This repository contains my progress for the challenge 100DaysOfMLCode, It is a committment to better my understanding of this powerful tool by dedicating at least 1 hour of my time everyday to studying and/or coding machine learning and deep learning for 100 days.
Today's Progress : I have setup all the things I needed to complete this challenge. I completed the first part of Introduction to Data Science in Python on Coursera to learn python fundamentals and use advanced Python features, including lambdas, list comprehensions and the numpy library.
Thoughts : Hope this will be exciting. The course is really good and it contain lots of good contents. It is good for a beginner.
Link of work: Introduction to Data Science with Python
Today's Progress : Finished the first part of the Machine Learning course on coursera by Andrew Ng up to Linear Regression with One Variable.
Thoughts : I learned the application of Linear Regression with one variable to housing price prediction, the notion of a cost function, and the gradient descent method for learning.
Link of work: Machine Learning Coursera
Today's Progress : Since Linear Algebra is necessary on learning Machine Learning, I review on basic linear algebra concepts. I finished the Linear Algebra Review on machine learning course on Coursera.
Thoughts : I learned about matrices and vectors, addition and scalar multiplication, matrix-vector and matrix-matrix multiplication, matrix multiplication properties, matrix inverse and matrix transpose operation.
Link of work: Machine Learning Coursera
Today's Progress : Learned linear regression using gradient descent and its equations.
Thoughts : The concepts are really good. The Math is explained in a practical way.
Link of work: Commit | How to Do Linear Regression using Gradient Descent
Today's Progress : Learned about Linear Regression with multiple variables, Polynomial Regression, Feature Scaling, and Normal Equation. I also learned using Octave and did some basic operations, plotting data, control statements, vectorization and finished the first programming assignment.
Thoughts : Some concepts are quite difficult at first but I'm able to understand it. I learned how linear regression can be extended to accommodate multiple input features and best practices for implementing linear regression.
Link of work: Commit | Machine Learning Coursera
Today's Progress : Learned about Logistic Regression for classification. I also learned about the notion of classification, the cost function for logistic regression, and the application of logistic regression to multi-class classification.
Thoughts : There's a lot of new concepts I learned in this topic. One of it is solving the problem of overfitting using regularization.
Link of work: Machine Learning Coursera
Today's Progress : Watched the Logistic Regression video on youtube by Siraj. I learned about logistic regression using Newton's method for optimization.
Thoughts : There's a lot of new terms that I encountered so I need to review them. One of the things I learned is Newton's method usually converges faster than gradient descent when maximizing logistic regression log likelihood.
Link of work: Logistic Regression by Siraj
Today's Progress : Finished the programming assignment for Logistic Regression in the Machine Learning Course on Coursera.
Thoughts : The assignment is challenging and difficult for me because I need to write the solution using Octave. The programming exercise tutorials and discussion forums of the course helped me in order to finish it.
Link of work: Commit
Today's Progress : Learned about how neural networks works and how it learns using backpropagation.
Thoughts : Artificial Neural Networks are pretty amazing.
Link of work: How do Neural Networks work | How do Neural Networks Learn | Neural Networks
Today's Progress : I decided to go through Andrew Trask's A Neural Network in 11 lines of Python to really learn how every line worked, and it's been very helpful.
Thoughts : I had to review some matrix math and look up some numpy function calls that he uses, but it was worth it.
Link of work: Commit | Neural Networks in Python Part 1
Today's Progress : Watched a video from Siraj Raval on how to make a neural network in python from scratch.
Thoughts : Learned more about neural networks and see how it is implemented in python code.
Link of work: Neural Networks from Scratch
Today's Progress : Continued my machine learning course on coursera which is on Neural Networks.
Thoughts : I learned more theory and intuition about neural networks.
Link of work: Machine Learning Coursera
Today's Progress : Learned more about using pandas, which is a Python library for data cleaning and processing. I also learned how to read in data into DataFrame structures, how to query these structures, and the details about such structures are indexed.
Thoughts : Pandas is a very powerful library. It allows you to perform complicated operations efficiently with a small amount of code.
Link of work: Introduction to Data Science with Python
Today's Progress : Continued my Machine Learning course on coursera which is on Week 4 (Neural Networks).
Thoughts : Learned about application of neural networks and its examples.
Link of work: Machine Learning Coursera
Today's Progress : Today, I decided to brush up my knowledge on Linear Algebra. I watched 3blue1brown video on youtube and finished up to matrix multiplication.
Thoughts : Having a good knowledge on linear algebra is important in learning ML.
Link of work: Essence of Linear Algebra
Today's Progress : Continued learning linear algebra. Finished up to dot products.
Thoughts : Having a good knowledge on linear algebra is important in learning ML.
Link of work: Essence of Linear Algebra
Today's Progress : Today, I watched the Google machine learning crash course up to validation part.
Thoughts : The course has a lot of good content and it is good for beginners.
Link of work: Machine Learning Crash Course
Today's Progress : Continued google machine learning crash course up to regularization.
Thoughts : Learned about representation,good habits in selecting features, and feature crosses. I also learned about regularization which is used to avoid overfitting.
Link of work: Machine Learning Crash Course
Today's Progress : Continued google machine learning crash course up to Introduction to neural nets. I learned about classification, confusion matrix and neural networks.
Thoughts : Regularization is important in logistic regression modeling. Accuracy alone doesn't tell the full story when you're working in an imbalanced dataset.
Link of work: Machine Learning Crash Course
Today's Progress : Continued google machine learning crash course up to multi-class neural nets.
Thoughts : Learned about multi-class neural networks using softmax and one vs all.
Link of work: Machine Learning Crash Course
Today's Progress : Learned about support vector machines which can be used for both classification and regression problems.
Thoughts : Support vector machines are great when you have small dataset. The decision of which classifier to choose depends on the dataset and complexity of the problem.
Link of work: Support Vector Machines
Today's Progress : Learned about k-means clustering which is a type of unsupervised learning algorithm.
Thoughts : K-means is usually used when your data is numeric because it doesn't work with categorical features. If you how many classes you want to find, use that as your value for k. If not, you can use the elbow method to find the number of clusters you want to find.
Link of work: K-Means Clustering
Today's Progress : Learned about convolutional neural networks which is used for image classification.
Thoughts : CNN is quite difficult for me, there's a lot concept that I need to review again.
Link of work: Convolutional Neural Networks
So, I decided to continue writing my progress on learning ML and DL. Luckily, I'm selected as one of the recipient of Udacity Pytorch Scholarship Challenge. Two weeks have already passed since the beginning of the challenge, from now on I will start writing my journey on learning Deep Learning. You can also take the course for free Intro to Deep Learning with Pytorch
Link of work: Pytorch challenge Scholarship Notes
Today's Progress : Back at it again! Today, I review some concepts of neural networks and study some basics of pytorch and create a simple neural network using pytorch from scratch.
Link of work: Commit
Today's Progress : Today, I build a neural network that can predict the digit in the image using the MNIST dataset. We can build one of these deep networks using only weight matrices as I did in the previous notebook, but in general it's very cumbersome and difficult to implement. PyTorch has a nice module nn that provides a nice way to efficiently build large neural networks.
Link of work: Commit
Today's Progress : I continued the notebook on classifying digits using MNIST dataset. So far, i've been using softmax activation function but in general any function can be used as activation function, but it must be non linear, here are some examples of activation function: sigmoid, Tanh(hyperbolic tangent) and ReLU (rectified linear unit). In practice, ReLU is usually used as activation function in hidden layers.
Link of work: Commit
Today's Progress : I haven't write code today, but I watched some videos. To review, Loss function evaluates how bad our model performs or how far we are from the actual value. To minimize the loss, we do a process called gradient descent which is used to update our weights. For single layer networks, gradient descent is straightforward to implement. Training multilayer networks is done through backpropagation which is really just an application of the chain rule from calculus. Through the nn module, PyTorch provides losses such as the cross-entropy loss (nn.CrossEntropyLoss), it also provides a module, autograd, for automatically calculating the gradients of tensors
Link of course: Intro to Deep Learning with Pytorch
Today's Progress : Today I read about regularization, it means we add a penalty on the different parameters of the model to reduce the freedom of the model. Hence, the model will be less likely to fit the noise of the training data and will improve the generalization abilities of the model. In other words, regularization discourages learning a more complex or flexible model, so as to avoid the risk of overfitting. There are two types of regularization, the L1 regularization adds a penalty equal to the sum of the absolute value of the coefficients, which will shrink some parameters to zero. The L2 regularization adds a penalty equal to the sum of the squared value of the coefficients, it will force the parameters to be relatively small, the bigger the penalization, the smaller (and the more robust) the coefficients are.
Link of article: Regularization
Today's Progress : Today I learned about using nn.Sequential in pytorch which is a convenient way to build networks where a tensor is passed sequentially through operations, and transforms, which is used to preprocess our data such as Normalize, Rescale, RandomCrop and chain it together using Compose
Today's Progress : It's been a long time since my last update,I should have finished it by now :( I've been awarded a scholarship for the Deep Learning Nanodegree last January 18, so I decided to continue write my progress on learning DL.
I already finished the first project, so I decided to review the previous lessons. Today, I reviewed on saving and loading models in pytorch, how to load images for training using ImageFolder, and how to peform data augmentation to introduce randomness in input data using transforms.
Link of work: Predicting Bike-Sharing Patterns
Today's Progress : Today I reviewed the lessons on transfer learning using PyTorch. Basically, transfer learning means using the learning of a previous model and reuse it on different task. I used a pretrained model called ResNet to classify dogs and cats images.
Link of work: Transfer learning in pytorch
Today's Progress : Today, I just watched lectures on Convolutional Neural Networks which is useful for image recognition because it can capture spatial information, I also learned about applications of CNN such as image classification and text classification.
Today's Progress : Today I review on classifying MNIST dataset using multilayer perceptron, I also learned about data normalization in PyTorch which is an important preprocessing step because it ensures that each image input comes from a standard distribution, in other words, one input image is in the same range as another image.
Today's Progress : The exact number of epochs to train a network that is accurate and not overfitting is hard to determine, one method to do it is to split the data into three sets, training set, validation set and test set. We use the training set to find the patterns and update the weights, and use validation set to check how the model generalizes in the validation set. After each epoch, we look at the training loss and validation loss, if the training loss is decreasing but the validation loss is increasing then the model is overfitting, and we need to stop training when the validation loss starts to increase.
Today's Progress : Today, I finished the exercise on training an Multilayer perceptron(MLP) to classify images from MNIST handwritten digit database.
Link of work: Multilayer Perceptron MNIST
Today's Progress : I added a Validation set to the MLP Mnist code. We use validation set to check how our model generalizes during training, it also tells us when to stop training the model(when the validation loss stops decreasing, especially when the validation loss starts increasing and tra training loss is still decreasing).
Link of work: Multilayer Perceptron MNIST with Validation Set
Today's Progress : Previously, I was using MLP to classifiy handwritten digits. But for complex image recognition problems, its better to use Convolutional Neural networks. In MLP, we always use fully connected layers, so in a 28 x 28 pixels of hand written image, we already used over half million of parameters, so imagine if we have more complex images then we will need million of parameters. Another problem is that, we throw away the 2D information in an image when we flatten the matrix into a vector. CNN's can address these problems. First, we only used sparsely connected layers. Also it accepts matrix as inputs, so we don't throw away the 2D information in an image. This spatial information or knowledege of where the pixels are connected in reference to each other is relevant in understanding the image.
Today's Progress : Today, I learned about filters in CNN, these filters produce an output that shows edges of objects and different textures.I also learned about frequency in images, we have high frequency in an image when the intensity changes a lot, level of brightness changes quickly from one pixel to the next. We have low frequency when the level of brightness changes very slowly. High frequency images corresponds to the edges of objects in an image, which can help us classify those objects.
Today's Progress : I learned about high-pass filters, which is used to sharpen an image, and enhance high frequency part of an image. I also learned about convolution kernels, which is just a matrix of numbers that modifies an image. Important note is that for edge detection, all elements must sum to 0 because this filter is computing the difference or change between its neighbor pixels. If these kernels did not add up to 0, it means it is postively or negatively weighted which will have the effect of brightening or darkening the entired filtered image. To apply this filter, an input image: F(x,y) is convolved with a kernel K, and convolution is represented by asterisk. K * F(x,y) = output image
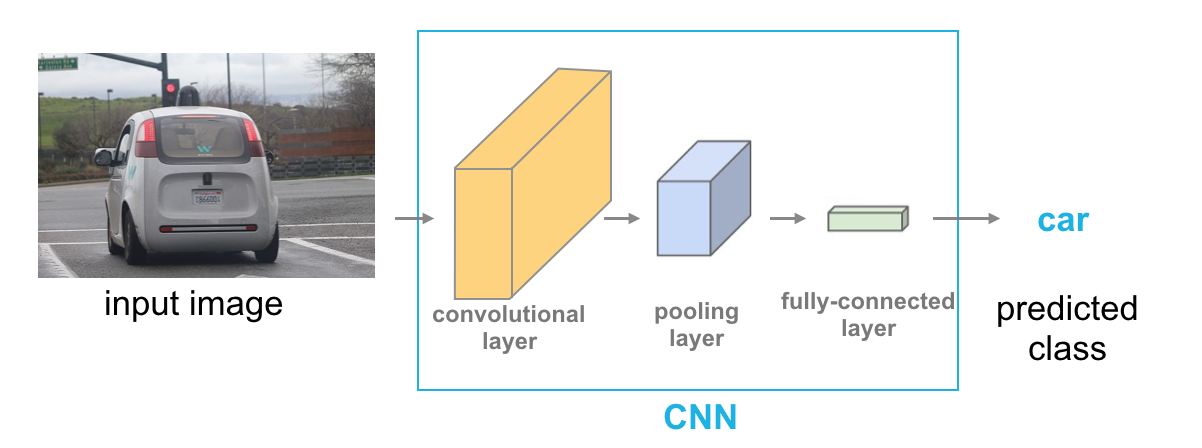
Today's Progress: Today I learned about convolutional layers, where it can learned spatial information, and extract features and detect edges. It is produced by applying series of many convolutional kernels, in other words, it is just a stack of feature maps, which is just the output of the filtered image. Convolutional layers are locally connected as opposed to fully connected layers, and it has also weight sharing. The CNN structure is: Input image -> Convolutional Layer -> Pooling Layer -> Full connected layer -> Class prediction.
Today's Progress:Today I learned about stride, which is just the amount or step size by which the filter slides over the image, and padding which means adding zeros to give the filter more space to move across the image. Another layer in CNN is the Pooling layer, which take convolutional layer as input. The purpose of pooling layer is to reduce the dimensionality of convolutional layer. There are two types of pooling layers: Maxpooling and Average pooling. Max pooling is often used because its better at noticing the most important features and edges of an image. A convolutional layer + activation function, followed by a pooling layer, and a linear layer (to create a desired output size) make up the basic layers of a CNN.
Today's Progress: So, I finished the first part on Convolutional Neural Networks lessons. In the last notebook, I trained a CNN model to classify images on CIFAR-10 database. Next, I will learn more details about Transfer Learning.
Link of work: CNN on CIFAR-10 Database
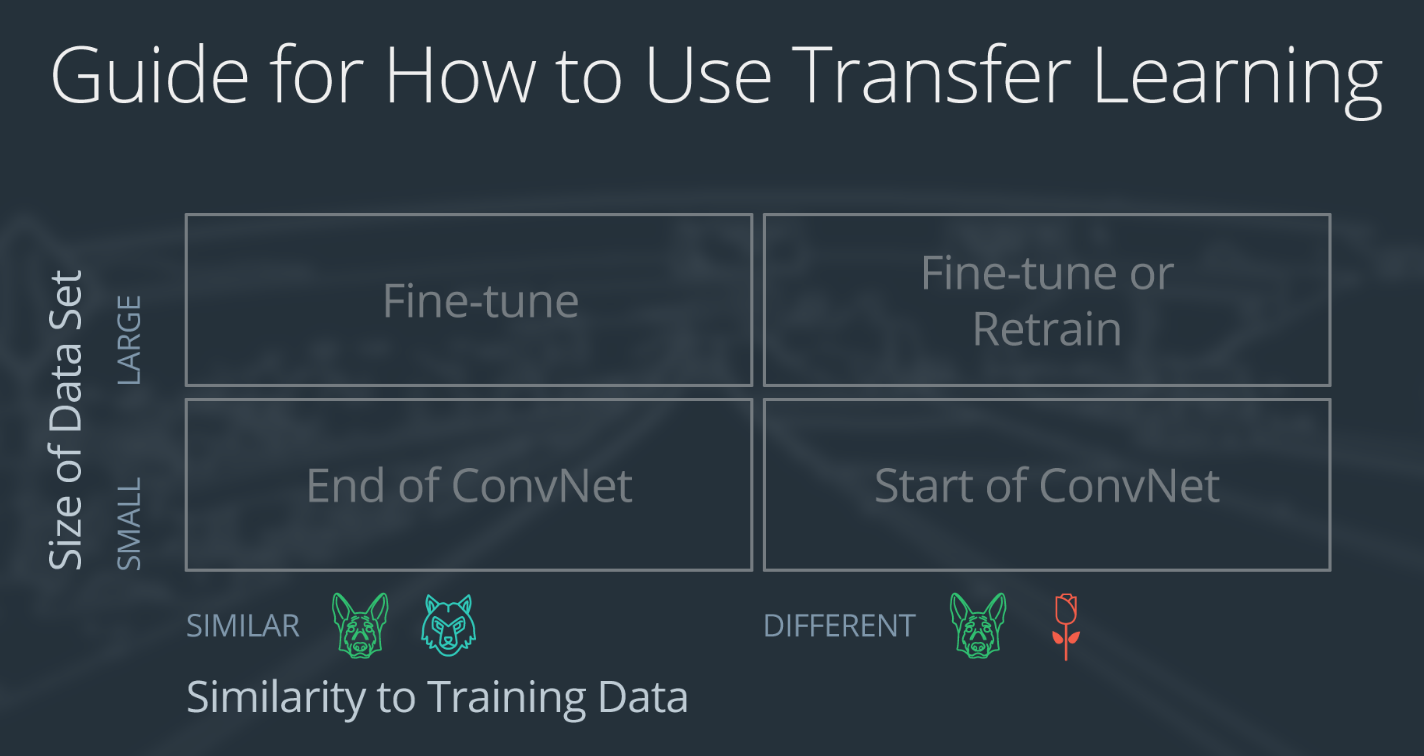
Today's Progress: To review, Transfer Learning is using a pre-trained Network to a new different dataset, instead of training a CNN from scratch, we use the knowledge of a pretrained Network to classify the image in the dataset. There are different strategies in using Transfer Learning. Say for example we use the VGG Network. In the first filters in the convolutional layers it can classify general features like edges and shapes, so we only need to remove the last layer that is specific and replace it with our new fully connected layer. This technique only works if our dataset is small and similar to ImageNet database, if we have bigger dataset and differet from Imagenet, we might need different approach. Here is the guide on how to use Transfer Learning.
Today's Progress: Today, I finished the transfer learning lessons. I used pretrained network which is VGG to classify flowers dataset. First, I loaded the pretrained model, then freeze the parameters so the network acts as a feature extractor. The VGG is trained on ImageNet database which contains 1000 classes so I removed the last layer and replaced it with a new layer to classify the flowers dataset.
Link of work: Transfer Learning on Flowers Dataset
Today's Progress: Today I started the second project on the nanodegree which is the Dog Breed Classifier. I finished the first step which is to detect how much percentage humans or dogs are there in the dataset using pretrained face detectors in OpenCV. Next is I will try to detect dogs using pre trained model CNN which is I learned in the previous lessons.
Today's Progress: Today, I worked on the step two of the project which is to used pretrained model to predict a single image. I still got errors and I'll try to fix it tomorrow.
Today's Progress: Today I finished making predictions to a single image with a pretrained model VGG. I was stuck at the mismatch size error but I was able to solve it by applying RandomResizeCrop to 224.
Today's Progress: Next step in the project is to write a Dog detector. VGG was trained using ImageNet which contains 1000 classes, and some of the datasets include dogs and if you look the dataset, it is on index 151 and 268 inclusive. So, I used this model to detect if there is a dog in the image if the prediction index is between 151 and 268.
Today's Progress: I haven't done the course today because I attended the Tensorflow Dev Summit Extended Manila. The topics discussed was about what's new in TF 2.0, model interpretability, google colab and some 5-minute talks about RNN for Filipino languages, and image classification for radiology and object detection for cars at night.
Today's Progress: Today I just created transforms and data loaders for train, valid, and test datasets of dog images. I preprocess the data by aplying some resize and randomcrop transforsm in the dataset.
Today's Progress I still got errors in the project. Due to busy schedule, i havent done any progress the course. And the dog breed classifier requires a lot of time so I decided to proceed to watch some short vidoes RNN lessons everyday and I will just come back after I finished this lessons.
Today's Progress So today I learned about Recurrent Neural networks which is we incorporate memory into neural networks and is useful for understanding sequential data. RNN are neural networks that can capture temporal dependencies, which are dependecies over time. Its called recurrent because we perform the same task for each input in the sequence.
Today's Progress I continued the RNN lessons. RNN has a key flaw which is the vanishing gradient problem, in which the contribution of information decays over time. In training our network we use backpropagation, In backpropagation we adjust our weight matrices using the gradient, In the process, the gradients are calculated by performing multiplication of derivatives, The value of these derivatives is so small, the continuous multiplication may cause the gradients to vanish. LSTM is the technique to overcome the vanishing gradient in RNN.
Today's Progress There are different applications of RNN and LSTM, for example, speech recognition, like Amazon Alexa, time series prediction to identify traffic patterns, movie selection, predicting stock price movement based on historical patterns of stock movements. Its also use for natural language processing like language translation, question answering like Google Analytics, chatbots, gesture recognition and many more.
Today's Progress So today I learned that you can combine CNN and RNN. For example, one can use cnn in the first layers for the purpose of feature extraction. and then use RNN for the final layers where memory needs to be considered, a popular application of this is gesture recognition.
Today's Progress In order to understand RNN's better, I need to review feedforward and backpropagation concepts. There are two main applications of feed forward neural networks. First is the classification, for example image classification. Then the second is Regression, for example predicting stock prices over the five days. The task of neural networks is the find the best set of weights.
Today's Progress When working with neural nets, we have two phases. Training and Evaluation. During the training phase, we take the data set (also called the training set), which includes many pairs of inputs and their corresponding targets (outputs). Our goal is to find a set of weights that would best map the inputs to the desired outputs. In the evaluation phase, we use the network that was created in the training phase, apply our new inputs and expect to obtain the desired outputs.
Today's Progress Activation functions allows the network to represent non-linear relationships. The most common loss functions are: Mean Squared Error (MSE) (usually used in regression problems) and the cross entropy (usually used in classification problems).
Today's Progress There are two difference between feedforward network and recurrent neural networks, the first is the manner how we define our inputs and outputs, instead of training single input, single output, we train our network in sequences since previous sequence matter. The second difference stems from memory elements that RNN host. Current inputs as well as activation serves as input to the next time step.
Today's Progress In feedforward network, we saw the information flow from the input to the output without any feedback. Now, the feedforward scheme changes and includes the feedback or memory elements. Memory is defined as the output of hidden layer neurons, which will serve as additional input to the network during next training step. We also called the output of hidden layer as state, referring to a system with memory.
Today's Progress The basic scheme of RNN is called Simple RNN or also known as Elman network. In FFNNs the hidden layer depended only on the current inputs and weights,In RNNs the state layer depended on the current inputs, their corresponding weights, the activation function and also on the previous state.
Today's Progress when we train RNN we also use backpropagation, but with a conceptual change. The process is similar to FFNN, with the exception that we need to consider previous timesteps, as the system has memory. This is called Backpropagation through time.
Today's Progress I've been busy again, but I will try to finish this challenge. So I decided to continue where I left on my Dog Breed Classifier project, which is to train CNN from scratch. I also added BatchNorm2d on each convolutional layer because I read that it can improve result and been reported to improve accuracy. I'm still training the model on 100 epochs on google colab and its pretty slow.
Today's Progress So today, I only trained the cnn for 10 epochs and got 8% accuracy (thats very low). So I decided to use pretrained model which is ResNet with 152 layers. I replaced only the last layer and freeze all the gradients since it was trained on ImageNet database which has some Dog dataset in it, so it is somehow similar to my dataset. The accuracy is still low so I decided to research on how to choose the best architecture and hyperparametrs to improve the accuracy.
Resources: 1.Tradeoff batch size vs. number of iterations to train a neural network
2.The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation in Image Classification using Deep Learning
Today's Progress I was busy this week and I didnt make progress in my nanodegree, but I came across this article by Andrej Karpathy which is a recipe for training Neural Networks. It shows the most common neural net mistakes and guides for training neural networks.
Link A Recipe for Training Neural Networks
Today's Progress Today I trained my dog breed classifier from scratch for 50 epochs and learning rate with 0.001 and got 13% accuracy, then I try to use different pretrained model VGG16 and replace the last layer, then trained on 20 epochs and got an accuracy of 83% which is enough to pass the project. Next, I will finish the remaining tasks in the notebook and submit it for review.
Today's Progress Today I learned more about Backpropagation through time which is used for recurrent neural networks. If we backpropagate on more than 10 timesteps, the gradients can be very small and this problem is called the vanishing gradient. We can solve this issue using LSTM. Another issue we can face on RNN is the exploding gradient problem which is the gradients can be very big. We can solve this by using Gradient clipping.
Today's Progress Today I read a blog post about RNNs and LSTM. I learned more about the intuition of RNNs and know why we use LSTM. One way to think about RNNs is they are a way to share weights over time.
Link: A Beginner's Guide to LSTMs and Recurrent Neural Networks
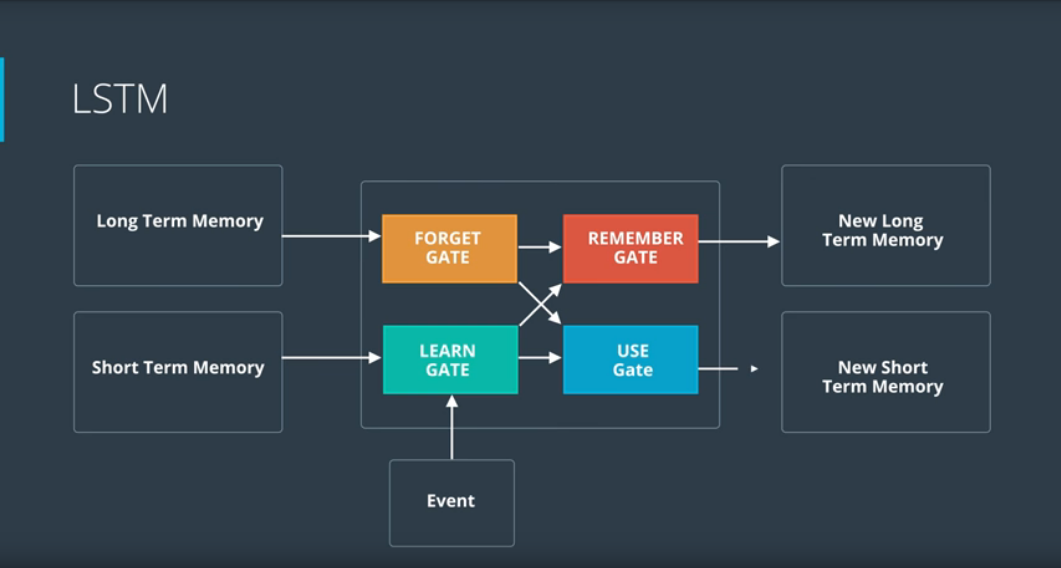
Today's Progress Today I learned about high level overview on how LSTM works. The architecture of LSTM contains four gates which are: Forget Gate, Learn Gate, Remember Gate and Use Gate.
Here's how it works, the long term memory goes to the forget gate and forgets everything that it doesnt consider useful.
The short term memory and event are joined together in the learn gate containing the information we recently learn and it removes unnecessary information.
Then the long term memory we haven't forgotten yet plus the new information we've learned get joined together in the remember gate, it combines the two gates and output an updated long term memory.
And the Use gate is the one that decides what information we use from what we previously know plus what we just learned to make a prediction, so it also takes those inputs as long term memory and the new information, joins them and decide what to output. The output becomes the prediction and the short term memory.
Today's Progress Today I just read Chris Olah's blog post to learn more the theory behind rnn and lstm.
Link: Understanding LSTM Networks
Today's Progress Today I finished the charRNN notebook where I created an LSTM to train character by character on some text, then generate new text character by character. I learned about sequence batching in training RNN, and also learn tips and tricks in obtaining the best model. One of it is to always make the network larger, as large as you're willing to wait to compute and then just apply dropout values. When the training loss is much lower than the validation loss, then it is overfitting, solution to this is to decrease the network size. When the training loss and validation are about equal, then it is underfitting, you need to increase the network size.
Today's Progress Today i learned more about choosing hyperparameters. There is no magic number that will work everytime, it depends on the task and number of dataset. The learning rate is the most important hyperparameter. Good starting point is usually 0.01. One technique we use is learning rate decay, where we decrease the learning rate throughout the training process. There are also algorthims that have apadtive learning rate. Another hyperparameter is the mini batch size, good choices are 32, 64, 128 and 256, depends on the data and task. In choosing the number of hidden layers, Andrej karpathy said that in practice, three layer net will always outperform two layer net but if we go deeper, it rarely helps much more, except on CNN because the deeper the network, the better it will perform. Two choices we need to make when creating RNN is to choose the cell type(LSTM, vanilla RNN or GRU), and how many layers we will stack.
Today's Progress Today I learned about word embedding which is a term for the model that can learn to map a set of words or phrases in a vocabulary to vectors of numerical values. In general, this technique is use to reduce the dimensionality of data but it can also learn interesting traits about words in a vocabulary. One of the popular example of word embedding is the word2vec. It can learn to map words into embeddings that contains semantic meaning, for example embeddings can learn the relationship between verbs in the present and past tense.
Today's Progress Today I read a blog post about word2vec and skip gram model. In simple words, word2vec just convert word into vectors that can learn context of the word. In word2vec, we will train a neural network with one hidden layer, and we will not use this network to perform a certain task, we just want to learn the weights of the hidden layer. There are two architectures for implementing word2vec: 1. CBOW(continous bag of words) and skip gram. In cbow, we give the model the context words and it tries to predict the word while in skip gram, we give the model the word it will predict the context. I've also read that skip gram performs better than cbow.
Link: Word2Vec Tutorial - The Skip-Gram Model
Today's Progress I read the part 2 of the article, here are the notes that I learned. Running gradient descent on a neural network that large is going to be slow. The authors of word2vec addressed these issue in their second paper with two improvements: subsampling and negative sampling. Words that show up often such as "the", "of", and "for" don't provide much context to the nearby words. If we discard some of them, we can remove some of the noise from our data and in return get faster training and better representations. This process is called subsampling. Negative sampling causes each training sample to update only a small percentage of the model’s weights. It’s worth noting that subsampling frequent words and applying Negative Sampling not only reduced the compute burden of the training process, but also improved the quality of their resulting word vectors as well.
Link: Word2Vec Tutorial Part 2 - Negative Sampling
Today's Progress Today I started the lesson on recurrent neural network that can perform sentiment analysis. The architecture of the network is, first we will pass the word into embedding layer to reduce dimensionality. Then the new embeddings will be pass to lstm cells, to add memory to our network. Lastly, pass it into sigmoid to obtain probability between 0 and 1 since we want to predict sentiment on either positive or negative(1 or o).