You are given an m x n integer matrix grid.
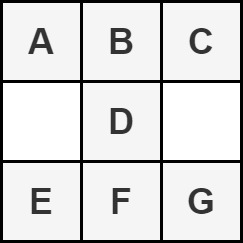
We define an hourglass as a part of the matrix with the following form:
Return the maximum sum of the elements of an hourglass.
Note that an hourglass cannot be rotated and must be entirely contained within the matrix.
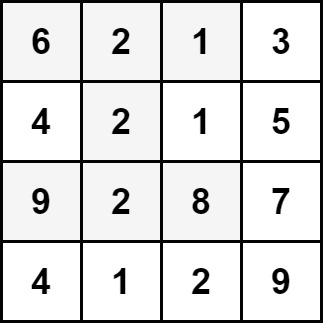
Input: grid = [[6,2,1,3],[4,2,1,5],[9,2,8,7],[4,1,2,9]] Output: 30 Explanation: The cells shown above represent the hourglass with the maximum sum: 6 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 9 + 2 + 8 = 30.
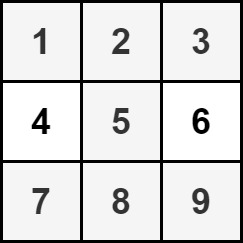
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: 35 Explanation: There is only one hourglass in the matrix, with the sum: 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 8 + 9 = 35.
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length3 <= m, n <= 1500 <= grid[i][j] <= 106
impl Solution {
pub fn max_sum(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let mut ret = 0;
for i in 1..grid.len() - 1 {
for j in 1..grid[0].len() - 1 {
ret = ret.max(
grid[i][j]
+ grid[i - 1][j]
+ grid[i + 1][j]
+ grid[i - 1][j - 1]
+ grid[i + 1][j - 1]
+ grid[i - 1][j + 1]
+ grid[i + 1][j + 1],
);
}
}
ret
}
}