Note
Asyncmachine-go is an AOP Actor Model library for distributed workflows, built on top of a lightweight state machine. It has atomic transitions, RPC, logging, TUI debugger, metrics, tracing, and soon diagrams.
/pkg/machine is a nondeterministic, multi-state, clock-based, relational, optionally-accepting, and non-blocking state machine. It can orchestrate blocking APIs into fully-controllable async state machines with ease. Write ops are state mutations and read ops are state checking.
flowchart LR
subgraph ActiveBefore[Before]
A1([A:1])
B1[B:0]
C1[C:0]
end
ActiveMutation([add B])
subgraph ActiveAfter[After]
A2([A:1])
B2([B:1])
C2[C:0]
end
ActiveBefore --> ActiveMutation
ActiveMutation --> ActiveAfter
flowchart LR
subgraph ClockStep1[ ]
A1([A:1])
B1([B:1])
C1[C:0]
end
ClockMutation1[remove B]
subgraph ClockStep2[ ]
A2([A:1])
B2[B:2]
C2[C:0]
end
ClockMutation2([add B])
subgraph ClockStep3[ ]
A3([A:1])
B3([B:3])
C3[C:0]
end
subgraph ClockCtxs[State contexts of B]
CtxB1([B:1])
CtxB3([B:3])
end
ClockStep1 --> ClockMutation1 --> ClockStep2
ClockStep2 --> ClockMutation2 --> ClockStep3
%% B1 --> CtxB1
%% B2 --> CtxB2
%% B3 --> CtxB3
flowchart LR
Machine[[Machine]]
Add1([add A])
Add2([add A])
Add3([add B])
Add1 -- 1 --> Machine
Add2 -- 2 --> Machine
Add3 -- 3 --> Machine
subgraph Queue
direction LR
QAdd1([add A])
QAdd2([add A])
QAdd3([add B])
QAdd1 --> QAdd2 --> QAdd3
end
Machine --> Queue
flowchart LR
subgraph HandlersBefore[ ]
A1([A:1])
B1[B:0]
C1[C:0]
end
subgraph HandlersAfter[ ]
A2([A:1])
B2([B:1])
C2[C:0]
end
HandlersMutation([add B])
HandlersBefore --> HandlersMutation
HandlersMutation --> HandlersAfter
HandlersMutation --> AB
HandlersMutation --> AnyB
HandlersMutation --> BEnter
HandlersMutation --> BState
subgraph Handlers
AB[["AB()"]]
AnyB[["AnyB()"]]
BEnter[["BEnter()"]]
BState[["BState()"]]
end
flowchart LR
subgraph NegotiationBefore[ ]
A1([A:1])
B1[B:0]
C1[C:0]
end
subgraph NegotiationAfter[ ]
A2([A:1])
B2[B:0]
C2[C:0]
end
NegotiationMutation([add B])
NegotiationBefore --> NegotiationMutation
NegotiationMutation --> NegotiationAfter
NegotiationMutation --> AB
NegotiationMutation --> AnyB
NegotiationMutation --> BEnter
BEnter == return ==> false
NegotiationMutation -. canceled .-x BState
subgraph Negotiation
false[[false]]
AB[["AB()"]]
AnyB[["AnyB()"]]
BEnter[["BEnter()"]]
BState[["BState()"]]
end
flowchart LR
Wet(Wet)
Dry(Dry)
Water(Water)
Wet -- Require --> Water
Dry -- Remove --> Wet
Water -- Add --> Wet
Water -- Remove --> Dry
flowchart LR
subgraph SubStates[ ]
direction LR
subgraph SubStep1[ ]
direction BT
A1([A:1])
B1([B:1])
C1[C:0]
end
SubMutation1[remove B]
subgraph SubStep2[ ]
A2([A:1])
B2[B:2]
C2[C:0]
end
SubMutation2([add B])
subgraph SubStep3[ ]
A3([A:1])
B3([B:3])
C3[C:0]
end
end
SubStep1 --> SubMutation1 --> SubStep2
SubStep2 --> SubMutation2 --> SubStep3
B2 .-> WhenNotB
A3 .-> WhenTimeB3
B3 .-> WhenTimeB3
subgraph Subs[ ]
WhenNotB>"WhenNot B"]
WhenTimeB3>"WhenTime A:1 B:3"]
end
val, err := someOp()
if err != nil {
mach.AddErr(err, nil)
return
}TransitionInit TransitionStart TransitionEnd HandlerStart HandlerEnd
MachineInit MachineDispose NewSubmachine QueueEnd StructChange VerifyStates
// ProcessingFile to FileProcessed
// 1 async and 1 sync state
package main
import am "github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/pkg/machine"
func main() {
// init the state machine
mach := am.New(nil, am.Struct{
"ProcessingFile": { // async
Remove: am.S{"FileProcessed"},
},
"FileProcessed": { // async
Remove: am.S{"ProcessingFile"},
},
"InProgress": { // sync
Auto: true,
Require: am.S{"ProcessingFile"},
},
}, nil)
mach.BindHandlers(&Handlers{
Filename: "README.md",
})
// change the state
mach.Add1("ProcessingFile", nil)
// wait for completed
select {
case <-time.After(5 * time.Second):
println("timeout")
case <-mach.WhenErr(nil):
println("err:", mach.Err())
case <-mach.When1("FileProcessed", nil):
println("done")
}
}
type Handlers struct {
Filename string
}
// negotiation handler
func (h *Handlers) ProcessingFileEnter(e *am.Event) bool {
// read-only ops
// decide if moving fwd is ok
// no blocking
// lock-free critical zone
return true
}
// final handler
func (h *Handlers) ProcessingFileState(e *am.Event) {
// read & write ops
// no blocking
// lock-free critical zone
mach := e.Machine
// tick-based context
stateCtx := mach.NewStateCtx("ProcessingFile")
// unblock
go func() {
// re-check the tick ctx
if stateCtx.Err() != nil {
return // expired
}
// blocking call
err := processFile(h.Filename, stateCtx)
if err != nil {
mach.AddErr(err, nil)
return
}
// re-check the tick ctx after a blocking call
if stateCtx.Err() != nil {
return // expired
}
// move to the next state in the flow
mach.Add1("FileProcessed", nil)
}()
}// wait until FileDownloaded becomes active
<-mach.When1("FileDownloaded", nil)
// wait until FileDownloaded becomes inactive
<-mach.WhenNot1("DownloadingFile", nil)
// wait for EventConnected to be activated with an arg ID=123
<-mach.WhenArgs("EventConnected", am.A{"ID": 123}, nil)
// wait for Foo to have a tick >= 6 and Bar tick >= 10
<-mach.WhenTime(am.S{"Foo", "Bar"}, am.Time{6, 10}, nil)
// wait for DownloadingFile to have a tick increased by 2 since now
<-mach.WhenTicks("DownloadingFile", 2, nil)
// wait for an error
<-mach.WhenErr(nil)// BasicStatesDef contains all the states of the Basic state machine.
type BasicStatesDef struct {
*am.StatesBase
// ErrNetwork indicates a generic network error.
ErrNetwork string
// ErrHandlerTimeout indicates one of state machine handlers has timed out.
ErrHandlerTimeout string
// Start indicates the machine should be working. Removing start can force
// stop the machine.
Start string
// Ready indicates the machine meets criteria to perform work, and requires
// Start.
Ready string
// Healthcheck is a periodic request making sure that the machine is still
// alive.
Healthcheck string
}
var BasicStruct = am.Struct{
// Errors
ssB.ErrNetwork: {Require: S{Exception}},
ssB.ErrHandlerTimeout: {Require: S{Exception}},
// Basics
ssB.Start: {},
ssB.Ready: {Require: S{ssB.Start}},
ssB.Healthcheck: {},
}// Example with typed state names (ssS) and typed arguments (A).
mach.Add1(ssS.KillingWorker, Pass(&A{
ConnAddr: ":5555",
WorkerAddr: ":5556",
}))Mutations are the heartbeat of asyncmachine, while relations define the rules of the flow. Check out the relations playground and quiz yourself (or a fancier playground).
mach := newMach("DryWaterWet", am.Struct{
"Wet": {
Require: am.S{"Water"},
},
"Dry": {
Remove: am.S{"Wet"},
},
"Water": {
Add: am.S{"Wet"},
Remove: am.S{"Dry"},
},
})
mach.Add1("Dry", nil)
mach.Add1("Water", nil)
// TODO quiz: is Wet active?- Relations playground
- Interactively use the TUI debugger with data pre-generated by
- libp2p-pubsub-simulator in
- web terminal: http://188.166.101.108:8080/wetty/ssh
- remote terminal:
ssh 188.166.101.108 -p 4444 - local terminal:
go run github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/tools/cmd/am-dbg@latest --import-data https://pancsta.github.io/assets/asyncmachine-go/am-dbg-exports/pubsub-sim.gob.br
- remote integration tests in
- web terminal: http://188.166.101.108:8081/wetty/ssh
- remote terminal:
ssh 188.166.101.108 -p 4445 - local terminal:
go run github.com/pancsta/asyncmachine-go/tools/cmd/am-dbg@latest --import-data https://pancsta.github.io/assets/asyncmachine-go/am-dbg-exports/remote-tests.gob.br
- libp2p-pubsub-simulator in
All examples and benchmarks can be found in /examples.
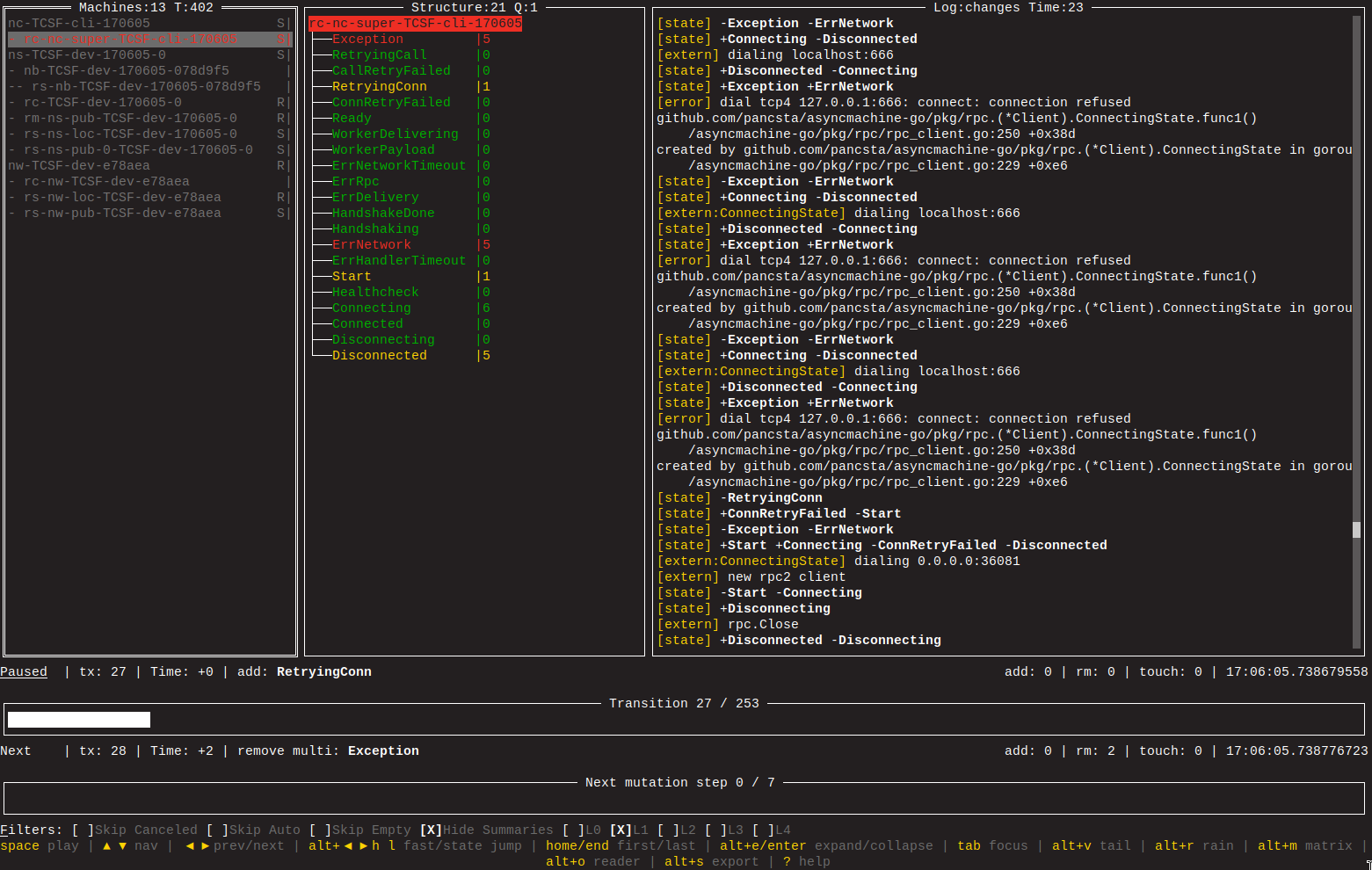
/tools/cmd/am-dbgMulti-client TUI debugger./tools/cmd/am-genGenerates states files and Grafana dashboards./tools/cmd/am-visPlanned.
Bigger implementations worth reading:
- libp2p PubSub Simulator Sandbox simulator for libp2p-pubsub.
- libp2p PubSub Benchmark Benchmark of libp2p-pubsub ported to asyncmachine-go.
- am-dbg TUI Debugger Single state machine TUI app.
The most common API methods are listed below. There's more for local state machines, but all of these are also implemented in the transparent RPC layer.
// A (arguments) is a map of named arguments for a Mutation.
type A map[string]any
// S (state names) is a string list of state names.
type S []string
type Time []uint64
type Clock map[string]uint64
type Result int
type Struct = map[string]State
// Api is a subset of Machine for alternative implementations.
type Api interface {
// ///// REMOTE
// Mutations (remote)
Add1(state string, args A) Result
Add(states S, args A) Result
Remove1(state string, args A) Result
Remove(states S, args A) Result
Set(states S, args A) Result
AddErr(err error, args A) Result
AddErrState(state string, err error, args A) Result
// Waiting (remote)
WhenArgs(state string, args A, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
// Getters (remote)
Err() error
// ///// LOCAL
// Checking (local)
IsErr() bool
Is(states S) bool
Is1(state string) bool
Not(states S) bool
Not1(state string) bool
Any(states ...S) bool
Any1(state ...string) bool
Has(states S) bool
Has1(state string) bool
IsTime(time Time, states S) bool
IsClock(clock Clock) bool
// Waiting (local)
When(states S, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
When1(state string, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenNot(states S, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenNot1(state string, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenTime(
states S, times Time, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenTicks(state string, ticks int, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenTicksEq(state string, tick uint64, ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
WhenErr(ctx context.Context) <-chan struct{}
// Getters (local)
StateNames() S
ActiveStates() S
Tick(state string) uint64
Clock(states S) Clock
Time(states S) Time
TimeSum(states S) uint64
NewStateCtx(state string) context.Context
Export() *Serialized
GetStruct() Struct
Switch(groups ...S) string
// Misc (local)
Log(msg string, args ...any)
Id() string
ParentId() string
SetLogId(val bool)
GetLogId() bool
SetLogger(logger Logger)
SetLogLevel(lvl LogLevel)
SetLoggerEmpty(lvl LogLevel)
SetLoggerSimple(logf func(format string, args ...any), level LogLevel)
Ctx() context.Context
String() string
StringAll() string
Inspect(states S) string
Index(state string) int
BindHandlers(handlers any) error
StatesVerified() bool
Tracers() []Tracer
DetachTracer(tracer Tracer) bool
BindTracer(tracer Tracer)
Dispose()
WhenDisposed() <-chan struct{}
IsDisposed() bool
}It's very easy to get a grasp of how asyncmachine works by reading the idiomatic test suite. Consider the example below of a method used to wait for certain arguments passing via a state activation:
func TestWhenArgs(t *testing.T) {
// init
m := NewRels(t, nil)
// bind
whenCh := m.WhenArgs("B", A{"foo": "bar"}, nil)
// incorrect args
m.Add1("B", A{"foo": "foo"})
select {
case <-whenCh:
t.Fatal("whenCh shouldnt be selected")
default:
// pass
}
// correct args
m.Add1("B", A{"foo": "bar"})
select {
case <-whenCh:
// pass
default:
t.Fatal("whenCh should be selected")
}
// dispose
m.Dispose()
<-m.WhenDisposed()
}Release Candidate, semantically versioned, not optimized yet.
Go back to the monorepo root to continue reading.