[TOC]
本文是 MongoDB 新手入门 系列的第一篇,在本文中,我们将会讲解 MongoDB 基本的增删改查操作,在学习完本文后,读者将会掌握对 MongoDB 的集合文档进行基本的新增,修改,删除以及基于多种条件的查询操作。
本文将会持续修正和更新,最新内容请参考我的 GITHUB 上的 程序猿成长计划 项目,欢迎 Star,更多精彩内容请 follow me。
在 MongoDB shell 中,插入文档有以下两个方法:
- 使用
db.collection.insertOne()插入单个文档 - 使用
db.collection.insertMany()插入多个文档
在插入文档时,如果 collection 不存在,插入操作将会自动创建 collection。如果文档没有 _id 字段, MongoDB 将会自动添加一个 _id 字段,类型为 ObjectId。
在 MongoDB 中,每一个文档都需要一个唯一的
_id字段作为主键,如果插入时没有指定_id字段,MongoDB 驱动将会自动生成一个类型为ObjectId的_id字段。
ObjectId是一种能够快速生成的,有序的,12 字节大小的唯一值,包含:
- 一个 4 字节的时间戳,代表了 ObjectId 的创建时间,取值为 Unix 时间戳(秒)
- 一个 5 字节的随机值,该值每个进程都只会生成一次,对每台服务器和进程来说该值是唯一的
- 一个 3 字节的自增值,初始为一个随机数
use sample_mflix
// 插入单个文档
db.movies.insertOne(
{
title: "The Favourite",
genres: [ "Drama", "History" ],
runtime: 121,
rated: "R",
year: 2018,
directors: [ "Yorgos Lanthimos" ],
cast: [ "Olivia Colman", "Emma Stone", "Rachel Weisz" ],
type: "movie"
}
)
// 插入多个文档
db.movies.insertMany([
{
title: "Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom",
genres: [ "Action", "Sci-Fi" ],
runtime: 130,
rated: "PG-13",
year: 2018,
directors: [ "J. A. Bayona" ],
cast: [ "Chris Pratt", "Bryce Dallas Howard", "Rafe Spall" ],
type: "movie"
},
{
title: "Tag",
genres: [ "Comedy", "Action" ],
runtime: 105,
rated: "R",
year: 2018,
directors: [ "Jeff Tomsic" ],
cast: [ "Annabelle Wallis", "Jeremy Renner", "Jon Hamm" ],
type: "movie"
}
])除了常用的 insertOne 和 insertMany 方法之外,还可以用以下方式插入文档
-
db.collection.bulkWrite() -
配合
upsert: true选项-
db.collection.updateOne() -
db.collection.updateMany() -
db.collection.findAndModify() -
db.collection.findOneAndUpdate()
-
最基本的查询方法是 db.collection.find() 和 db.collection.findOne() ,在 MongoDB 中插入以下文档
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }
]);// 等价 SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory
db.inventory.find({})
// 等价 SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory LIMIT 1
db.inventory.findOne({})// 等价 SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "D"
db.inventory.find({status: "D"})
// 等价 SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status != "D"
db.inventory.find({ status: { $ne: "D" } })// 等价 SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status in ("A", "D")
db.inventory.find({status: { $in: ["A", "D"]}})
// 等价 SQL: SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status NOT IN ("A", "D")
db.inventory.find({ status: { $nin: ["A", "D"] } })// SQL: SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE qty >= 50 AND qty < 100
db.inventory.find({ qty: { $gte: 50, $lt: 100 } })比较操作符支持这些: $lt,$gt,$gte,$lte。
// SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND qty < 30
db.inventory.find({ status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } })// SQL:SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" OR qty < 30
db.inventory.find({ $or: [ { status: "A"}, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] })// SQL: SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND ( qty < 30 OR item LIKE "p%" )
db.inventory.find({
status: "A",
$or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ]
})// 查询 qty 模 5 值为 1 的所有文档,这里匹配的 qty 可能值为 1, 6, 11, 16 等
db.inventory.find({ qty: { $mod: [5, 1] } })
// 查询 qty 模 5 值部位 1 的所有文档,可能值为2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12 等
db.inventory.find({ qty: { $not: { $mod: [5, 1] } } })查询所有 size 等于 { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } 的文档
db.inventory.find( { size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } } )查询所有 size 中 uom 等于 in 的文档
db.inventory.find( { "size.uom": "in" } )在 MongoDB 中插入以下文档
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, tags: ["red", "blank"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, tags: ["red", "blank", "plain"], dim_cm: [ 14, 21 ] },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, tags: ["blank", "red"], dim_cm: [ 22.85, 30 ] },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, tags: ["blue"], dim_cm: [ 10, 15.25 ] }
]);下面的示例查询所有字段 tags 值只包含元素 "red" 和 "blank"(顺序一致) 的文档
db.inventory.find({ tags: ["red", "blank"]})如果只是查询同时包含 "red" 和 "blank" 两个值,并且不关心排序或者数组中是否包含其它元素,则可以使用 $all 操作符
db.inventory.find({ tags: { $all: ["red", "blank"] } })查询 tags 包含 "red" 的文档
db.inventory.find({ tags: "red" })查询所有 dim_cm 包含至少一个大于值 25 的所有文档
db.inventory.find({ dim_cm: { $gt: 25} })查询所有 dim_cm 包含至少一个值大于 15 或者 小于 20 的所有文档
db.inventory.find({ dim_cm: { $gt: 15, $lt: 20 } })查询所有 dim_cm 包含至少一个值大于 22 且小于 30 的所有文档
db.inventory.find({ dim_cm: { $elemMatch: { $gt: 22, $lt: 30} } })查询数组 dim_cm 的第二个值大于 25
db.inventory.find({ "dim_cm.1": { $gt: 25 }})查询数组 tags 拥有 3 个元素的所有文档
db.inventory.find({ "tags": { $size: 3 } })默认情况下,MongoDB 的查询会返回匹配文档中所有的字段,通过 projection 可以返回指定的字段。
// SQL: SELECT _id, item, status FROM inventory WHERE status = "A"
db.inventory.find({ status: "A" }, { item: 1, status: 1 })查询结果中会自动返回 _id 字段,可以通过设置 _id: 0 来主动消除该字段。
// SQL: SELECT item, status FROM inventory WHRE status = "A"
db.inventory.find( { status: "A" }, { item: 1, status: 1, _id: 0 } )db.inventory.find({ status: "A" }, { status: 0, instock: 0 })使用 $slice 操作符返回 instock 数组中最后一个元素
db.inventory.find({ status: "A" }, { item: 1, status: 1, instock: { $slice: -1 } })在 MongoDB 中,不同的查询操作符对 null 的处理方式是不同的。在 MongoDB 中插入以下文档
db.inventory.insertMany([
{ _id: 1, item: null },
{ _id: 2 }
])查询 item 值为 null 或者不包含 item 字段的所有文档
db.inventory.find({ item: null })查询所有 item 值为 null 的文档
db.inventory.find({ item: { $type: 10} })这里的
$type = 10对应了 BSON 类型Null
查询所有不包含字段 item 的文档
db.inventory.find({ item: { $exists: false } })查询所有包含 item 字段,但是值为 null 的文档
db.inventory.find({ item: { $eq: null, $exists: true } })// 只查询 3 条数据
db.inventory.find({}).limit(3)
// 从第 2 条开始,查询 3 条数据
db.inventory.find({}).limit(3).skip(2)排序方向 1 为正序, -1 为倒序。
db.inventory.find({}).sort({item: 1, qty: -1})该方法用于查询匹配条件的文档数量,语法为
db.collection.count(query, options)示例
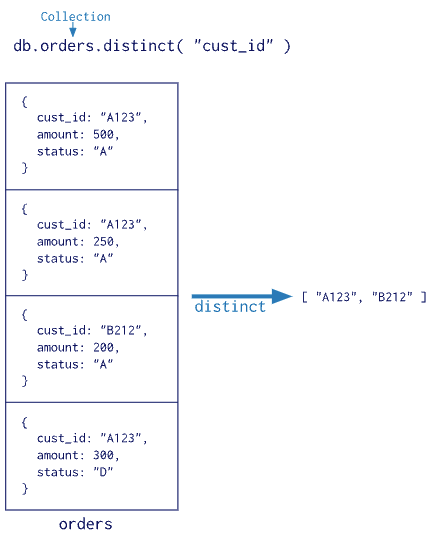
db.orders.count( { ord_dt: { $gt: new Date('01/01/2012') } } )查询集合中字段的唯一值,语法为
db.collection.distinct(field, query, options)| 类别 | 操作符 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| Comparison | $eq |
等值判断 |
| Comparison | $gt |
大于某个值 |
| Comparison | $gte |
大于等于某个值 |
| Comparison | $in |
当前值在数组中 |
| Comparison | $lt |
小于某个值 |
| Comparison | $lte |
小于等于某个值 |
| Comparison | $ne |
不等于某个值 |
| Comparison | $nin |
当前值不再数组中 |
| Logical | $and |
AND |
| Logical | $not |
反转查询条件 |
| Logical | $nor |
所有查询条件都不匹配 |
| Logical | $or |
OR |
| Element | $exists |
字段存在性检查 |
| Element | $type |
字段类型检查 |
| Evaluation | $expr |
在查询表达式中使用聚合语法 |
| Evaluation | $jsonSchema |
验证文档符合指定的 JSON 模型 |
| Evaluation | $mod |
对字段值进行取模运算 |
| Evaluation | $regex |
选择匹配正则表达式的文档 |
| Evaluation | $text |
执行文本搜索 |
| Evaluation | $where |
JavaScript 表达式匹配 |
| Geospatial | $geoIntersects |
地理坐标匹配 |
| Geospatial | $geoWithin |
地理坐标匹配 |
| Geospatial | $near |
地理坐标匹配 |
| Geospatial | $nearSphere |
地理坐标匹配 |
| Array | $all |
匹配包含查询中指定的所有元素的数组 |
| Array | $elemMatch |
数组中的元素匹配表达式则返回文档 |
| Array | $size |
选择数组大小为 size 的文档 |
| Bitwise | $bitsAllClear |
二进制匹配 |
| Bitwise | $bitsAllSet |
二进制匹配 |
| Bitwise | $bitsAnyClear |
二进制匹配 |
| Bitwise | $bitsAnySet |
二进制匹配 |
| Miscellaneous | $comment |
在查询中添加注释 |
| Miscellaneous | $rand |
随机生成一个 0-1 之间的浮点值 |
常用的文档更新方法有以下三种
db.collection.updateOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)更新单个文档db.collection.updateMany(<filter>, <update>, <options>)更新多个文档db.collection.replaceOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)替换单个文档
我们这里以 updateOne() 方法为例进行讲解,updateOne() 方法的语法如下
db.collection.updateOne(
<filter>, // 要更新的文档筛选条件
<update>, // 文档更新命令
{
upsert: <boolean>, // 设置为 true 时,如果 filter 没有匹配到文档,则自动新增文档
writeConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>,
arrayFilters: [ <filterdocument1>, ... ],
hint: <document|string> // Available starting in MongoDB 4.2.1
}
)更新 item=paper 的文档
db.inventory.updateOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "cm", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)更新操作符如下
$set操作符指定了要更新匹配文档的size.uom为cm,status为p$currentDate操作符用于更新lastModified字段为当前的日期,如果lastModified字段不存在,则自动创建
更新文档,如果不存在则新增
db.restaurant.updateOne(
{ "name" : "Pizza Rat's Pizzaria" },
{ $set: {"_id" : 4, "violations" : 7, "borough" : "Manhattan" } },
{ upsert: true }
);更多字段操作符如下
| 操作符 | 用途 |
|---|---|
$currentDate |
设置字段值为当日期,可以是日期或者是时间戳 |
$inc |
将字段的值加上某个数值 |
$min |
只有指定的值小于已经存在的值时才更新 |
$max |
只有指定的额值大于已经存在的值才更新 |
$mul |
将字段的值乘以某个数值 |
$rename |
重命名指定字段 |
$set |
设置文档中要更新的字段值 |
$setOnInsert |
如果当前操作新增了文档,则设置字段的值。如果更新操作只是修改一个已经存在的文档,则该操作符无效 |
$unset |
从文档中移除指定字段 |
除了常用的三个方法,还有以下方法也可以用于更新文档
db.collection.findOneAndReplace().db.collection.findOneAndUpdate().db.collection.findAndModify().db.collection.bulkWrite().
在 MongoDB 中,通常使用以下方法删除文档
删除所有为文档
db.inventory.deleteMany({})删除所有匹配条件的文档
db.inventory.deleteMany({ status : "A" })删除匹配条件的一个文档
db.inventory.deleteOne( { status: "D" } )除了常用的两个方法外,还可以用以下方法删除文档
-
db.collection.findOneAndDelete().findOneAndDelete() 提供了一个
sort选项,该选项允许删除按照指定排序规则排序后匹配的第一个文档 -
db.collection.findAndModify().db.collection.findAndModify()提供了一个sort选项,该选项允许删除按照指定排序规则排序后匹配的第一个文档
MongoDB 提供了一种对单个 Collection 执行批量写入的操作能力,使用 db.collection.bulkWrite() 方法实现批量的插入、更新和删除操作。
批量写操作可以试有序的(ordered)或者无序(unordered)的,对于有序操作,MongoDB 会串行的执行操作,如果写操作过程中发生错误,MongoDB 将会直接返回,后面的操作将不会被执行。无序操作则无法保证这种行为,当发生错误的时候,MongoDB 将会继续处理剩余的文档。
对于分片的集合来说,执行有序的批量操作通常会比较慢,因为每一个操作都必须等待上一个操作的完成。默认情况下,bulkWrite() 执行的是有序的操作,可以通过设置 ordered: false 选项来启用无序操作模式。
bulkWrite() 支持以下写操作
假设一个名为 characters 的集合中包含下面的文档
{ "_id" : 1, "char" : "Brisbane", "class" : "monk", "lvl" : 4 },
{ "_id" : 2, "char" : "Eldon", "class" : "alchemist", "lvl" : 3 },
{ "_id" : 3, "char" : "Meldane", "class" : "ranger", "lvl" : 3 }下面的 bulkWrite() 方法对该集合执行多个操作
db.characters.bulkWrite(
[
{ insertOne :
{
"document" :
{
"_id" : 4, "char" : "Dithras", "class" : "barbarian", "lvl" : 4
}
}
},
{ insertOne :
{
"document" :
{
"_id" : 5, "char" : "Taeln", "class" : "fighter", "lvl" : 3
}
}
},
{ updateOne :
{
"filter" : { "char" : "Eldon" },
"update" : { $set : { "status" : "Critical Injury" } }
}
},
{ deleteOne :
{ "filter" : { "char" : "Brisbane" } }
},
{ replaceOne :
{
"filter" : { "char" : "Meldane" },
"replacement" : { "char" : "Tanys", "class" : "oracle", "lvl" : 4 }
}
}
]
);操作返回以下内容
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"deletedCount" : 1,
"insertedCount" : 2,
"matchedCount" : 2,
"upsertedCount" : 0,
"insertedIds" : {
"0" : 4,
"1" : 5
},
"upsertedIds" : {
}
}