在给定的 m x n 网格 grid 中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
- 值
0代表空单元格; - 值
1代表新鲜橘子; - 值
2代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,腐烂的橘子 周围 4 个方向上相邻 的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回 直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
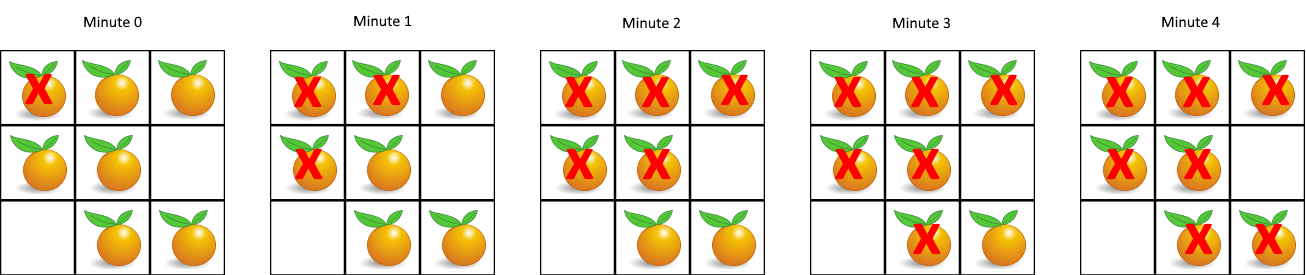
输入:grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]] 输出:4
示例 2:
输入:grid = [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]] 输出:-1 解释:左下角的橘子(第 2 行, 第 0 列)永远不会腐烂,因为腐烂只会发生在 4 个正向上。
示例 3:
输入:grid = [[0,2]] 输出:0 解释:因为 0 分钟时已经没有新鲜橘子了,所以答案就是 0 。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10grid[i][j]仅为0、1或2
首先需要确定的是,网格当中存在多少个新鲜橘子,这关系到什么时候结束。
其次,腐烂橘子的坐标在哪,这些坐标要作为中心点,将腐烂传播给四方的新鲜橘子。
步骤:
- 扫描网格,统计新鲜橘子的数量,记录腐烂橘子的坐标。
- 如果新鲜橘子的数量为 0,返回重复 2 - 5 步骤的轮数(也就是分钟)。
- 如果不存在有效的腐烂橘子,而现存的新鲜橘子不为 0,则为不可能,返回 -1。
- 遍历当前已记录的腐烂橘子,将四方的新鲜橘子污染。如果有新鲜橘子被污染成功,便记录该橘子的坐标,在下一轮使用(不参与本轮行动)。
- 回到第 2 步。
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
q = deque()
cnt = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 2:
q.append((i, j))
elif grid[i][j] == 1:
cnt += 1
ans = 0
while q and cnt:
ans += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] == 1:
cnt -= 1
grid[x][y] = 2
q.append((x, y))
return ans if cnt == 0 else -1class Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int cnt = 0;
Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
q.offer(new int[] {i, j});
} else if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
++cnt;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
int[] dirs = {1, 0, -1, 0, 1};
while (!q.isEmpty() && cnt > 0) {
++ans;
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) {
int[] p = q.poll();
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
int x = p[0] + dirs[j];
int y = p[1] + dirs[j + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
grid[x][y] = 2;
--cnt;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
}
return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int cnt = 0;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
queue<pii> q;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2)
q.emplace(i, j);
else if (grid[i][j] == 1)
++cnt;
}
}
int ans = 0;
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty() && cnt > 0) {
++ans;
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; --i) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
int x = p.first + dirs[j];
int y = p.second + dirs[j + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1) {
--cnt;
grid[x][y] = 2;
q.emplace(x, y);
}
}
}
}
return cnt > 0 ? -1 : ans;
}
};func orangesRotting(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
cnt := 0
var q [][]int
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 2 {
q = append(q, []int{i, j})
} else if grid[i][j] == 1 {
cnt++
}
}
}
ans := 0
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for len(q) > 0 && cnt > 0 {
ans++
for i := len(q); i > 0; i-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for j := 0; j < 4; j++ {
x, y := p[0]+dirs[j], p[1]+dirs[j+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 1 {
cnt--
grid[x][y] = 2
q = append(q, []int{x, y})
}
}
}
}
if cnt > 0 {
return -1
}
return ans
}function orangesRotting(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
let count = 0;
const queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
count++;
} else if (grid[i][j] === 2) {
queue.push([i, j]);
}
}
}
let res = 0;
const dris = [1, 0, -1, 0, 1];
while (count !== 0 && queue.length !== 0) {
for (let i = queue.length; i > 0; i--) {
const [x, y] = queue.shift();
for (let j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
const newX = x + dris[j];
const newY = y + dris[j + 1];
if (
newX >= 0 &&
newX < m &&
newY >= 0 &&
newY <= n &&
grid[newX][newY] === 1
) {
grid[newX][newY] = 2;
queue.push([newX, newY]);
count--;
}
}
}
res++;
}
if (count != 0) {
return -1;
}
return res;
}use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn oranges_rotting(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
// 新鲜橘子数量
let mut count = 0;
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
match grid[i][j] {
1 => count += 1,
2 => queue.push_back([i as i32, j as i32]),
_ => (),
}
}
}
let mut res = 0;
let dirs = [1, 0, -1, 0, 1];
while count != 0 && queue.len() != 0 {
let mut len = queue.len();
while len != 0 {
let [x, y] = queue.pop_front().unwrap();
for i in 0..4 {
let new_x = x + dirs[i];
let new_y = y + dirs[i + 1];
if new_x >= 0
&& new_x < m as i32
&& new_y >= 0
&& new_y < n as i32
&& grid[new_x as usize][new_y as usize] == 1
{
grid[new_x as usize][new_y as usize] = 2;
queue.push_back([new_x, new_y]);
count -= 1;
}
}
len -= 1;
}
res += 1;
}
if count != 0 {
return -1;
}
res
}
}