Contents:
- Common Design Patterns
- Clean Code Principles
- Refactoring Strategies
- Code Smells
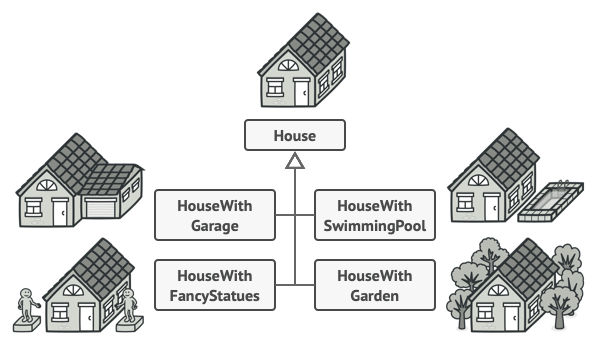
In their classic book the authors define: Creational, Structural and Behavioral design patterns:
- Creational Patterns: are about systematically creating objects or families of objects based on required criterion
- Structural Patterns: helping to organize and structure code so that objects can form a larger cohesive structure
- Behavioral Patterns: abstracting common interactions between objects
In the following few selected patterns (for each category of pattern type) are explained in detail
public class Task {
private final long id;
private String summary = "";
private String description = "";
private boolean done = false;
private Date dueDate;
public Task(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Task(long id, String summary, String description, boolean done,
Date dueDate) {
this.id = id;
this.summary = summary;
this.description = description;
this.done = done;
this.dueDate = dueDate;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getSummary() {
return summary;
}
public void setSummary(String summary) {
this.summary = summary;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public boolean isDone() {
return done;
}
public void setDone(boolean done) {
this.done = done;
}
public Date getDueDate() {
return new Date(dueDate.getTime());
}
public void setDueDate(Date dueDate) {
this.dueDate = new Date(dueDate.getTime());
}
}public class TaskBuilder {
private final long id;
private String summary = "";
private String description = "";
private boolean done = false;
private Date dueDate;
public TaskBuilder(long id, String summary, String description, boolean done,
Date dueDate) {
this.id = id;
this.summary = summary;
this.description = description;
this.done = done;
this.dueDate = dueDate;
}
public TaskBuilder setSummary(String summary) {
this.summary = summary;
return this;
}
public TaskBuilder setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
return this;
}
public TaskBuilder setDone(boolean done) {
this.done = done;
return this;
}
public TaskBuilder setDueDate(Date dueDate) {
this.dueDate = new Date(dueDate.getTime());
return this;
}
public Task build() {
return new Task(id,summary, description,done, dueDate);
}
} Task task = new TaskBuilder(5).setDescription("Hello").setSummary("Test").build();
System.out.println(task);public interface Animal {
String getAnimal();
String makeSound();
}public class Duck implements Animal {
@Override
public String getAnimal() {
return "Duck";
}
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Squeks";
}
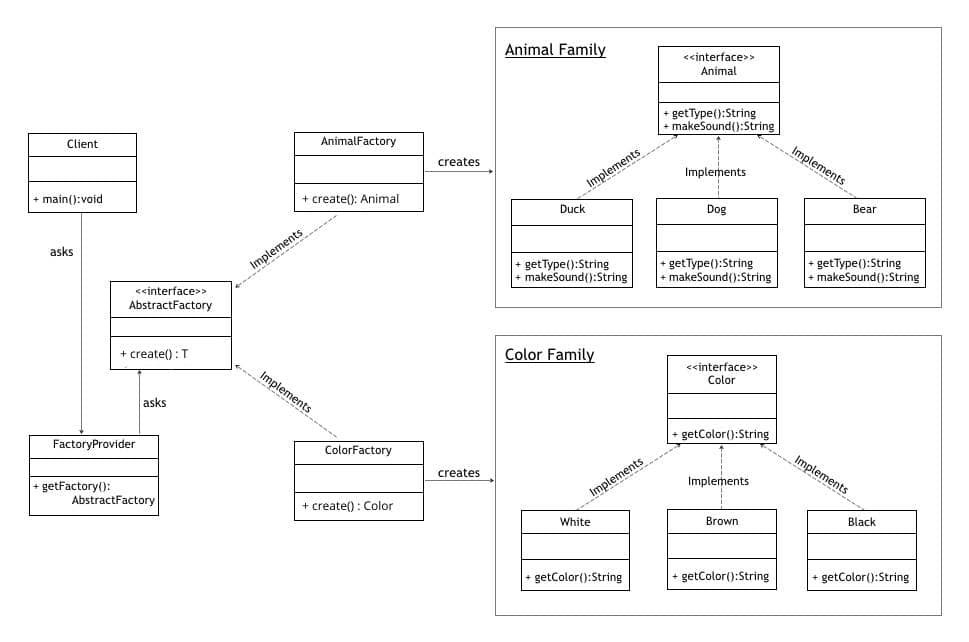
}public interface AbstractFactory<T> {
T create(String animalType) ;
}public class AnimalFactory implements AbstractFactory<Animal> {
@Override
public Animal create(String animalType) {
if ("Dog".equalsIgnoreCase(animalType)) {
return new Dog();
} else if ("Duck".equalsIgnoreCase(animalType)) {
return new Duck();
}
return null;
}
}public class FactoryProvider {
public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String choice){
if("Animal".equalsIgnoreCase(choice)){
return new AnimalFactory();
}
else if("Color".equalsIgnoreCase(choice)){
return new ColorFactory();
}
return null;
}
}airFlowController.takeAir()
fuelInjector.on()
fuelInjector.inject()
starter.start()
coolingController.setTemperatureUpperLimit(DEFAULT_COOLING_TEMP)
coolingController.run()
catalyticConverter.on()fuelInjector.off()
catalyticConverter.off()
coolingController.cool(MAX_ALLOWED_TEMP)
coolingController.stop()
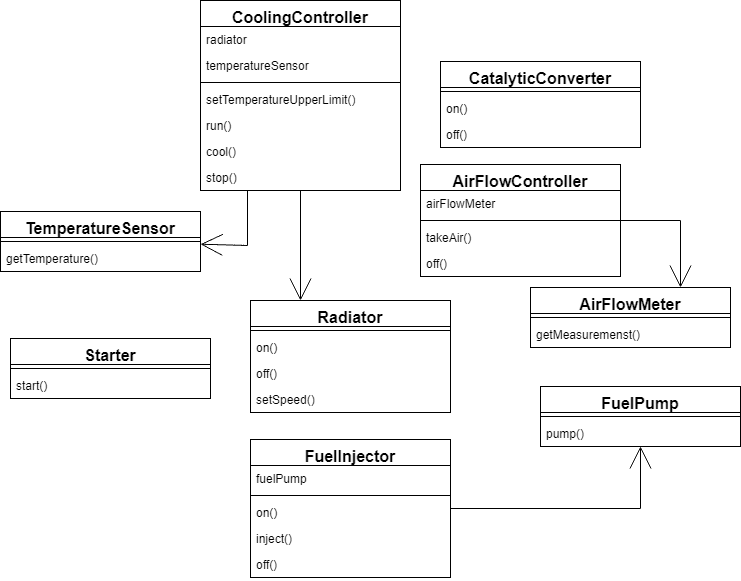
airFlowController.off()public class CarEngineFacade {
private static int DEFAULT_COOLING_TEMP = 90;
private static int MAX_ALLOWED_TEMP = 50;
private FuelInjector fuelInjector = new FuelInjector();
private AirFlowController airFlowController = new AirFlowController();
private Starter starter = new Starter();
private CoolingController coolingController = new CoolingController();
private CatalyticConverter catalyticConverter = new CatalyticConverter();
public void startEngine() {
fuelInjector.on();
airFlowController.takeAir();
fuelInjector.on();
fuelInjector.inject();
starter.start();
coolingController.setTemperatureUpperLimit(DEFAULT_COOLING_TEMP);
coolingController.run();
catalyticConverter.on();
}
public void stopEngine() {
fuelInjector.off();
catalyticConverter.off();
coolingController.cool(MAX_ALLOWED_TEMP);
coolingController.stop();
airFlowController.off();
}facade.startEngine();
// ...
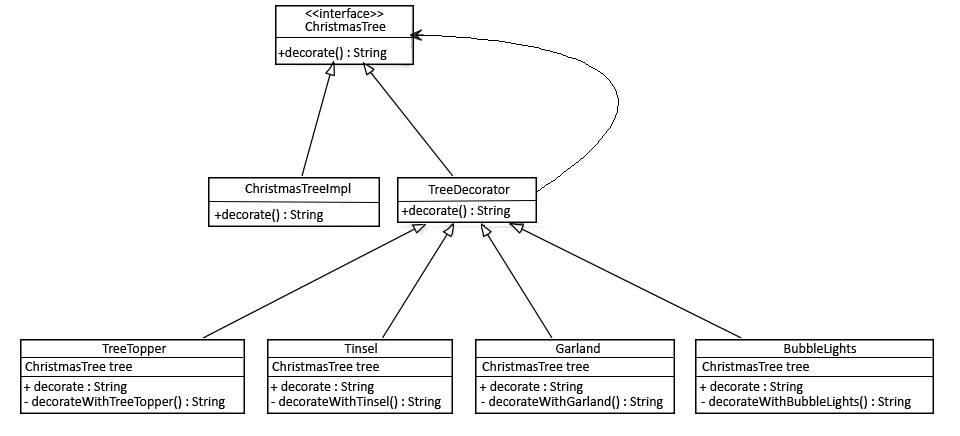
facade.stopEngine();public interface ChristmasTree {
String decorate();
}public class ChristmasTreeImpl implements ChristmasTree {
@Override
public String decorate() {
return "Christmas tree";
}
}public abstract class TreeDecorator implements ChristmasTree {
private ChristmasTree tree;
// standard constructors
@Override
public String decorate() {
return tree.decorate();
}
}public class BubbleLights extends TreeDecorator {
public BubbleLights(ChristmasTree tree) {
super(tree);
}
public String decorate() {
return super.decorate() + decorateWithBubbleLights();
}
private String decorateWithBubbleLights() {
return " with Bubble Lights";
}
}@Test
public void whenDecoratorsInjectedAtRuntime_thenConfigSuccess() {
ChristmasTree tree1 = new Garland(new ChristmasTreeImpl());
assertEquals(tree1.decorate(),
"Christmas tree with Garland");
ChristmasTree tree2 = new BubbleLights(
new Garland(new Garland(new ChristmasTreeImpl())));
assertEquals(tree2.decorate(),
"Christmas tree with Garland with Garland with Bubble Lights");
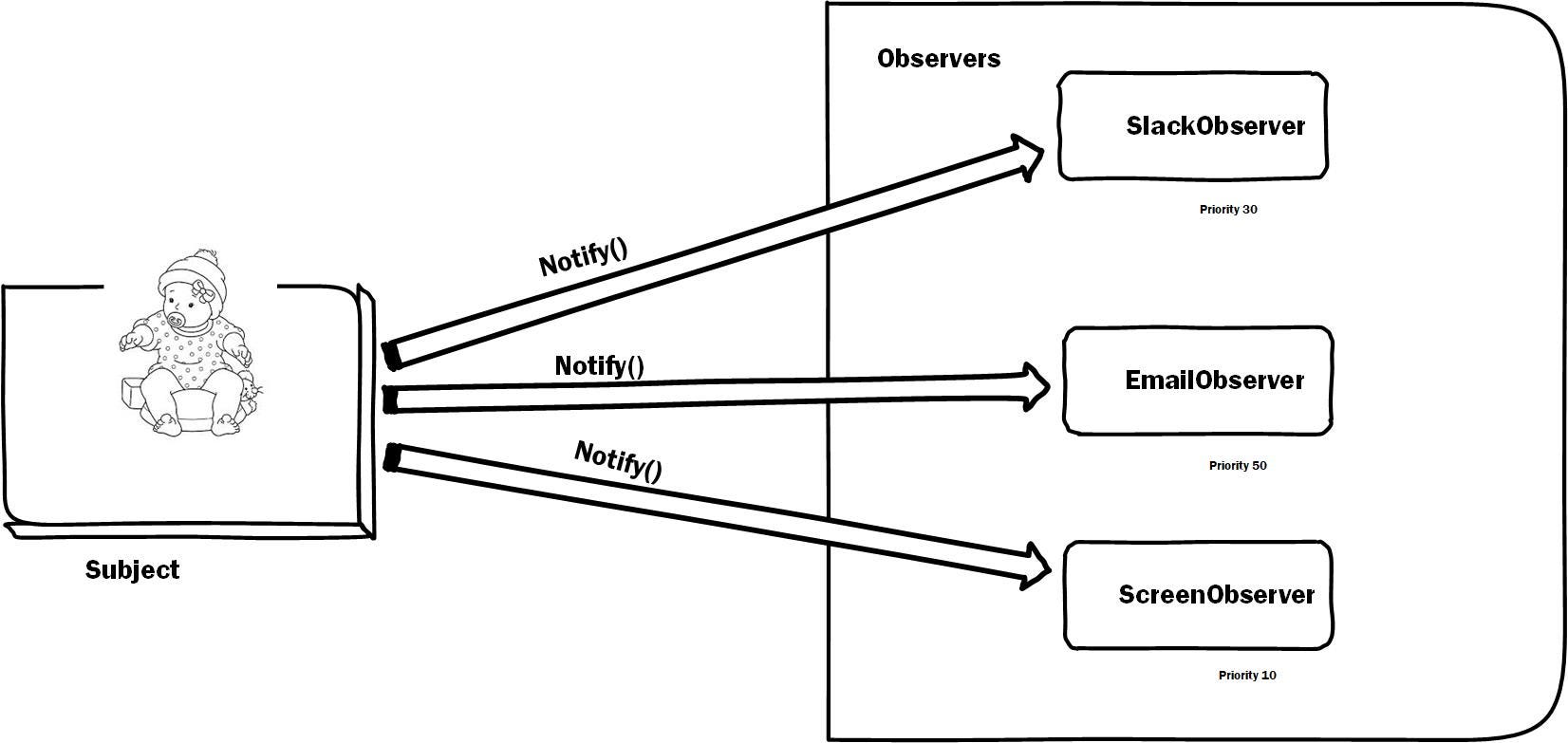
}public class NewsAgency {
private String news;
private List<Channel> channels = new ArrayList<>();
public void addObserver(Channel channel) {
this.channels.add(channel);
}
public void removeObserver(Channel channel) {
this.channels.remove(channel);
}
public void setNews(String news) {
this.news = news;
for (Channel channel : this.channels) {
channel.update(this.news);
}
}
}public class NewsChannel implements Channel {
private String news;
@Override
public void update(Object news) {
this.setNews((String) news);
}
}public interface Channel {
public void update(Object o);
}NewsAgency observable = new NewsAgency();
NewsChannel observer = new NewsChannel();
observable.addObserver(observer);
observable.setNews("news");
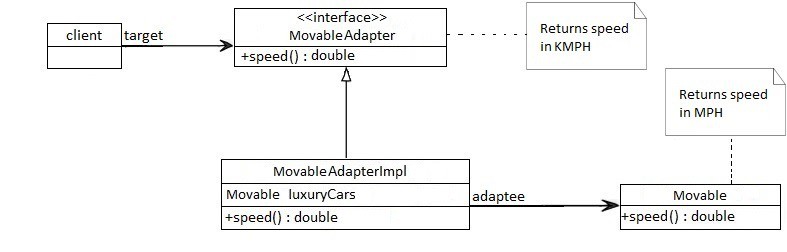
assertEquals(observer.getNews(), "news");public interface Movable {
// returns speed in MPH
double getSpeed();
}public class BugattiVeyron implements Movable {
@Override
public double getSpeed() {
return 268;
}
}public interface MovableAdapter {
// returns speed in KM/H
double getSpeed();
}public class MovableAdapterImpl implements MovableAdapter {
private Movable luxuryCars;
// standard constructors
@Override
public double getSpeed() {
return convertMPHtoKMPH(luxuryCars.getSpeed());
}
private double convertMPHtoKMPH(double mph) {
return mph * 1.60934;
}
}Movable bugattiVeyron = new BugattiVeyron();
MovableAdapter bugattiVeyronAdapter = new MovableAdapterImpl(bugattiVeyron);
assertEquals(bugattiVeyronAdapter.getSpeed(), 431.30312, 0.00001);public String weekday1(int day) {
switch (day) {
case 1:
return "Monday";
case 2:
return "Tuesday";
case 3:
return "Wednesday";
case 4:
return "Thursday";
case 5:
return "Friday";
case 6:
return "Saturday";
case 7:
return "Sunday";
default:
throw new InvalidOperationException("day must be in range 1 to 7");
}
}
public String weekday2(int day) {
if ((day < 1) || (day > 7)) throw new InvalidOperationException("day must be in range 1 to 7");
string[] days = {
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday",
"Sunday"
};
return days[day - 1];
}public class Calculator {
public int total(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public double average(int a, int b) {
int sum = a + b;
return sum / 2;
}
}public class Calculator {
public int total(int a, int b) {
int sum = a + b;
System.out.println("Total=" + sum);
return sum;
}
public double average(int a, int b) {
int sum = total(a, b);
return sum / 2;
}
}- Single Responsibility
- Open/Closed
- Liskov Substitution
- Interface Segregation
- Dependency Inversion
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private String text;
//constructor, getters and setters
}...
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private String text;
//constructor, getters and setters
// methods that directly relate to the book properties
public String replaceWordInText(String word){
return text.replaceAll(word, text);
}
public boolean isWordInText(String word){
return text.contains(word);
}
}...
public class Book {
//...
void printTextToConsole(){
// our code for formatting and printing the text
}
}
// methods for outputting text
void printTextToConsole(String text){
//our code for formatting and printing the text
}
void printTextToAnotherMedium(String text){
// code for writing to any other location..
}
}public class Guitar {
private String make;
private String model;
private int volume;
//Constructors, getters & setters
}public class SuperCoolGuitarWithFlames extends Guitar {
private String flameColor;
//constructor, getters + setters
}"subclasses should be substitutable for their base classes" Robert C. Martin
public interface Car {
void turnOnEngine();
void accelerate();
}public class MotorCar implements Car {
private Engine engine;
//Constructors, getters + setters
public void turnOnEngine() {
//turn on the engine!
engine.on();
}
public void accelerate() {
//move forward!
engine.powerOn(1000);
}
}public class ElectricCar implements Car {
public void turnOnEngine() {
throw new AssertionError("I don't have an engine!");
}
public void accelerate() {
//this acceleration is crazy!
}
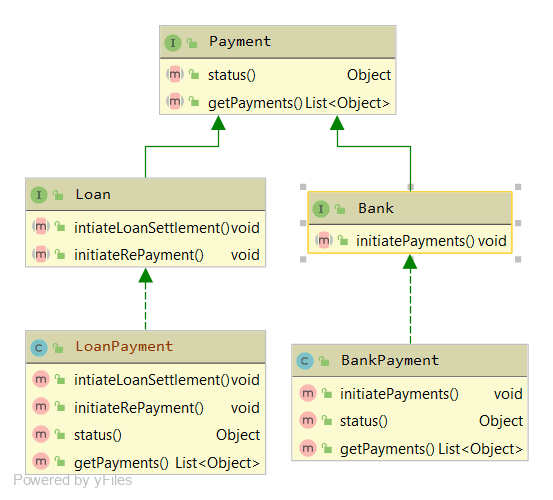
}public interface Payment {
void initiatePayments();
Object status();
List<Object> getPayments();
}public class BankPayment implements Payment {
@Override
public void initiatePayments() {
// ...
}
@Override
public Object status() {
// ...
}
@Override
public List<Object> getPayments() {
// ...
}
}....
public interface Payment {
// original methods
...
void intiateLoanSettlement();
void initiateRePayment();
}public class LoanPayment implements Payment {
@Override
public void initiatePayments() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This is not a bank payment");
}
@Override
public Object status() {
// ...
}
@Override
public List<Object> getPayments() {
// ...
}
@Override
public void intiateLoanSettlement() {
// ...
}
@Override
public void initiateRePayment() {
// ...
}
}public class BankPayment implements Payment {
@Override
public void initiatePayments() {
// ...
}
@Override
public Object status() {
// ...
}
@Override
public List<Object> getPayments() {
// ...
}
@Override
public void intiateLoanSettlement() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This is not a loan payment");
}
@Override
public void initiateRePayment() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This is not a loan payment");
}
}public interface Payment {
Object status();
List<Object> getPayments();
}public interface Bank extends Payment {
void initiatePayments();
}public interface Loan extends Payment {
void intiateLoanSettlement();
void initiateRePayment();
}public class BankPayment implements Bank {
@Override
public void initiatePayments() {
// ...
}
@Override
public Object status() {
// ...
}
@Override
public List<Object> getPayments() {
// ...
}
}public class LoanPayment implements Loan {
@Override
public void intiateLoanSettlement() {
// ...
}
@Override
public void initiateRePayment() {
// ...
}
@Override
public Object status() {
// ...
}
@Override
public List<Object> getPayments() {
// ...
}
}public class Logger {
public void logInformation(String logInfo) {
System.out.println(logInfo);
}
}
// "High level module" Policy equivalent.
public class Foo {
// direct dependency of a low level module.
private Logger logger = new Logger();
public void doStuff() {
logger.logInformation("Something important.");
}
}public interface ILogger {
void logInformation(String logInfo);
}
public class Logger implements ILogger {
@Override
public void logInformation(string logInfo) {
System.out.println(logInfo);
}
}
public class Foo {
private ILogger logger;
public void setLoggerImpl(ILogger loggerImpl) {
this.logger = loggerImpl;
}
public void doStuff() {
logger.logInformation("Something important.");
}
}Foo foo = new Foo();
ILogger logger = new Logger();
foo.setLoggerImpl(logger);
foo.doStuff();public class LoggerToDb implements ILogger {
@Override
public void logInformation(string logInfo) {
DbContext databaseContext = new DbContext();
databaseContext.insertLog(logInfo);
}
}Foo foo = new Foo();
ILogger logger = new LoggerToDb();
foo.setLoggerImpl(logger);
foo.doStuff();void printOwing() {
printBanner();
// Print details.
System.out.println("name: " + name);
System.out.println("amount: " + getOutstanding());
}void printOwing() {
printBanner();
printDetails(getOutstanding());
}
void printDetails(double outstanding) {
System.out.println("name: " + name);
System.out.println("amount: " + outstanding);
}void renderBanner() {
if ((platform.toUpperCase().indexOf("MAC") > -1) &&
(browser.toUpperCase().indexOf("IE") > -1) &&
wasInitialized() && resize > 0 )
{
// do something
}
}void renderBanner() {
final boolean isMacOs = platform.toUpperCase().indexOf("MAC") > -1;
final boolean isIE = browser.toUpperCase().indexOf("IE") > -1;
final boolean wasResized = resize > 0;
if (isMacOs && isIE && wasInitialized() && wasResized) {
// do something
}
}class PizzaDelivery {
// ...
int getRating() {
return moreThanFiveLateDeliveries() ? 2 : 1;
}
boolean moreThanFiveLateDeliveries() {
return numberOfLateDeliveries > 5;
}
}class PizzaDelivery {
// ...
int getRating() {
return numberOfLateDeliveries > 5 ? 2 : 1;
}
}int discount(int inputVal, int quantity) {
if (inputVal > 50) {
inputVal -= 2;
}
// ...
}int discount(int inputVal, int quantity) {
int result = inputVal;
if (inputVal > 50) {
result -= 2;
}
// ...
}public void doSomething(String name, int id, String deptCode, String regNumber) {
...
}public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
//constructor, getters and setters
}
public void doSomething(Student student) {
...
}try {
throw new Exception();
} catch {
// do nothing
}for i from 1 to 52
j := i + randomInt(53 - i) - 1
a.swapEntries(i, j)constant int deckSize := 52
for i from 1 to deckSize
j := i + randomInt(deckSize + 1 - i) - 1
a.swapEntries(i, j)i=0
i=i+1
PRINT i; "squared=";i*i
IF i>=100 THEN GOTO 6
GOTO 2
PRINT "Program Completed."
ENDFOR i=1 TO 100
PRINT i;"squared=";i*i
NEXT i
PRINT "Program Completed."
ENDUSER_ADMIN_ROLE = 1