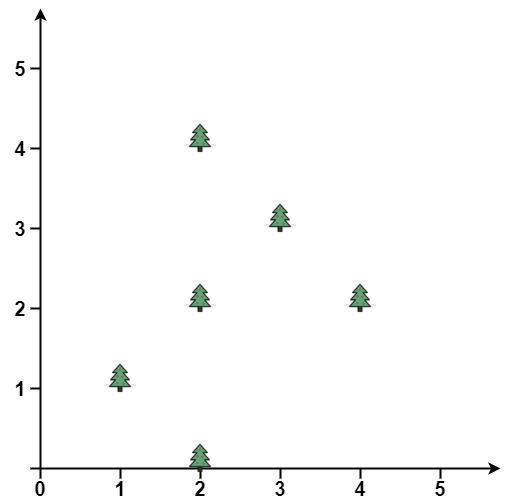
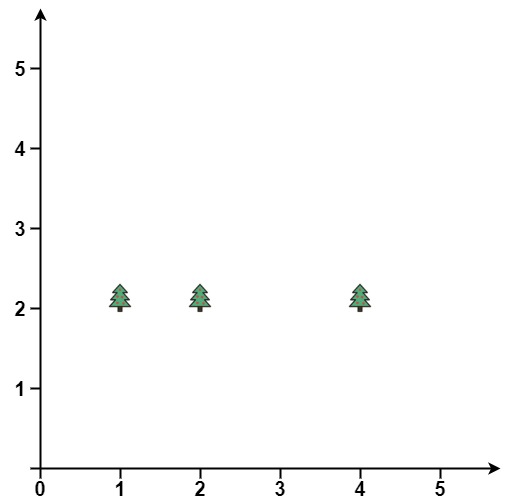
You are given an array trees where trees[i] = [xi, yi] represents the location of a tree in the garden.
Fence the entire garden using the minimum length of rope, as it is expensive. The garden is well-fenced only if all the trees are enclosed.
Return the coordinates of trees that are exactly located on the fence perimeter. You may return the answer in any order.
Input: trees = [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]] Output: [[1,1],[2,0],[4,2],[3,3],[2,4]] Explanation: All the trees will be on the perimeter of the fence except the tree at [2, 2], which will be inside the fence.
Input: trees = [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]] Output: [[4,2],[2,2],[1,2]] Explanation: The fence forms a line that passes through all the trees.
1 <= trees.length <= 3000trees[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 100- All the given positions are unique.
use std::collections::HashSet;
impl Solution {
pub fn outer_trees(trees: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut trees = trees;
let mut stack = vec![];
let mut used = HashSet::new();
trees.sort_unstable();
stack.push(trees[0].clone());
used.insert(trees[0].clone());
for i in 1..trees.len() {
let (x0, y0) = (trees[i][0], trees[i][1]);
while stack.len() > 1 {
let (x1, y1) = (stack[stack.len() - 1][0], stack[stack.len() - 1][1]);
let (x2, y2) = (stack[stack.len() - 2][0], stack[stack.len() - 2][1]);
if (x1 - x2) * (y0 - y1) < (x0 - x1) * (y1 - y2) {
used.remove(&vec![x1, y1]);
stack.pop();
} else {
break;
}
}
used.insert(vec![x0, y0]);
stack.push(vec![x0, y0]);
}
for i in (0..trees.len() - 1).rev() {
let (x0, y0) = (trees[i][0], trees[i][1]);
if i > 0 && used.contains(&vec![x0, y0]) {
continue;
}
while stack.len() > 1 {
let (x1, y1) = (stack[stack.len() - 1][0], stack[stack.len() - 1][1]);
let (x2, y2) = (stack[stack.len() - 2][0], stack[stack.len() - 2][1]);
if (x1 - x2) * (y0 - y1) < (x0 - x1) * (y1 - y2) {
used.remove(&vec![x1, y1]);
stack.pop();
} else {
break;
}
}
used.insert(vec![x0, y0]);
stack.push(vec![x0, y0]);
}
used.into_iter().collect()
}
}