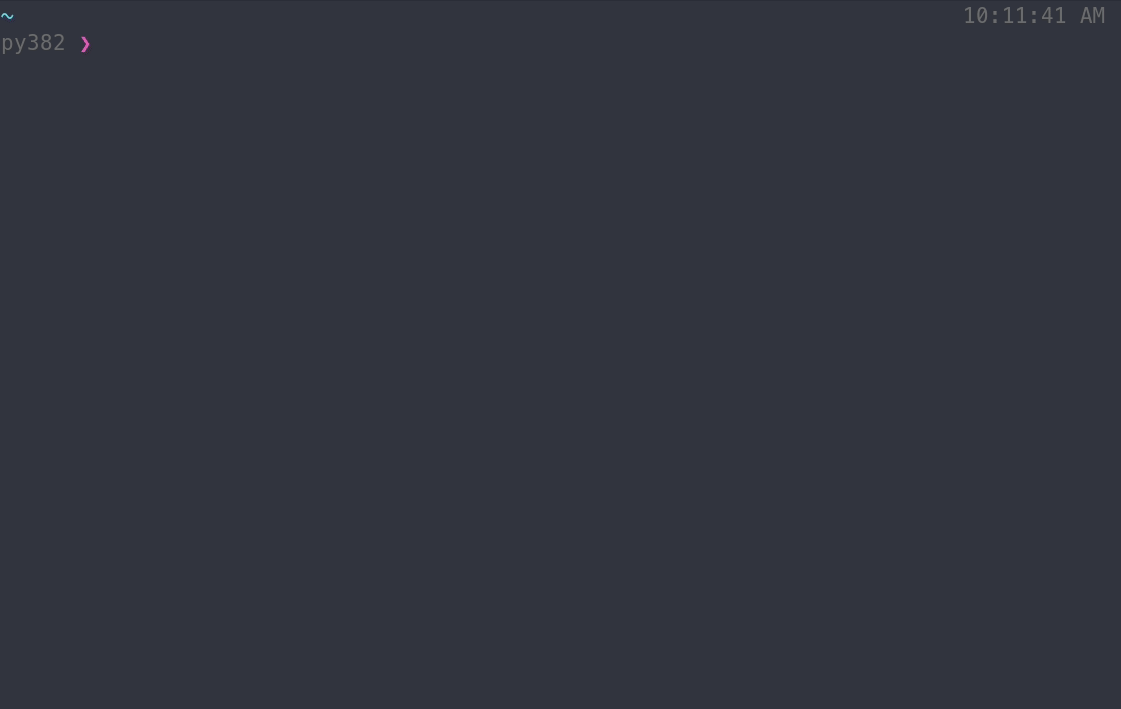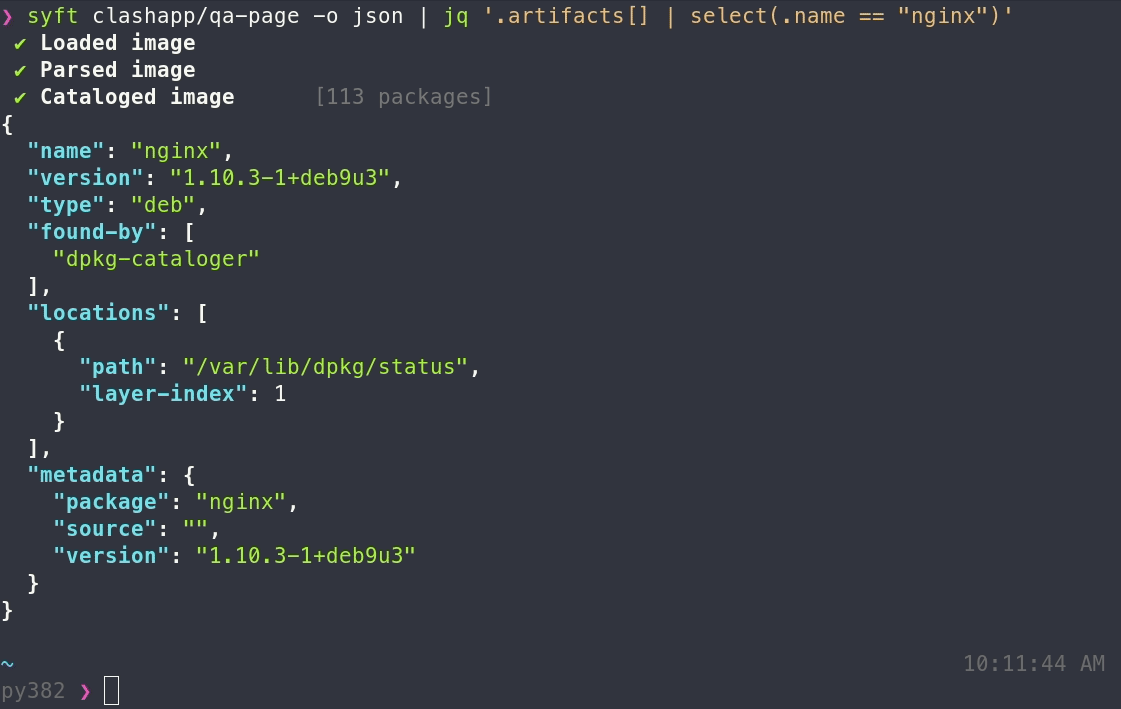
json: Use this to get as much information out of Syft as possible!text: A row-oriented, human-and-machine-friendly output.cyclonedx: A XML report conforming to the CycloneDX 1.3 specification.cyclonedx-json: A JSON report conforming to the CycloneDX 1.3 specification.spdx: A tag-value formatted report conforming to the SPDX 2.2 specification.spdx-json: A JSON report conforming to the SPDX 2.2 JSON Schema.table: A columnar summary (default).
Syft can also output multiple files in differing formats by appending
=<file> to the option, for example to output Syft JSON and SPDX JSON:
syft <image> -o json=sbom.syft.json -o spdx-json=sbom.spdx.jsonWhen a container runtime is not present, Syft can still utilize credentials configured in common credential sources (such as ~/.docker/config.json). It will pull images from private registries using these credentials. The config file is where your credentials are stored when authenticating with private registries via some command like docker login. For more information see the go-containerregistry documentation.
An example config.json looks something like this:
{
"auths": {
"registry.example.com": {
"username": "AzureDiamond",
"password": "hunter2"
}
}
}You can run the following command as an example. It details the mount/environment configuration a container needs to access a private registry:
docker run -v ./config.json:/config/config.json -e "DOCKER_CONFIG=/config" anchore/syft:latest <private_image>
Here's a simple workflow to mount this config file as a secret into a container on Kubernetes.
-
Create a secret. The value of
config.jsonis important. It refers to the specification detailed here. Below this section is thesecret.yamlfile that the pod configuration will consume as a volume. The keyconfig.jsonis important. It will end up being the name of the file when mounted into the pod.# secret.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: registry-config namespace: syft data: config.json: <base64 encoded config.json>
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml -
Create your pod running syft. The env
DOCKER_CONFIGis important because it advertises where to look for the credential file. In the below example, settingDOCKER_CONFIG=/configinforms syft that credentials can be found at/config/config.json. This is why we usedconfig.jsonas the key for our secret. When mounted into containers the secrets' key is used as the filename. ThevolumeMountssection mounts our secret to/config. Thevolumessection names our volume and leverages the secret we created in step one.# pod.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: syft-k8s-usage spec: containers: - image: anchore/syft:latest name: syft-private-registry-demo env: - name: DOCKER_CONFIG value: /config volumeMounts: - mountPath: /config name: registry-config readOnly: true args: - <private_image> volumes: - name: registry-config secret: secretName: registry-config
kubectl apply -f pod.yaml -
The user can now run
kubectl logs syft-private-registry-demo. The logs should show the Syft analysis for the<private_image>provided in the pod configuration.
Using the above information, users should be able to configure private registry access without having to do so in the grype or syft configuration files. They will also not be dependent on a Docker daemon, (or some other runtime software) for registry configuration and access.
Configuration search paths:
.syft.yaml.syft/config.yaml~/.syft.yaml<XDG_CONFIG_HOME>/syft/config.yaml
Configuration options (example values are the default):
# the output format(s) of the SBOM report (options: table, text, json, spdx, ...)
# same as -o, --output, and SYFT_OUTPUT env var
# to specify multiple output files in differing formats, use a list:
# output:
# - "json=<syft-json-output-file>"
# - "spdx-json=<spdx-json-output-file>"
output: "table"
# suppress all output (except for the SBOM report)
# same as -q ; SYFT_QUIET env var
quiet: false
# same as --file; write output report to a file (default is to write to stdout)
file: ""
# enable/disable checking for application updates on startup
# same as SYFT_CHECK_FOR_APP_UPDATE env var
check-for-app-update: true
# a list of globs to exclude from scanning. same as --exclude ; for example:
# exclude:
# - "/etc/**"
# - "./out/**/*.json"
exclude: []
# os and/or architecture to use when referencing container images (e.g. "windows/armv6" or "arm64")
# same as --platform; SYFT_PLATFORM env var
platform: ""
# cataloging packages is exposed through the packages and power-user subcommands
package:
# search within archives that do contain a file index to search against (zip)
# note: for now this only applies to the java package cataloger
# SYFT_PACKAGE_SEARCH_INDEXED_ARCHIVES env var
search-indexed-archives: true
# search within archives that do not contain a file index to search against (tar, tar.gz, tar.bz2, etc)
# note: enabling this may result in a performance impact since all discovered compressed tars will be decompressed
# note: for now this only applies to the java package cataloger
# SYFT_PACKAGE_SEARCH_UNINDEXED_ARCHIVES env var
search-unindexed-archives: false
cataloger:
# enable/disable cataloging of packages
# SYFT_PACKAGE_CATALOGER_ENABLED env var
enabled: true
# the search space to look for packages (options: all-layers, squashed)
# same as -s ; SYFT_PACKAGE_CATALOGER_SCOPE env var
scope: "squashed"
# cataloging file classifications is exposed through the power-user subcommand
file-classification:
cataloger:
# enable/disable cataloging of file classifications
# SYFT_FILE_CLASSIFICATION_CATALOGER_ENABLED env var
enabled: true
# the search space to look for file classifications (options: all-layers, squashed)
# SYFT_FILE_CLASSIFICATION_CATALOGER_SCOPE env var
scope: "squashed"
# cataloging file contents is exposed through the power-user subcommand
file-contents:
cataloger:
# enable/disable cataloging of secrets
# SYFT_FILE_CONTENTS_CATALOGER_ENABLED env var
enabled: true
# the search space to look for secrets (options: all-layers, squashed)
# SYFT_FILE_CONTENTS_CATALOGER_SCOPE env var
scope: "squashed"
# skip searching a file entirely if it is above the given size (default = 1MB; unit = bytes)
# SYFT_FILE_CONTENTS_SKIP_FILES_ABOVE_SIZE env var
skip-files-above-size: 1048576
# file globs for the cataloger to match on
# SYFT_FILE_CONTENTS_GLOBS env var
globs: []
# cataloging file metadata is exposed through the power-user subcommand
file-metadata:
cataloger:
# enable/disable cataloging of file metadata
# SYFT_FILE_METADATA_CATALOGER_ENABLED env var
enabled: true
# the search space to look for file metadata (options: all-layers, squashed)
# SYFT_FILE_METADATA_CATALOGER_SCOPE env var
scope: "squashed"
# the file digest algorithms to use when cataloging files (options: "sha256", "md5", "sha1")
# SYFT_FILE_METADATA_DIGESTS env var
digests: ["sha256"]
# cataloging secrets is exposed through the power-user subcommand
secrets:
cataloger:
# enable/disable cataloging of secrets
# SYFT_SECRETS_CATALOGER_ENABLED env var
enabled: true
# the search space to look for secrets (options: all-layers, squashed)
# SYFT_SECRETS_CATALOGER_SCOPE env var
scope: "all-layers"
# show extracted secret values in the final JSON report
# SYFT_SECRETS_REVEAL_VALUES env var
reveal-values: false
# skip searching a file entirely if it is above the given size (default = 1MB; unit = bytes)
# SYFT_SECRETS_SKIP_FILES_ABOVE_SIZE env var
skip-files-above-size: 1048576
# name-regex pairs to consider when searching files for secrets. Note: the regex must match single line patterns
# but may also have OPTIONAL multiline capture groups. Regexes with a named capture group of "value" will
# use the entire regex to match, but the secret value will be assumed to be entirely contained within the
# "value" named capture group.
additional-patterns: {}
# names to exclude from the secrets search, valid values are: "aws-access-key", "aws-secret-key", "pem-private-key",
# "docker-config-auth", and "generic-api-key". Note: this does not consider any names introduced in the
# "secrets.additional-patterns" config option.
# SYFT_SECRETS_EXCLUDE_PATTERN_NAMES env var
exclude-pattern-names: []
# options when pulling directly from a registry via the "registry:" scheme
registry:
# skip TLS verification when communicating with the registry
# SYFT_REGISTRY_INSECURE_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY env var
insecure-skip-tls-verify: false
# use http instead of https when connecting to the registry
# SYFT_REGISTRY_INSECURE_USE_HTTP env var
insecure-use-http: false
# credentials for specific registries
auth:
# the URL to the registry (e.g. "docker.io", "localhost:5000", etc.)
# SYFT_REGISTRY_AUTH_AUTHORITY env var
- authority: ""
# SYFT_REGISTRY_AUTH_USERNAME env var
username: ""
# SYFT_REGISTRY_AUTH_PASSWORD env var
password: ""
# note: token and username/password are mutually exclusive
# SYFT_REGISTRY_AUTH_TOKEN env var
token: ""
# - ... # note, more credentials can be provided via config file only
# generate an attested SBOM
attest:
# path to the private key file to use for attestation
# SYFT_ATTEST_KEY env var
key: "cosign.key"
# password to decrypt to given private key
# SYFT_ATTEST_PASSWORD env var, additionally responds to COSIGN_PASSWORD
password: ""
log:
# use structured logging
# same as SYFT_LOG_STRUCTURED env var
structured: false
# the log level; note: detailed logging suppress the ETUI
# same as SYFT_LOG_LEVEL env var
level: "error"
# location to write the log file (default is not to have a log file)
# same as SYFT_LOG_FILE env var
file: ""
# uploading package SBOM is exposed through the packages subcommand
anchore:
# (feature-preview) the Anchore Enterprise Host or URL to upload results to (supported on Enterprise 3.0+)
# same as -H ; SYFT_ANCHORE_HOST env var
host: ""
# (feature-preview) the path after the host to the Anchore External API (supported on Enterprise 3.0+)
# same as SYFT_ANCHORE_PATH env var
path: ""
# (feature-preview) the username to authenticate against Anchore Enterprise (supported on Enterprise 3.0+)
# same as -u ; SYFT_ANCHORE_USERNAME env var
username: ""
# (feature-preview) the password to authenticate against Anchore Enterprise (supported on Enterprise 3.0+)
# same as -p ; SYFT_ANCHORE_PASSWORD env var
password: ""
# (feature-preview) path to dockerfile to be uploaded with the syft results to Anchore Enterprise (supported on Enterprise 3.0+)
# same as -d ; SYFT_ANCHORE_DOCKERFILE env var
dockerfile: ""syft attest --output [FORMAT] --key [KEY] [SOURCE] [flags]
SBOMs themselves can serve as input to different analysis tools. Grype, a vulnerability scanner CLI tool from Anchore, is one such tool. Publishers of container images can use attestations to enable their consumers to trust Syft-generated SBOM descriptions of those container images. To create and provide these attestations, image publishers can run syft attest in conjunction with the cosign tool to attach SBOM attestations to their images.
Note for the following example replace docker.io/image:latest with an image you own. You should also have push access to
its remote reference. Replace $MY_PRIVATE_KEY with a private key you own or have generated with cosign.
syft attest --key $MY_PRIVATE_KEY docker.io/image:latest > image_latest_sbom_attestation.json
cosign attach attestation --attestation image_latest_sbom_attestation.json docker.io/image:latestVerify the new attestation exists on your image.
cosign verify-attestation -key $MY_PUBLIC_KEY docker.io/image:latest | jq '.payload | @base64d | .payload | fromjson | .predicate'You should see this output along with the attached SBOM:
Verification for docker.io/image:latest --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- The signatures were verified against the specified public key
- Any certificates were verified against the Fulcio roots.
Consumers of your image can now trust that the SBOM associated with your image is correct and from a trusted source.