Python implementation of Deepstack w/ Numpy, Tensorflow 1.13. Works on Windows, Linux.
- Run:
git clone https://github.com/doas3140/PyStack.git
cd PyStack
unzip empty_folders.zip
cd src/TerminalEquity/matrices/
unzip texas_lookup.zip
- Install Anaconda (optional, for using conda install)
- Install python packages:
conda install numpy tqdm tensorflow # (can use pip install, but numpy, tf will be slower)
pip install flask flask_socketio # (optional, for playing vs bot GUI)
pip install selenium # (optional, for playing against Slumbot) (needs selenium* installed)
pip install graphviz # (optional, for displaying tree's) (needs graphviz* installed)
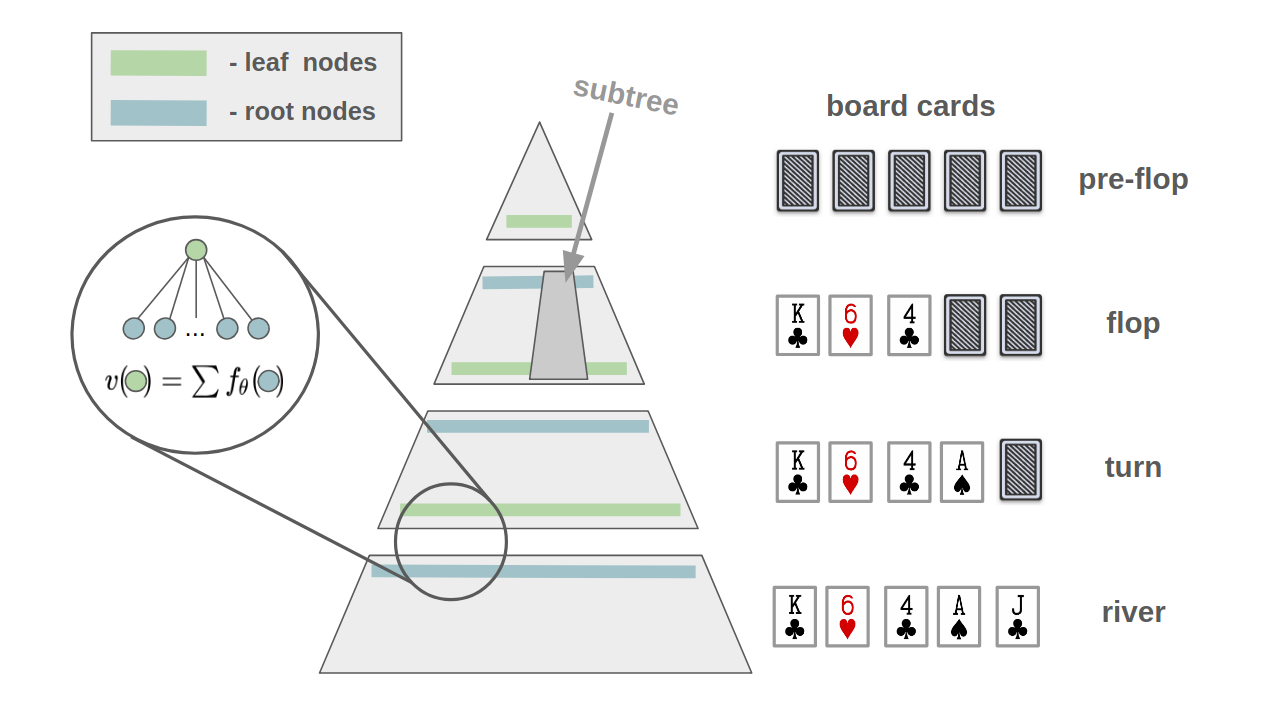
Solving the whole Heads-Up No-Limit (HUNL) poker tree with information sets is impossible (space and time problems). So we try to approximate each round values using neural networks. We will approximate all root nodes for each round in HUNL poker (blue lines), so in total with 3 neural networks. When we will be solving randomly generated situations at turn round, we will use river round root nodes approximation (neural network), and when we will be solving flop round root nodes, we will use turn round root nodes approximation.
Actually, we don't have to look at next round root nodes approximation, we can look only at current rounds leaf nodes. For example, approximating turn round leaf nodes using river round root nodes neural network. We are trading speed (no need to predict root nodes values) for accuracy (more accurate predictions). So, it is optional to use leaf nodes approximation, but it's faster and less accurate. CFR algorithms are iterative (traverses the whole subtree multiple times, ex. 1000) and we can use both: first iterations approximating with leaf nodes neural network (faster) and last iterations with root nodes neural network (more accurate).
We also cache pre-flop round calculation results, to not do expensive approximation (flop round opens 3 cards, so a total of (52*51*50)/(2*3) possible outcomes). With 1000 CFR iterations we have to use neural network more than 22 million times for only one action!
Generated solved situations: river: 2mil., other rounds: 0.5mil w/ 1000 CPU nodes. Using 1000 CFR iterations.
Neural network loss was unexpectedly big (so there might be some bugs).
| Train | Test | Deepstack (train/test) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pre-flop | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.00005 / 0.00005 |
| flop | 0.153 | 0.283 | 0.0008 / 0.034 |
| turn | 0.198 | 0.261 | 0.016 / 0.024 |
| river | 0.035 | 0.106 | - / - |
Thinking time:
| CPU | CPU + GPU(only nn) | Deepstack(only GPU) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pre-flop | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| flop | 36.2 | 25.2 | 5.9 |
| turn | 33.7 | 23.1 | 5.5 |
| river | 3.2 | 3.2 | 2.2 |
pseudo-code:
next_street_nn = None # no need neural network for river round
for street in [river, turn, flop, pre-flop]:
data = generate_data(street, next_steet_nn) # solve root nodes
tf_data = convert_to_tf_data(data)
next_street_nn = train_neural_network(tf_data)
commands:
generate_data: python generate_data.py --street 4 --approximate root_nodes
train_neural_network: python train_nn.py --street 4 --approximate root_nodes
convert_to_tf_data: python convert_npy_to_tfrecords.py --street 4 --approximate root_nodes
-
Make sure you are in
PyStack/scriptsdirectory. All data is saved inPyStack/datadirectory. -
--street arg is a number 1,2,3,4 corresponding to rounds pre-flop, flop, turn, river
-
To modify CFR iterations modify
cfr_itersvariable inPyStack/src/Settings/arguments.py. Sugested variables:cfr_iters = 800,cfr_skip_iters = 500.
Modify starting index of file and num cores (num programs to run) and num files to create (per program) in scripts/distribute_work.sh. Instead of running python generate_data.py run sh distribute_work.sh.
pseudo-code:
for street in [turn, flop, pre-flop]:
data = generate_data(street, root_nodes_nn[street]) # solve leaf nodes
tf_data = convert_to_tf_data(data)
street_leaf_nn = train_neural_network(tf_data)
commands:
generate_data: python generate_data.py --street 3 --approximate leaf_nodes
train_neural_network: python train_nn.py --street 3 --approximate leaf_nodes
convert_to_tf_data: python convert_npy_to_tfrecords.py --street 3 --approximate leaf_nodes
- To modify number of leaf nodes approximation iterations modify
leaf_nodes_iterationsvariable inPyStack/src/Settings/arguments.py.
Run python play_against_bot.py. If web browser doesn't open, then open PyStack/src/GUI/client/game.html manually. Make sure that only one game tab is opened.
python play_against_slumbot.py