给你一棵二叉搜索树(BST)的根结点 root 和一个整数 target 。请将该树按要求拆分为两个子树:其中一个子树结点的值都必须小于等于给定的目标值;另一个子树结点的值都必须大于目标值;树中并非一定要存在值为 target 的结点。
除此之外,树中大部分结构都需要保留,也就是说原始树中父节点 p 的任意子节点 c ,假如拆分后它们仍在同一个子树中,那么结点 p 应仍为 c 的父结点。
返回 两个子树的根结点的数组 。
示例 1:
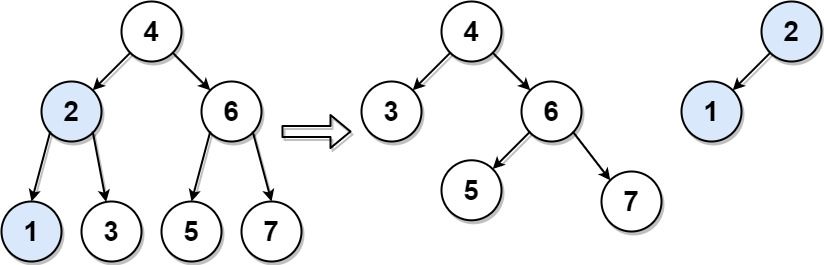
输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3,5,7], target = 2 输出:[[2,1],[4,3,6,null,null,5,7]]
示例 2:
输入: root = [1], target = 1 输出: [[1],[]]
提示:
- 二叉搜索树节点个数在
[1, 50]范围内 0 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
方法一:递归
判断 root 节点的情况:
- 若
root为空,直接返回[null, null]; - 若
root.val <= target,说明root及其左孩子所有节点的值均小于等于target,那么我们递归root.right,得到ans。然后将root.right指向ans[0],最后返回[root, ans[1]]; - 若
root.val > target,说明root及其右孩子所有节点的值均大于target,那么我们递归root.left,得到ans。然后将root.left指向ans[1],最后返回[ans[0], root]。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def splitBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: int) -> List[Optional[TreeNode]]:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return [None, None]
if root.val <= target:
l, r = dfs(root.right)
root.right = l
return [root, r]
else:
l, r = dfs(root.left)
root.left = r
return [l, root]
return dfs(root)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int t;
public TreeNode[] splitBST(TreeNode root, int target) {
t = target;
return dfs(root);
}
private TreeNode[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new TreeNode[] {null, null};
}
if (root.val <= t) {
TreeNode[] ans = dfs(root.right);
root.right = ans[0];
ans[0] = root;
return ans;
} else {
TreeNode[] ans = dfs(root.left);
root.left = ans[1];
ans[1] = root;
return ans;
}
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int t;
vector<TreeNode*> splitBST(TreeNode* root, int target) {
t = target;
return dfs(root);
}
vector<TreeNode*> dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {nullptr, nullptr};
if (root->val <= t) {
auto ans = dfs(root->right);
root->right = ans[0];
ans[0] = root;
return ans;
} else {
auto ans = dfs(root->left);
root->left = ans[1];
ans[1] = root;
return ans;
}
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func splitBST(root *TreeNode, target int) []*TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return []*TreeNode{nil, nil}
}
if root.Val <= target {
ans := splitBST(root.Right, target)
root.Right = ans[0]
ans[0] = root
return ans
} else {
ans := splitBST(root.Left, target)
root.Left = ans[1]
ans[1] = root
return ans
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} target
* @return {TreeNode[]}
*/
var splitBST = function (root, target) {
let ans = [null, null];
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
if (root.val <= target) {
ans = splitBST(root.right, target);
root.right = ans[0];
ans[0] = root;
} else {
ans = splitBST(root.left, target);
root.left = ans[1];
ans[1] = root;
}
return ans;
};