-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 17
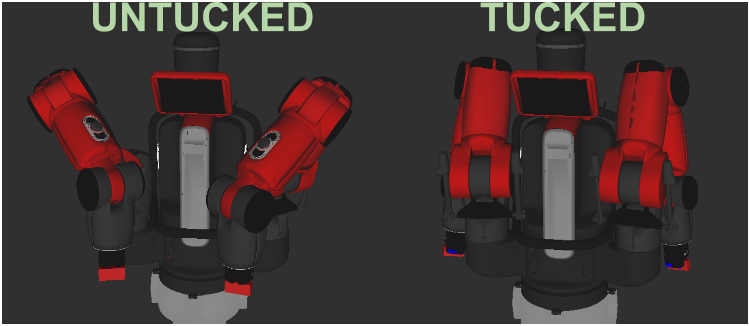
Tuck Arms Example
The tuck arms example program will allow you to tuck/untuck Baxter's arms to/from 'shipping pose'.
To Untuck the robot's arms:
$ rosrun tools tuck_arms.py -u
To Tuck the robot's arms:
$ rosrun tools tuck_arms.py -t
The pose that Baxter is shipping in is referred to as 'shipping pose'. This tool is particularly useful for the initial unpacking of Baxter. This tools is also useful for subsequent movements of Baxter (ie. moving Baxter through doorways etc.) as this is the most compact form for Baxter's transportation.
Important Note: Please make sure no other control programs are running as this tools disables collision avoidance.
To get help on tuck_arms use the -h argument:
$ rosrun tools tuck_arm.py -h
Help screen:
tuck_arms.py [ARGUMENTS]
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-t, --tuck tuck arms
-t, --untuck untuck arms
Use -t to tuck Baxter's arms.
$ rosrun tools tuck_arms.py -t
If not already in 'tucked' position, the robot will come to a neutral pose, disable collision avoidance and tuck the arms into the 'tucked' position, disabling on completion.
Use -u to untuck Baxter's arms.
$ rosrun tools tuck_arms.py -u
If Baxter is in the 'tucked' position, collision avoidance will be disabled, and the arms will untuck into the 'untucked' pose where the robot will remain enabled. If Baxter is not tucked at program start, collision avoidance will remain enabled, and Baxter will move to the 'untucked' position.
Make sure that your network connection is configured allowing you to make commands to the robot: https://github.com/RethinkRobotics/sdk-docs/wiki/Connecting-and-Testing-the-Development-Workstation
Particularly that your ROS_HOSTNAME is resolvable to the robot, or alternatively setting your ROS_IP to your current ip address (make sure that your ROS_HOSTNAME is not set when using this approach). http://www.ros.org/wiki/ROS/NetworkSetup#Name_resolution
If your robot "fails to reset" when you running untuck/tuck arms example, the first thing to check is if the E-Stop is engaged:
$ rosrun tools enable_robot -s
enabled: False
stopped: True
error: True
estop_button: 1
estop_source: 1 If the estop_button: field says '1', it means the E-Stop is engaged (from [baxter_msgs/AssemblyState][baxter_msgs-AssemblyState] message: uint8 ESTOP_BUTTON_PRESSED=1).
Disengage the E-Stop by twisting the red top until it 'pops'-up, then try resetting the robot.
$ rosrun tools enable_robot -r[baxter_msgs-AssemblyState]: http://github.com/RethinkRobotics/sdk-examples/blob/master/baxter/baxter_msgs/msg/AssemblyState.msg
© 2008-2013 Rethink Robotics. All rights reserved. ![]()