-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 91
Getting started
This Quick Start guide will get you up and performing scanning as quickly as possible. All steps described in this guide are required for the integration.
This guide sets up basic Machine readable travel document (MRTD) and US Driver's license (USDL) scanning functionality. It closely follows the BlinkId-sample app. We highly recommend you try to run the sample app. The sample app should compile and run on your device, and in the iOS Simulator.
The source code of the sample app can be used as the reference during the integration.
- If you wish to use version v1.4.0 or above, you need to install Git Large File Storage by running these comamnds:
brew install git-lfs
git lfs install-
Project dependencies to be managed by CocoaPods are specified in a file called
Podfile. Create this file in the same directory as your Xcode project (.xcodeproj) file. -
Copy and paste the following lines into the TextEdit window:
platform :ios, '8.0'
target 'TargetName' do
pod 'PPBlinkID', '~> 2.18.2'
end- Install the dependencies in your project:
$ pod install- From now on, be sure to always open the generated Xcode workspace (
.xcworkspace) instead of the project file when building your project:
open <YourProjectName>.xcworkspace- Download latest release (Download .zip or .tar.gz file starting with BlinkID.
Note: DO NOT download Source Code as GitHub does not fully support Git LFS)
- Besides downloading, you can clone this git repository. You need to install Git Large File Storage by running these commands:
brew install git-lfs
git lfs install- To clone, run the following shell command:
git clone [email protected]:BlinkID/blinkid-ios.git-
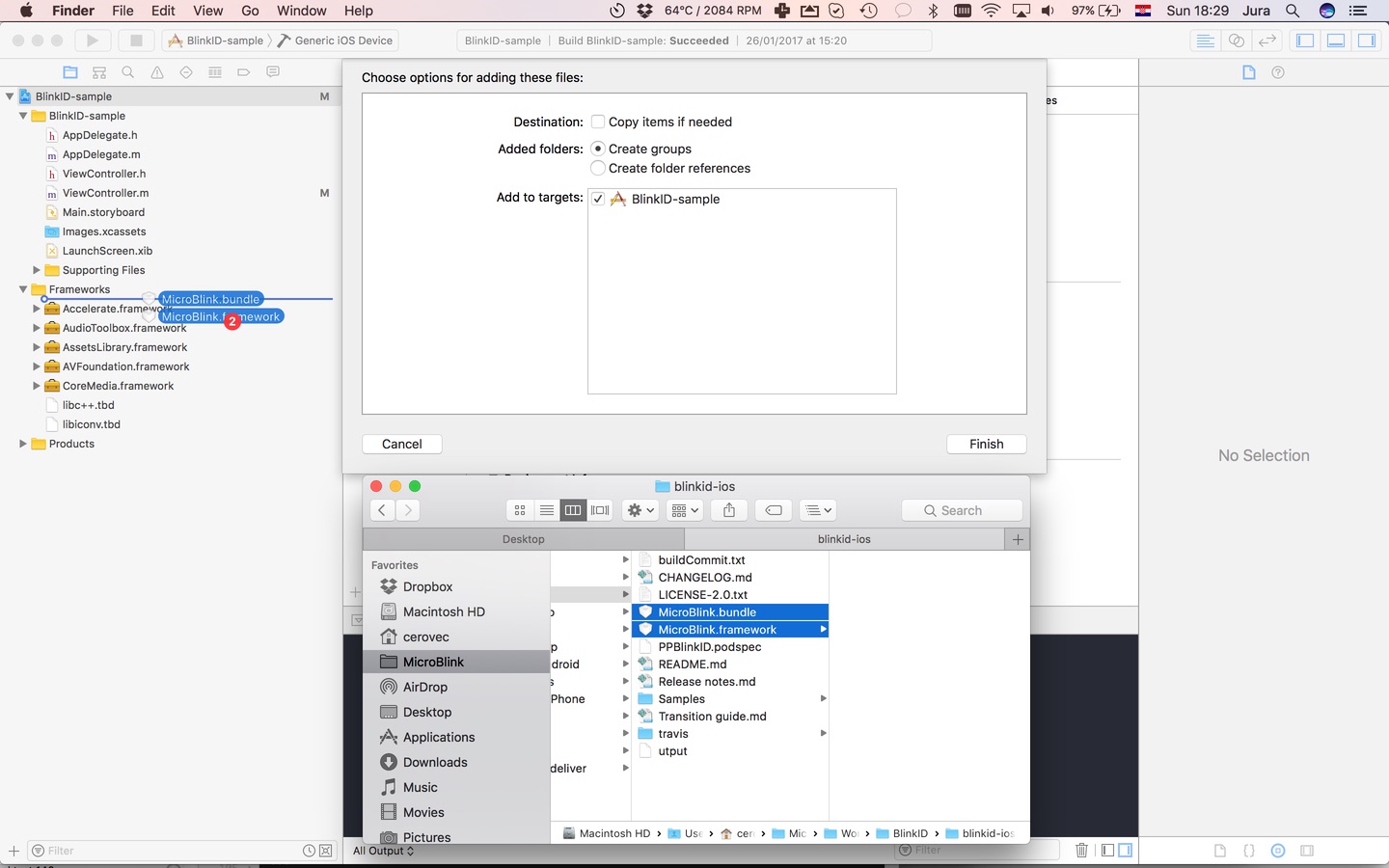
Copy MicroBlink.framework and MicroBlink.bundle to your project folder.
-
In your Xcode project, open the Project navigator. Drag MicroBlink.framework and MicroBlink.bundle files to your project, ideally in the Frameworks group, together with other frameworks you're using. When asked, choose "Create groups", instead of the "Create folder references" option.
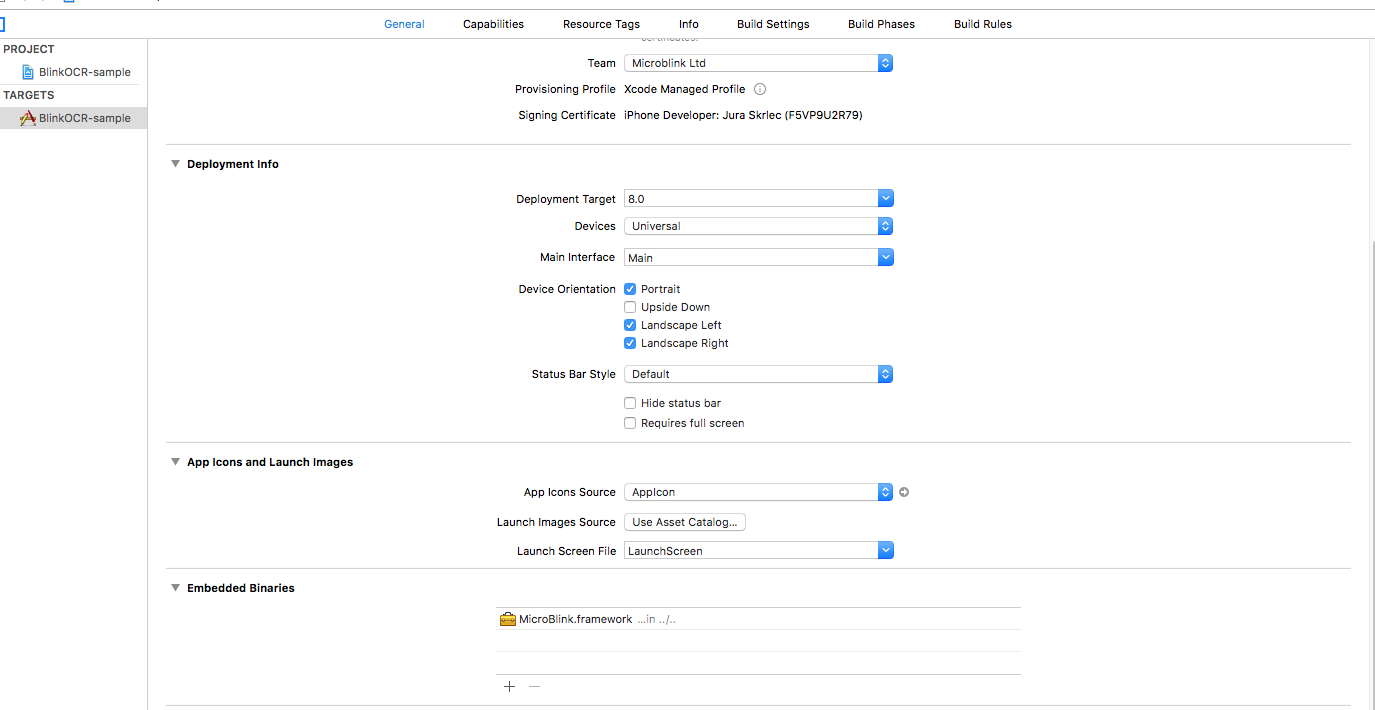
- Since Microblink.framework is a dynamic framework, you also need to add it to embedded binaries section in General settings of your target.
-
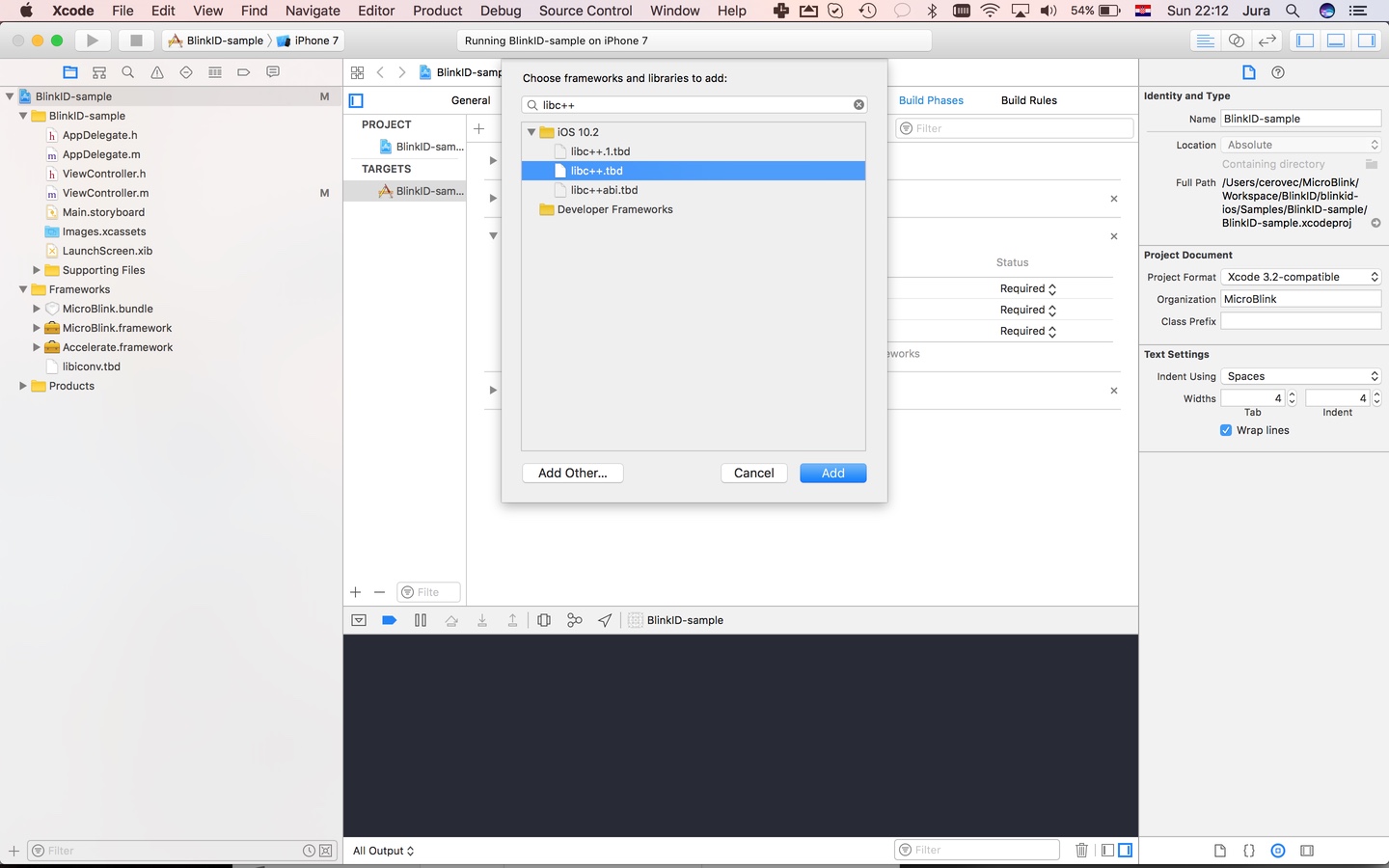
Include the additional frameworks and libraries into your project in the "Linked frameworks and libraries" section of your target settings.
- libc++.tbd
- libz.tbd
- libiconv.tbd
- Accelerate.framework
Step by step guide how to start BlinkID in Xcode 8. A tutorial flows from git clone to successfully deployed demo application on iOS device with real-time screen mirroring. Application demo contains simple use of MRTD recognizer with Croatian ID card.
In files in which you want to use scanning functionality place import directive.
#import <MicroBlink/MicroBlink.h>To initiate the scanning process, first decide where in your app you want to add scanning functionality. Usually, users of the scanning library have a button which, when tapped, starts the scanning process. Initialization code is then placed in touch handler for that button. Here we're listing the initialization code as it looks in a touch handler method.
/**
* Method allocates and initializes the Scanning coordinator object.
* Coordinator is initialized with settings for scanning
* Modify this method to include only those recognizer settings you need. This will give you optimal performance
*
* @param error Error object, if scanning isn't supported
*
* @return initialized coordinator
*/
- (PPCameraCoordinator *)coordinatorWithError:(NSError**)error {
/** 0. Check if scanning is supported */
if ([PPCameraCoordinator isScanningUnsupportedForCameraType:PPCameraTypeBack error:error]) {
return nil;
}
/** 1. Initialize the Scanning settings */
// Initialize the scanner settings object. This initialize settings with all default values.
PPSettings *settings = [[PPSettings alloc] init];
/** 2. Setup the license key */
// Visit www.microblink.com to get the license key for your app
settings.licenseSettings.licenseKey = @"<your license key here>";
/**
* 3. Set up what is being scanned. See detailed guides for specific use cases.
* Here's an example for initializing MRTD and USDL scanning
*/
// To specify we want to perform MRTD (machine readable travel document) recognition, initialize the MRTD recognizer settings
PPMrtdRecognizerSettings *mrtdRecognizerSettings = [[PPMrtdRecognizerSettings alloc] init];
// Add MRTD Recognizer setting to a list of used recognizer settings
[settings.scanSettings addRecognizerSettings:mrtdRecognizerSettings];
// To specify we want to perform USDL (US Driver's license) recognition, initialize the USDL recognizer settings
PPUsdlRecognizerSettings *usdlRecognizerSettings = [[PPUsdlRecognizerSettings alloc] init];
// Add USDL Recognizer setting to a list of used recognizer settings
[settings.scanSettings addRecognizerSettings:usdlRecognizerSettings];
/** 4. Initialize the Scanning Coordinator object */
PPCameraCoordinator *coordinator = [[PPCameraCoordinator alloc] initWithSettings:settings];
return coordinator;
}
- (IBAction)didTapScan:(id)sender {
/** Instantiate the scanning coordinator */
NSError *error;
PPCameraCoordinator *coordinator = [self coordinatorWithError:&error];
/** If scanning isn't supported, present an error */
if (coordinator == nil) {
NSString *messageString = [error localizedDescription];
[[[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"Warning"
message:messageString
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"
otherButtonTitles:nil, nil] show];
return;
}
/** Allocate and present the scanning view controller */
UIViewController<PPScanningViewController>* scanningViewController = [PPViewControllerFactory cameraViewControllerWithDelegate:self coordinator:coordinator error:nil];
/** You can use other presentation methods as well */
[self presentViewController:scanningViewController animated:YES completion:nil];
}In the previous step, you instantiated PPScanningViewController object with a delegate object. This object gets notified on certain events in scanning lifecycle. In this example we set it to self. The protocol which the delegate has to implement is PPScanningDelegate protocol. You can use the following default implementation of the protocol to get you started.
- (void)scanningViewControllerUnauthorizedCamera:(UIViewController<PPScanningViewController> *)scanningViewController {
// Add any logic which handles UI when app user doesn't allow usage of the phone's camera
}
- (void)scanningViewController:(UIViewController<PPScanningViewController> *)scanningViewController
didFindError:(NSError *)error {
// Can be ignored. See description of the method
}
- (void)scanningViewControllerDidClose:(UIViewController<PPScanningViewController> *)scanningViewController {
// As scanning view controller is presented full screen and modally, dismiss it
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}
- (void)scanningViewController:(UIViewController<PPScanningViewController> *)scanningViewController
didOutputResults:(NSArray *)results {
// Here you process scanning results. Scanning results are given in the array of PPRecognizerResult objects.
// first, pause scanning until we process all the results
[scanningViewController pauseScanning];
NSString* message;
NSString* title;
// Collect data from the result
for (PPRecognizerResult* result in results) {
if ([result isKindOfClass:[PPMrtdRecognizerResult class]]) {
PPMrtdRecognizerResult* mrtdResult = (PPMrtdRecognizerResult*)result;
title = @"MRTD";
message = [mrtdResult description];
}
if ([result isKindOfClass:[PPUsdlRecognizerResult class]]) {
PPUsdlRecognizerResult* usdlResult = (PPUsdlRecognizerResult*)result;
title = @"USDL";
message = [usdlResult description];
}
};
// present the alert view with scanned results
UIAlertView *alertView = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:title message:message delegate:self cancelButtonTitle:@"OK" otherButtonTitles:nil];
[alertView show];
}
// dismiss the scanning view controller when user presses OK.
- (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex {
[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:nil];
}With this performed, you've successfully integrated the scanning functionality in your app.
For next steps, you will either want to:
-
Know more about obtaining scanning results in general.
-
Jump directly to using different recognizers:
- Using MRTD recognizer for scanning Machine readable travel documents like passports, visas and ID cards
- Using USDL recognizer for scanning and parsing US Driver Licenses
- Using EUDL recognizer for scanning UK Driving Licenses
- Using other BlinkID recognizers for scanning other supported documents
- Using PDF417 recognizer for scanning PDF417 barcodes
- Using BarDecoder recognizer for Code 39 and Code 128 1D barcodes
- Using ZXing recognizer for all other 1D and 2D barcode types
- Using Detector Recognizer for detecting documents based on their edges or for detecting documents with Machine readable zone
- Using OCR recognizer for generic OCR on images.
- Using Templating API for scanning custom documents.
-
Know more about customizing Camera UI.
-
Learn about Direct Processing API which you can use to process UIImage objects directly, without using camera management in the SDK.
For additional help, contact us directly at help.microblink.com.
- Getting Started with BlinkID SDK
- Obtaining scanning results
- Using Direct Processing API
- Customizing Camera UI
- Creating customized framework
- Upgrading from older versions
- Troubleshoot