Leafy Spurge Dataset is a challenging real-world benchmark to galvanize efforts to find and remove invasive plants within drone imagery of the Montana prairie, and restore natural ecosystems in Montana.
Paper | Website | HuggingFace | 🌱 Leafy Spurge + Data Augmentation
🌱 Leafy Spurge Dataset can be installed using our pip package.
pip install leafy-spurge-datasetThis will install all necessary dependencies.
The benchmark includes a torch.utils.data.Dataset compatible loader for 🌱 Leafy Spurge Dataset, and a simple training, evaluation, and plotting interface. This loader can be imported using:
from leafy_spurge_dataset import LeafySpurgeDataset
dataset = LeafySpurgeDataset(
split="train",
version="crop",
)
print(len(dataset))
# 800
print(dataset[0])
# (PIL.Image.Image, 0)Iterating through the dataset returns tuples of PIL.Image.Image and a class label. Additional metadata is available for each training example, including example idx, latitude, longitude, easting, northing, elevation, time, and plant cluster id. These can be returned by the dataset by setting output_dict=True as below:
from leafy_spurge_dataset import LeafySpurgeDataset
dataset = LeafySpurgeDataset(
split="train",
version="crop",
output_dict=True,
)
print(dataset[0])
# {'image': PIL.Image.Image, 'label': 0, 'idx': 104, 'longitude': -114.03648818, 'latitude': 46.70476716, 'easting': 726534.8359659711, 'northing': 5176622.677234786, 'elevation': 1001.154, 'time': 20230612120503.7, 'cluster': 1}Our LeafySpurgeDataset is compatible with the PyTorch DataLoader, and transforms. The following example shows how to load random batches of 32 images from the 🌱 Leafy Spurge training set, at resolution 224x224, normalized using ImageNet statistics.
from leafy_spurge_dataset import LeafySpurgeDataset
from torchvision.transforms import v2
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
transform = v2.Compose([
v2.Resize(size=(224, 224), antialias=True),
v2.ToImage(),
v2.ToDtype(torch.float32, scale=True),
v2.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225],
),
])
train_dataset = LeafySpurgeDataset(
split="train",
version="crop",
output_dict=True,
transform=transform,
)
dataloader = DataLoader(
train_dataset,
batch_size=32,
shuffle=True,
)Cheers, and happy model training!
The benchmark can generate starter files that fine-tune DINOv2 with LoRA to classify 🌱 Leafy Spurge. Running the following command in your terminal:
leafy-spurge quickstartWill generate two files in your current directory: leafy_spurge_train_classifier.py for training DINOv2, and leafy_spurge_plot_results.py for plotting results that were logged by the training script.
The training script can be called with:
python leafy_spurge_train_classifier.py \
--batch_size 32 \
--num_epochs 100 \
--lr 0.0001 \
--seed 42 \
--output_dir outputRunning this script will train DINOv2 to classify 🌱 Leafy Spurge using LoRA, and will save results in a folder called output. This folder will contain a data.csv file with logged training, and validation classification accuracy every epoch, and final test accuracy on the official test set.
The results in data.csv can be plotted using:
python leafy_spurge_plot_results.py \
--csv_file_name output/data.csv \
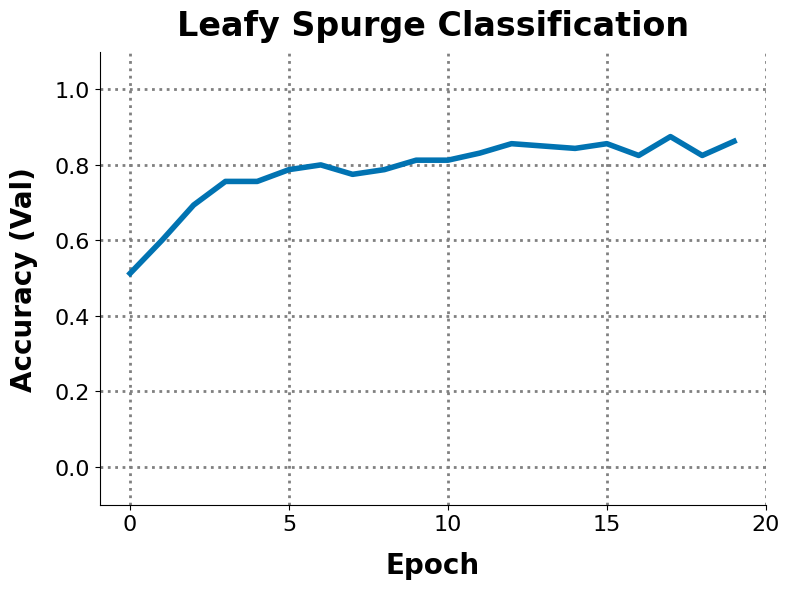
--plot_file_name plot.pngThis will create a file plot.png (shown above) that visualizes the validation accuracy per epoch. If you have multiple runs, changing to --csv_file_name */data.csv will use glob to load multiple data.csv files, and the resulting plot.png will contain a legend if more than one method is present.
The quickstart plotting script will compute a 95% confidence interval if multiple trials of the same method are present in */data.csv.
The default training script is also available via a command-line interface.
leafy-spurge train \
--batch_size 32 \
--num_epochs 100 \
--lr 0.0001 \
--seed 42 \
--output_dir outputSimilarly, the default plotting script is available via a command-line interface.
leafy-spurge plot \
--csv_file_name output/data.csv \
--plot_file_name plot.pngThese can reproduce the results in our paper, without you writing a single line of code.
If you use our dataset, you can support our work by citing our benchmark paper.
@misc{Doherty2024LeafySpurgeDataset,
title={Leafy Spurge Dataset: Real-world Weed Classification Within Aerial Drone Imagery},
howpublished={https://leafy-spurge-dataset.github.io/static/paper.pdf},
author={
Kyle Doherty,
Max Gurinas,
Erik Samsoe,
Charles Casper,
Beau Larkin,
Philip Ramsey,
Brandon Trabucco,
Ruslan Salakhutdinov},
year={2024},
}
And our paper on few-shot learning with 🌱 Leafy Spurge Dataset.
@misc{Trabucco2023DataAugmentation,
title={Effective Data Augmentation With Diffusion Models},
author={
Brandon Trabucco,
Kyle Doherty,
Max Gurinas,
Ruslan Salakhutdinov},
year={2023},
eprint={2302.07944},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}