Note: an improved version of the FUSE algorithm, and with a python interface is available at https://github.com/Aurelien-Pelissier/AlphaFUSE.
Dataset often contains many features that are either redundant or irrelevant, and can thus be removed without incurring much loss of information. Decreasing the number of feature have the advantage of reducing overfitting, simplifying models, and also involve shorter training time, which makes it a key aspect in machine learning.
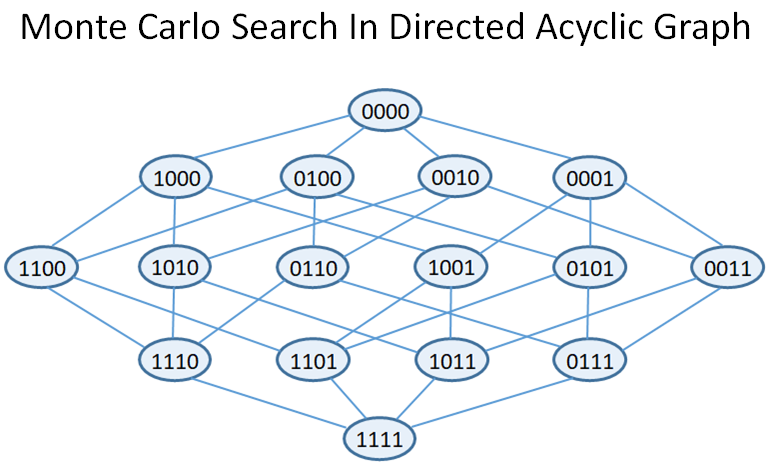
This repository contains the source code to perform feature selection with a reinforcement learning approach, where the feature set state space is represented by a Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG). It provides the C++ implementation of two Monte Carlo DAG Search algorithms. The first one, FUSE [1], starts from the empty feature subset and relies on UCT to identify the best feature subest in the DAG with a fixed budget, while the second one, BLI-MCDS [2] solve the Best Arm Identification problem at different stage in the DAG in the fixed confidence setting.
Both algorithm are available in the src/ foler, they require the boost library (available at https://www.boost.org/) and a c++14 compiler. To compile the code, you can either open the project file src/Feature_Selection.cbp in Code::Blocks, or run the Cmake_build/Makefile in a command prompt if you are using Make. The Makefiles were generated for MinGW, but it is possible to generate other Makefiles with Cmake if you are using different compilers.
The dataset is implemented as a matrix L[n][f+1] where n is the number of training example and f the number of features, the last colomun in the matrix correspond to the labels. The folder contains different functions to read dataset files such as read_dataset(), and all the code related to the training set is implemented in dataset.cpp.
FUSE relies on the well known UCT algorithm to perform Monte Carlo seach in the feature DAG, and stop when the given number of iteration is reached. At the end of the search, the recommended feature subset is the one at the end of the path with highest average.
for a node F, the selected child f node is the one maximizing its UCB Score:

TF is the number of visit of node F, and due to the high branching factor of the tree, the exploration is limited to an Allowed feature set, which restrict the number of considered child nodes depending of TF. A new child node is added whenever int[TF^b] is incremented.
To know which feature to add, we consider the one maximizing its RAVE score, which depends on the average reward over all final node F containing f.
When a node with TF=0 is reached, we evaluate the node by performing random exploration until the stopping feature fs is added. The probability of chosing the stopping feature at depth d is set to 1-q^d.
Once the stopping feature has been selected, the exploration stops and the reward is computed based on a k-Nearest-Neighboor (kNN) classifier. The advantage of kNN is that it requires no prerequisite training, and is not too computationally expensive. The complexity of the reward calculation is scaling as O(n^2*f/r) and is limiting the algorithm to dataset with less than 10000 examples.
The original FUSE algorithm backpropagate the reward only for the nodes withing the current path. Updating all the parents might results in unpracticle updating time as the number of nodes to be updated at depth d scales as d!. Updating all the parents also does not guarantee the convergence of the UCT algorithm.
The main simulation parameters can be changed in src/Main.cpp.
Nt = 100000; //Number of iterations of the simulation
q = 0.98; //Random expansion parameter, used to control the average depth in the random phase, |q|<1
k = 5; //Number of nearest neighbors involved in the reward calculation
m = 50; //Size of the small subsample for the reward calculation
ce = 0.5; //UCB exploration control parameter
cl = 200; //l-RAVE/g-RAVE weight in RAVE score
b = 0.2; //Discrete heuristic exploration parameter, |b|<1
L[n][f+1] = read_dataset("dataset.dat"); //Training set matrixFor details about the parameters, please refer to the implementation details described in [1].
When the simulation is finished, the program mainly return :
- The best feature subset (considered to be the path with highest average at the end of the search)
Path with Highest average: [ 4-0.9605 2-0.9802 5-0.9823 fs-0.9879 ]
- The reward and depth search after each iteration
By running
plot_reward.py(requiresPython 3), we can plot the evelution of the reward during the search:
All the informations are available in output files Output_Tree.txt, Output_Reward.txt and Result.txt.
BLI-MCDS solve the Best Arm Identification problem at different nodes in the DAG to select the best feature subset in the fixed confidence setting, which means that the algorithm stops when the returned feature set is theoretically guaranteed with confidence 1 - delta and precision epsilon.
The main simulation parameters can be changed in src/Main.cpp.
eps = 0.005; //accuracy parameter
delta = 0.1; //risk parameter
b = 0.3; //expansion parameter 0 < b < 1
q = 0.98; //Random expansion parameter, used to control the average depth in the random phase, |q|<1
k = 5; //Number of nearest neighbors involved in the reward calculation
m = 50; //Size of the small subsample for the reward calculation
cl = 200; //l-RAVE/g-RAVE weight in RAVE score
L[n][f+1] = read_dataset("dataset.dat"); //Training set matrixFor details about the parameters, please refer to the implementation details described in [2].
When the simulation is finished, the program return the candidate for the best feature set and the number of leaf evaluated during the search.
Best feature subset after 278306 iterations: [ 5 1 2 ] with reward [ 0.5907 0.9412 0.9943 ]
[1]: Gaudel, Romaric, and Michele Sebag. "Feature selection as a one-player game." International Conference on Machine Learning. 2010. [https://hal.inria.fr/inria-00484049/document].
[2]: A. Pelissier, A. Nakamura, and K. Tabata. "Feature selection as Monte-Carlo Search in Growing Single Rooted Directed Acyclic Graph by Best Leaf Identification". Proceedings of the 2019 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining. 2019. [https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.07531].