我们知道,webpack 的打包产物为一个 bundle.js, 当用户进入页面时,浏览器会请求 bundle.js, 随后据此渲染页面。
此时,就可能面临下述情况:
- 使用了 router, 切换 rooter 都会请求一次 bundle.js.
- 页面中某个组件过于庞大,导致 bundle.js 体积较大,随后导致白屏时间过长。
- ...
代码分割便可以解决上述问题,它将 bundle.js 分割成多个文件,之后按需请求资源,并发请求,渲染页面。
假设文件目录结构如下:
/
-- index.html
-- index.js
-- lib.js
-- webpack.config.jsindex.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>index.js:
import { add } from './lib';
console.log(add(1,2))lib.js:
export function add(a,b) {
return a + b;
}webpack.config.js:
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = () => {
return {
entry: './index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js',
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: 'webpack-learn',
inject: 'body',
scriptLoading: 'blocking',
template: './index.html'
})
],
}
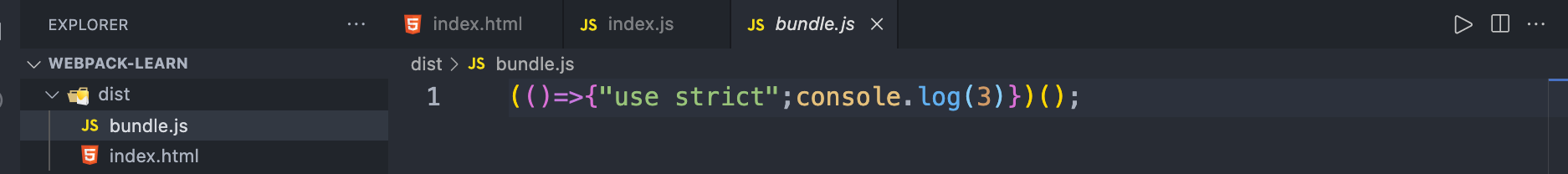
}此时,执行 npx webpack 后,结果为:
上述代码仅供演示,实际项目中打包产物不可能这么优雅。
将 webpack.config.js 的 entry, output 更改为:
{
entry: {
index: './index.js',
lib: './lib.js'
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].js',
},
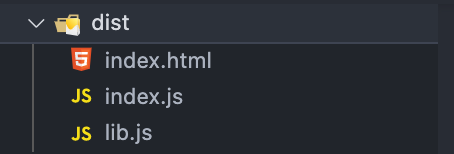
}此时打包产物为:
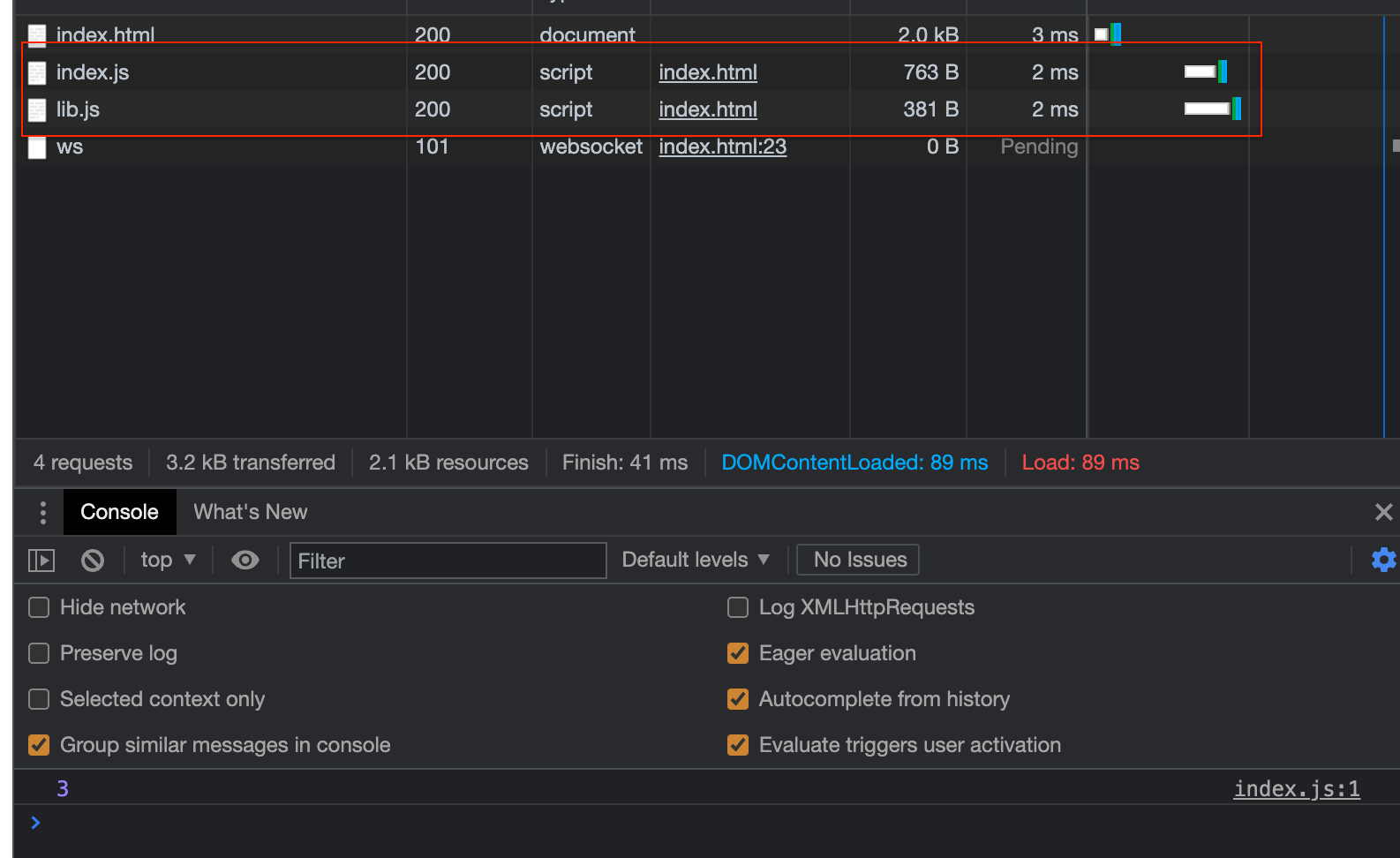
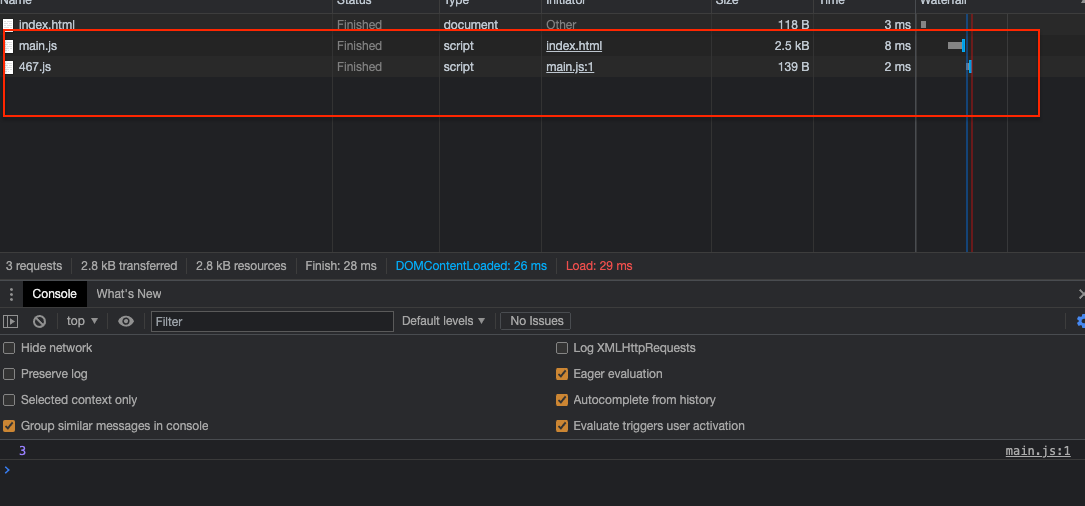
随后,访问 html, 可见其请求了两次 http:
但是,多入口实现代码分割的方式存在一些问题:
- 大型项目中,会出现多次手动配置,太过繁琐。
- 还需要配置
optimization.runtimeChunk: 'single', 否则会出现重复引用的问题。
不改动 webpack 配置文件,转而更改 js 代码,使得实现动态引入:
更改 index.js 为:
const clc = async () => {
const {add} = await import('./lib');
console.log(add(1,2));
}
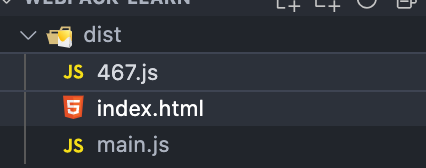
clc()随后,npx webpack 的结果为:
随后,访问 html, 它也是请求了两次 http:
动态导入还可以适用于 polyfill, layload 等。