Skeleton application for ZoneMTA based SMTP servers.
This is a skeleton application to run ZoneMTA based MTA/MSA servers. Download it, tweak it and run it to have a high performance SMTP server.
ZoneMTA is a modern open source MTA/MSA server. You can use it as a SMTP smarthost or a MSA host, it is fast and scalable, you can send many millions of emails a day with it.
ZoneMTA also comes with features usually available only for commercial SMTP servers like Virtual MTAs (or "sending zones" in ZoneMTA speak), IP pooling and rotation, IP warm-up, IP blacklist detection and mitigation, clustered setup with a shared queue and so on. ZoneMTA is battle tested with more than 100 million successful deliveries from a single server.
ZoneMTA is not a MX server. You can use it as such but it lacks all the utilities that are needed to fight inbound spam. Better look at Haraka if you are in need of a good MX server.
It is also not meant to deliver marketing emails. You can obviously do it but the intended use case is to cater the needs of an ISP, where a continous and neverending flow of variously sized messages (from simple "thanks!" to 30MB PDF attachments) are sent by its users. Marketing emails usually mean huge spikes where a large amount of rather small messages are inserted to the sending queue at once. ZoneMTA should handle this at ease as well, even though it was built for something different.
- Node.js
- MongoDB
- Redis
- Avast (optional) virus scanner (get it here)
Fetch the ZoneMTA application template
$ git clone git://github.com/zone-eu/zone-mta-template.git
$ cd zone-mta-template
$ npm install --production
$ npm start
If everything succeeds then you should have a SMTP relay with no authentication running on localhost port 2525 (does not accept remote connections).
If you want to use Avast for scanning messages for viruses, then install Avast Core Security to the same machine you are running ZoneMTA from and then enable the virus scanner plugin which is disabled by default.
The default SMTP interface called "feeder" has authentication enabled with default username as "user" and password as "secret". Authentication can be enabled disabled with the authentication switch. If authentication is enabled then username and password can be validated with a plugin. There's an example authentication plugin that can be used to create custom auth logic.
All configuration files reside in the config directory. If you want to move that directory to somewhere else then you can do that, though you would have to provide the new location as a command line argument.
$ mv config /etc/zonemta
$ node index.js --config=/etc/zonemta/zonemta.toml
You can find an example systemd unit file from the setup folder.
To see the current config run the following. This shows the fully merged config tree:
$ npm run config
> { name: 'ZoneMTA',
ident: 'zone-mta',
dbs:
{ mongo: ...
ZoneMTA exposes monitoring data for Prometheus from http://localhost:12080/metrics
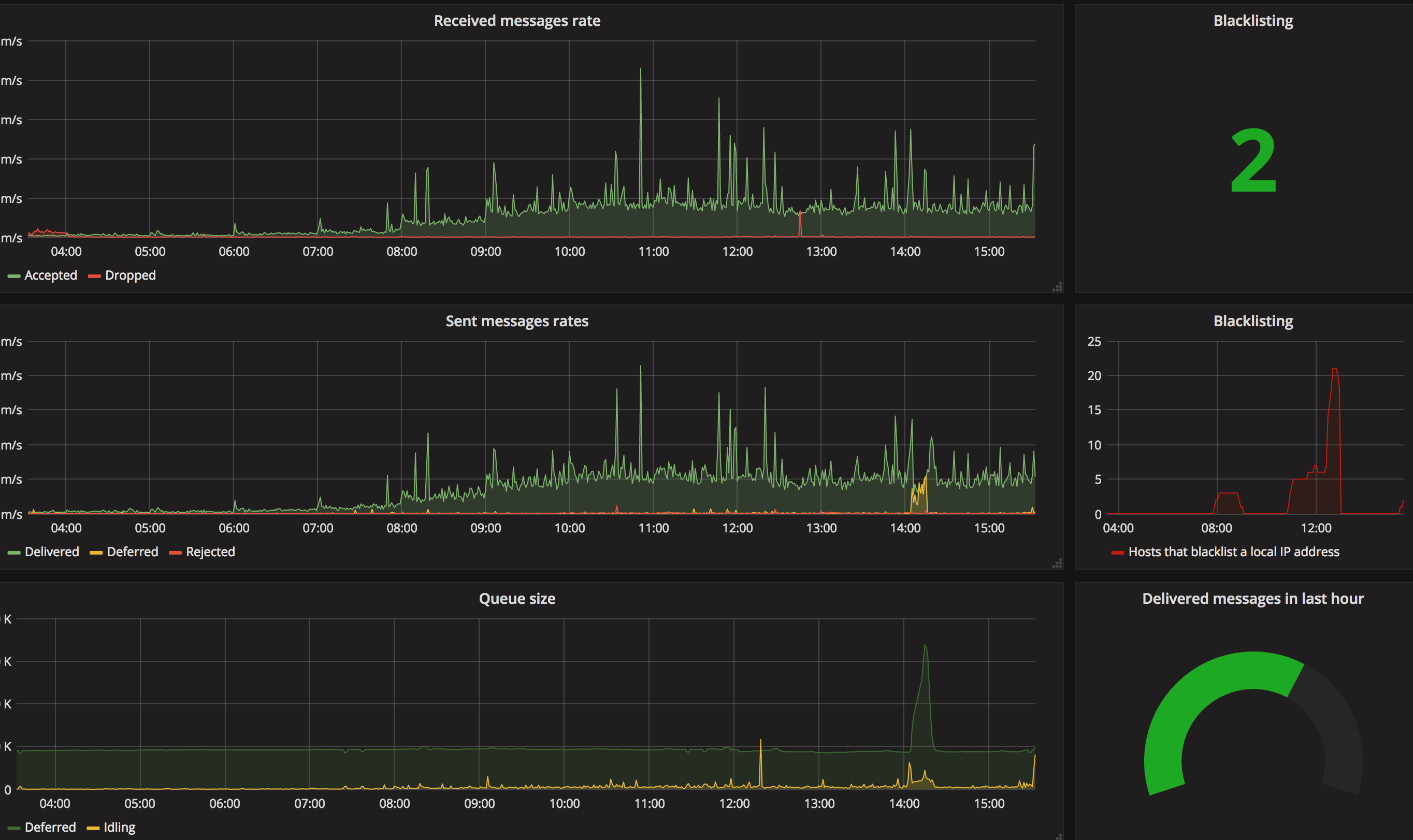
Here's an example of visualizing ZoneMTA data in Grafana:
Metrics used in this chart:
- Received messages rate
rate(zonemta_message_push[1m])rate(zonemta_message_drop[1m])
- Sent messages rate
rate(zonemta_delivery_status{status="delivered"}[1m])rate(zonemta_delivery_status{status="deferred"}[1m])rate(zonemta_delivery_status{status="rejected"}[1m])
- Queue size
zonemta_queue_size{type="deferred"}zonemta_queue_size{type="queued"}
- Blacklisting
zonemta_blacklisted - Delivered in 1h
increase (zonemta_delivery_status{status="delivered"}[1h])