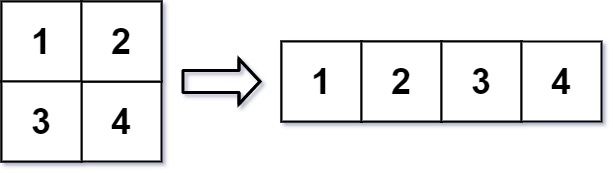
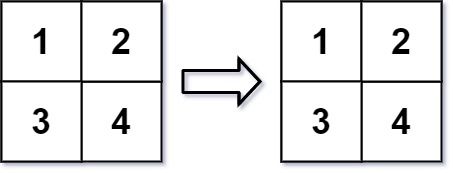
In MATLAB, there is a handy function called reshape which can reshape an m x n matrix into a new one with a different size r x c keeping its original data.
You are given an m x n matrix mat and two integers r and c representing the number of rows and the number of columns of the wanted reshaped matrix.
The reshaped matrix should be filled with all the elements of the original matrix in the same row-traversing order as they were.
If the reshape operation with given parameters is possible and legal, output the new reshaped matrix; Otherwise, output the original matrix.
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 1, c = 4 Output: [[1,2,3,4]]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 2, c = 4 Output: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-1000 <= mat[i][j] <= 10001 <= r, c <= 300
class Solution:
def matrixReshape(self, mat: List[List[int]], r: int, c: int) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
if m * n != r * c:
return mat
ans = [[0] * c for _ in range(r)]
for i in range(m * n):
ans[i // c][i % c] = mat[i // n][i % n]
return ansclass Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] mat, int r, int c) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
if (m * n != r * c) {
return mat;
}
int[][] ans = new int[r][c];
for (int i = 0; i < m * n; ++i) {
ans[i / c][i % c] = mat[i / n][i % n];
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> matrixReshape(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int r, int c) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
if (m * n != r * c) {
return mat;
}
vector<vector<int>> ans(r, vector<int>(c));
for (int i = 0; i < m * n; ++i) {
ans[i / c][i % c] = mat[i / n][i % n];
}
return ans;
}
};func matrixReshape(mat [][]int, r int, c int) [][]int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
if m*n != r*c {
return mat
}
ans := make([][]int, r)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]int, c)
}
for i := 0; i < m*n; i++ {
ans[i/c][i%c] = mat[i/n][i%n]
}
return ans
}function matrixReshape(mat: number[][], r: number, c: number): number[][] {
let m = mat.length,
n = mat[0].length;
if (m * n != r * c) return mat;
let ans = Array.from({ length: r }, v => new Array(c).fill(0));
let k = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
ans[Math.floor(k / c)][k % c] = mat[i][j];
++k;
}
}
return ans;
}function matrixReshape(mat: number[][], r: number, c: number): number[][] {
const m = mat.length;
const n = mat[0].length;
if (m * n !== r * c) {
return mat;
}
const ans = Array.from({ length: r }, () => new Array(c).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < r * c; i++) {
ans[Math.floor(i / c)][i % c] = mat[Math.floor(i / n)][i % n];
}
return ans;
}impl Solution {
pub fn matrix_reshape(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>, r: i32, c: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let r = r as usize;
let c = c as usize;
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
if m * n != r * c {
return mat;
}
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = 0;
(0..r)
.into_iter()
.map(|_| {
(0..c)
.into_iter()
.map(|_| {
let res = mat[i][j];
j += 1;
if j == n {
j = 0;
i += 1;
}
res
})
.collect()
})
.collect()
}
}/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int **matrixReshape(int **mat, int matSize, int *matColSize, int r, int c, int *returnSize, int **returnColumnSizes) {
if (matSize * matColSize[0] != r * c) {
*returnSize = matSize;
*returnColumnSizes = matColSize;
return mat;
}
*returnSize = r;
*returnColumnSizes = malloc(sizeof(int) * r);
int **ans = malloc(sizeof(int *) * r);
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = c;
ans[i] = malloc(sizeof(int) * c);
}
for (int i = 0; i < r * c; i++) {
ans[i / c][i % c] = mat[i / matColSize[0]][i % matColSize[0]];
}
return ans;
}