-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
ACI workflow
This folder contains matlab files that load an example RevSTEM image and then fit atom columns in STEM image using 2D Gaussian distribution and then index the atom columns to a matrix representation.
The matlab file "ACI_flow.m" contains the sections that can run in sequence by using the command "Run section" in Matlab software. The same result should be expected as shown in "html/ACI_flow.html".
</style>
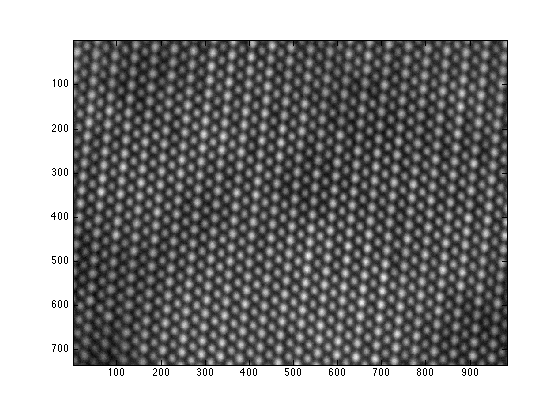
- load the RevSTEM image. The gray-scale image is loaded to the variable 'ImageSum_R'
- display the RevSTEM image
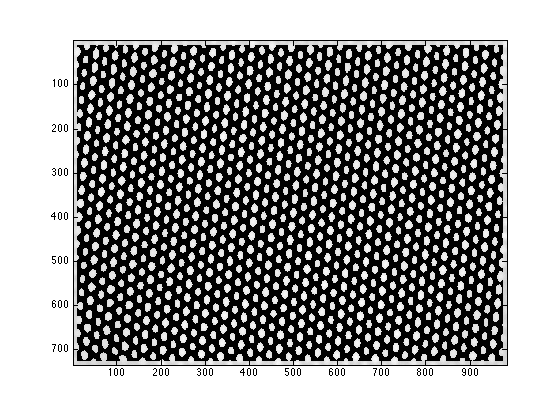
- find the atom column locations using normalized cross correlation data
- find the atom column locations using experimental RevSTEM data
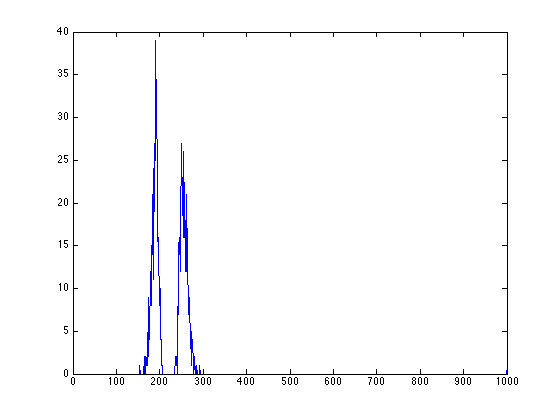
- distance histogram calculated from the fitting result
- calculate PSD for the example image
- we can then use the point-PSD to find exactly locations of peaks at roughly 85 degrees and -5 degrees (175 degrees in the plot)
- note the output from matlab says 'find image aligned a long xxx degree at index yyy', use the index yyy to plot the projected profile
- the matrix representation is stored in 'mini_E'
the RevSTEM image has not been filtered note that our code can also work on regular STEM images the 'serReader.m' script can be used to read a converntiaonl STEM image acquired by TIA
load example.mat
figure;
imagesc(ImageSum_R);
axis image;
colormap(gray);
function [fitresult,oimage,zfit, fiterr, zerr, resnorm,... rr,image1,image2,object_index,mass_center,C,D,StartPoint,h_area]=... find_atomic_columns(raw_image,sigma,threshold,max_peak_num,sign,style,... area_threshold,initial_values,fit_shift,verbose);
% the main output 'fitresult_N' has a cell structure, % each cell is a 1x7 array [amp, ang, sx, sy, xo, yo, zo] containing the peak fitting result % amp: amplitude % ang: rotation angle of the two main axes % sx: sigma along the first main axis % sy: sigma along the second main axis % xo: x coordinate of the peak center % yo: y coordinate of the peak center % zo: background intensity% Meaning of inputs of 'find_atom_clolumns' % raw_image: The input STEM image % sigma: sigma of the gaussian distribution for normalized cross-correlation, % when the number is 0, the program decides the best sigma for ncc % threshold: threshold to separate the atom columns % max_peak_num: the limit of peak numbers % sign: 1: find the peaks; 2: find the valleys (for ABF) % style: 1: use ncc data to fit the peak; 2: use experimental data % area_threshold: only areas within the area_threshold range are used for fitting % initial_values: starting values for peak fitting, can be set as 0 % fit_shift: for future use, 0 % verbose: show the ncc threshold map and area size histogram [fitresult_N,oimage,zfit, fiterr, zerr, resnorm, rr,image1,image2,object_index,mass_center_N]=... find_atomic_columns(ImageSum_R,0,0.1,6000,1,1,[100 400],0,0,1);
gaussian template sigma=8 total peaks found: 974 areas range from 154 to 37563 peaks with areas larger than 10 pixels: 974 peaks with areas larger than 20 pixels: 974
style is set to 2 to use experimental data for fitting starting points are set to be fitresult_N
[fitresult_E,oimage_E,zfit_E, fiterr_E, zerr_E, resnorm_E, rr_E,image1_E,image2_E,startpoint_E,mass_center_E]=...
find_atomic_columns(ImageSum_R,0,0.1,6000,1,2,[100 400],fitresult_N,0,0);
gaussian template sigma=8 total peaks found: 974 areas range from 154 to 37563 peaks with areas larger than 10 pixels: 974 peaks with areas larger than 20 pixels: 974
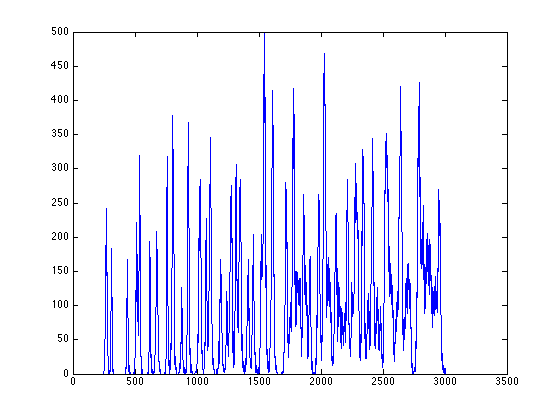
figure; [xydist_E,h_E]=position_analysis(fitresult_E,ImageSum_R,300,30); plot(h_E);
figure; [Iproj,Iavg,Istd]=project_image_RD(ImageSum_R,100,-90:1:90); plot(Istd);
Elapsed time is 5.352220 seconds.
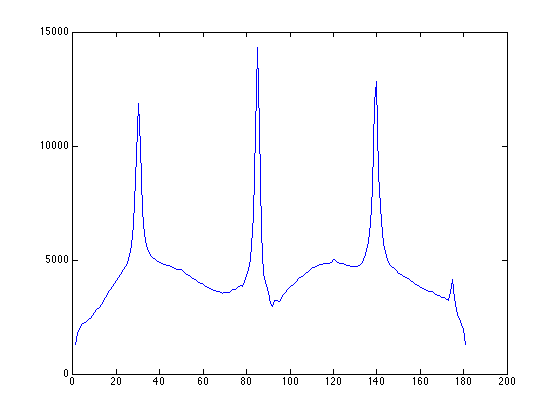
we can then use the point-PSD to find exactly locations of peaks at roughly 85 degrees and -5 degrees (175 degrees in the plot)
figure;
[d_E,proj_acc_E,projx_E,peak_index_E,row_map_E,col_map_E,mini_E,row_stat_E,col_stat_E,coord_angle_E]...
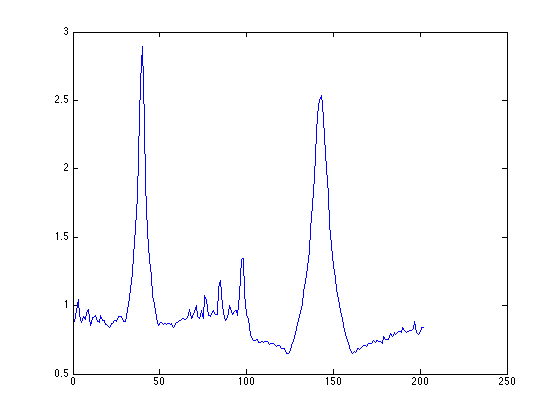
=assign_xy_to_peaks(ImageSum_R,fitresult_E,200,-5,85,1,1);
plot(projx_E);
find image aligned along -6.100000 degree at index 40 find image aligned along 84.100000 degree at index 143
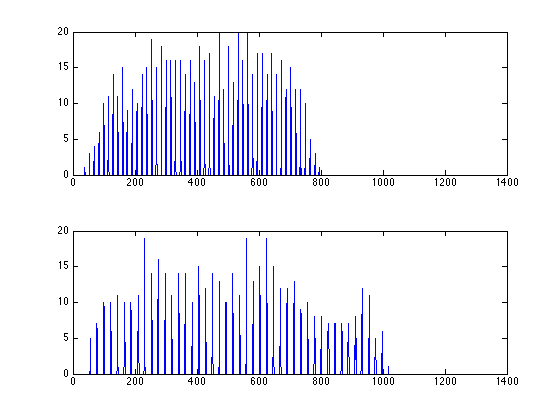
note the output from matlab says 'find image aligned a long xxx degree at index yyy', use the index yyy to plot the projected profile
figure; subplot(2,1,1); plot(proj_acc_E(40,:)); subplot(2,1,2); plot(proj_acc_E(143,:));
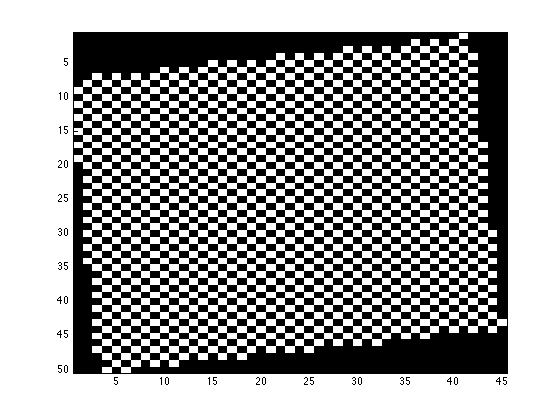
mini_E is a 2D matrix with each node containing the index of the peak fitting result in fitresult_R
figure; imagesc(mini_E>0); daspect([1 sqrt(2) 1]); colormap(gray);
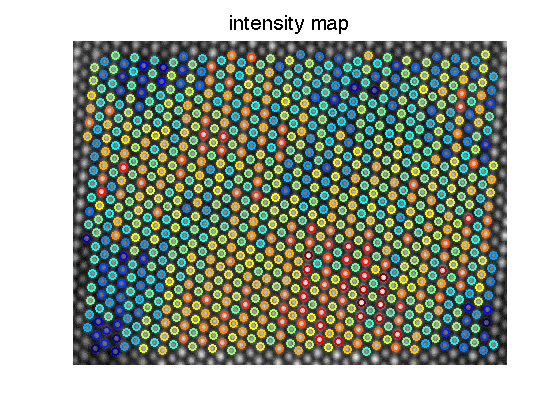
col_int_E=get_col_int( ImageSum_R,fitresult_E,0,0); % the circle around each atom coloumn shows the intensity figure; imagesc(ImageSum_R); axis image axis off colormap(gray); hold on;[sx,sy]=size(mini_E); hold all; jets=jet(256); upper=max(col_int_E); lower=min(col_int_E); for i=1:1:sx for j=1:1:sy if mini_E(i,j) == 0 continue; end p1=mini_E(i,j); if col_int_E(p1)==0 continue; end color_temp=round((col_int_E(p1)-lower)/(upper-lower)*256); if(color_temp<1) color_temp=1; end if(color_temp>256) color_temp=256; end plot(fitresult_E{p1}(5), fitresult_E{p1}(6),'or','color',jets(color_temp,:),'markersize',9,'linewidth',2); end end title('intensity map','fontsize',20);
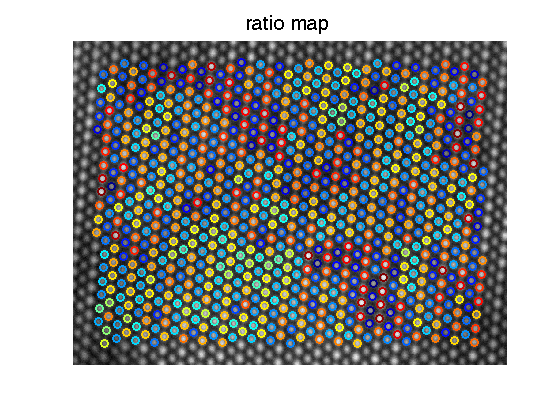
[ratio_E,ratio_E_matrix,col_int_matrix]=get_ratio(fitresult_E,mini_E,col_int_E,1,1);figure; imagesc(ImageSum_R); axis image axis off colormap(gray); hold on;
[sx,sy]=size(mini_E); hold all; jets=jet(256); upper=max(ratio_E); lower=min(ratio_E(ratio_E>0)); for i=1:1:sx for j=1:1:sy if mini_E(i,j) == 0 continue; end p1=mini_E(i,j); if ratio_E(p1)==0 continue; end color_temp=round((ratio_E(p1)-lower)/(upper-lower)*256); if(color_temp<1) color_temp=1; end if(color_temp>256) color_temp=256; end plot(fitresult_E{p1}(5), fitresult_E{p1}(6),'or','color',jets(color_temp,:),'markersize',9,'linewidth',2); end end title('ratio map','fontsize',20);