This documents describe various kinds of authentication and authorization
Certification identify someone or something, and authentication confirm the identity. from redhat doc.
When talking about server authentication and client authentiction, we are talking about x509 certification based authentication. In general, server authentication means server side provide the something to let the client side verify, and client authentication means client side provide something to let the server side to verify.
Server certificate authentication Server send its certification to client side, and client side leverage the trust CA to verify the signature of the server certification to decide trust or not trust.
Those are all server authentication:
-
web server enabled the https, and client side verify the server certification.
-
client use jdbc to connect to database which enabled the ssl, client need to provide the truststore. the truststore is used to store the trust certifications which provided by the server side (self-signed), or use public CA if server is configured CA based certification.
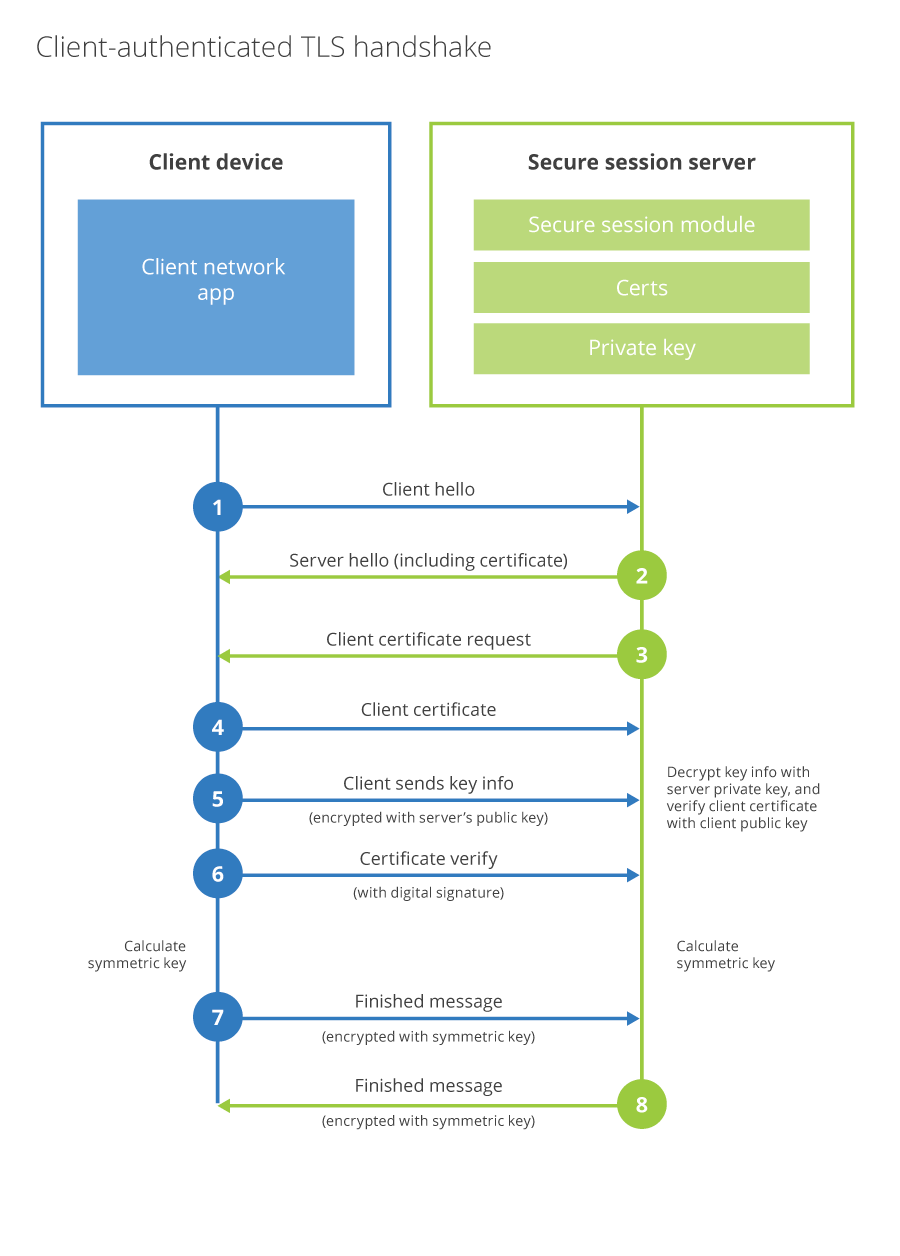
Client certificate authentication Enabled in server side, happens after the client verify the server certification. client send its certification to server side, and the server verfiy the certification. this is an optional steps defined in following diagram
if we are not only talking about the certification authentication, all the password based authentication can belongs to client authentication, as username and password are provided by the client and server do the verification.
Reference: Certification and Authentication Reference: Client Authentication
Http basic authentication is server requests a username and password from the client and server verify the username and password pairs. basic authentication is not a secure authentication mechanism, basic authentication sends the user names and passwords over the internet as base64 encoded text and the target server is not authenticated. however, if the secure http channel is used like SSL or security at the network level such as IPSEC or VPN, some of those concern could be alleviated.
Basic authentication in http header
use -u or --user to specific the user.
curl -u "username:password" http://example.com
curl --user "username:password" http://example.com
Reference: Basic authentication
Like HTTP Basic Authentication, Http Digest Authentication authenticates against username and password, unlike basic authentication, digest authentication send the password hash to the server side.
curl --digest --user daniel:secret http://example.com/
Form based authentication is putting the username and password into http body not in http headers, it is not secure unless ssl is used.
curl -X POST http://example.com -d "{"username":<>,"password":<>}"
Open Authorization, open standard for token-based authentication and authorization on internet. Started in Dec,2007. The purpose of OAUTH is providing a way to access the resource but not provide the credentials, solve the authorization problem. Reference: https://oauth1.wp-api.org/docs/basics/Auth-Flow.html .
Steps:
- Init. client send request to the authentication server for auth token (oauth_token, and oauth_token_secrets)
- Authentication. client redirect the request to authentication server for user login and trust the oauth_token
- Token exchange. client send send the oauth_token to server to exchange to long term access token for resource access.
OAUHT2 is the next verison of OAUTH1.0, but not support OAUTH1.0 backwords. OAUTH2 define the following roles
- Client: website A
- Resource Owner: User
- Resource Server: google
- Authorization Server: google
Client want to visit the reource hold by the resource owner.
- Client redirect the request to the
Authentication Serverwithcall back urlandResponse Type - Authentication Server Authenticated the user credentials, and let user interact whether approve the resource check.
- If user agree,
Authentication Serverredirect the url to thecall back urlalong withauthentication code - Client then in backends use the
authentication code,clientidandclient passwordto exchange theaccessTokenandrefresh tokenwithAuthentication Server - Client use access token to interact with
Resource Ownerfor resource exchange.
grant type:
- code Authentication code returned with redirect uri
- token access token is returned directly with redirect uri
- password Resource owner password credentials
- client credential
Reference: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/an-introduction-to-oauth-2#oauth-roles
OAUTH2 is used to solve the authorization problem, whileas OPENID is used to solve the authentication problem.
In OAUTH2 grant_code=code catagory, when retrieve the access token, client can also send a ID_TOKEN to the server,
the ID_TOKEN is a private key encrypted JWT Token which include the user basic information.
Security Assertion Markup Language is an XML-based, open-standard data format for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, in particular, between an identity provider and a service provider. SAML authorization is a two step process and you are expected to implement support for both.
Central Authentication Service
when talking about JWT, we are compared it with SWT and SAML tokens . JWT and SAML can use private/public key sign, while SWT can only signed by symmetrically shared secrets header.payload.signature. 自认证token.
header: alg: HS256 typ: JWT payload: registered claims: iss, exp, sub, aud ... signature: signature = HMACSHA256( (base64URL(header) + “." + base64URL(payload)), secrets)
HMACSHA256 is HMAC + SHA256. HMAC mixes a secrets with message data, hashes the result with hash functions. mixes the hash value and secrets agains and hashes the result, output is 256 bits length.