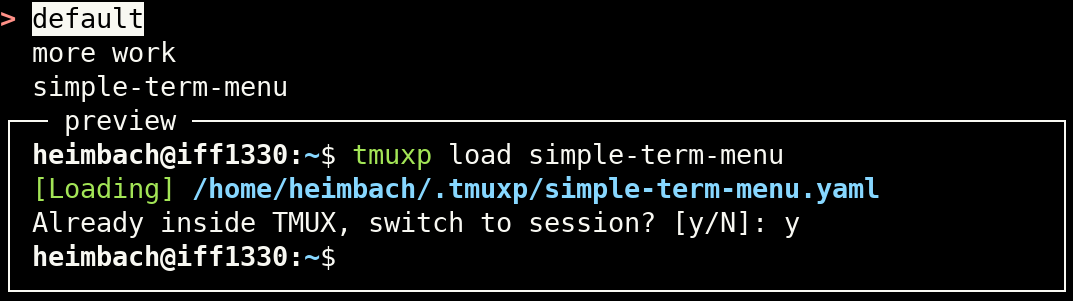
simple-term-menu creates simple menus for interactive command line programs. It can be used to offer a choice of
different options to the user. Menu entries can be selected with the arrow or j/k keys. The module uses the terminfo
database to detect terminal features automatically and disables styles that are not available.
Currently, Linux and macOS are supported.
If you update from version 0.x to 1.x, please consider these breaking changes:
-
The
TerminalMenuconstructor now only takes keyword-only arguments (except for the first parameter which contains the menu entries). This makes it easier to add new parameters in future releases and allows to keep a well-arranged parameter list. -
The command line interface was revised. It now uses
-instead of_to separate words consistently and rearranges short options. Only the most important short options were kept to save free letters for future releases.
-
The
multi_select_keyparameter is now namedmulti_select_keysand takes an iterable of keys and by defaultspaceandtabare now used as multi-select keys. This allows to toggle selected items in search mode. -
The
shortcut_parentheses_highlight_styleparameter is renamed toshortcut_brackets_highlight_styleto be more consistent with the newmulti_select_cursor_brackets_styleparameter.
simple-term-menu is available on PyPI for Python 3.5+ and can be installed with pip:
python3 -m pip install simple-term-menuIf you use Arch Linux or one of its derivatives, you can also install simple-term-menu from the
AUR:
yay -S python-simple-term-menuYou also find self-contained executables for 64-bit Linux distributions and macOS High Sierra and newer on the releases page. They are created with PyInstaller and only require glibc >= 2.17 on Linux (should be fine on any recent Linux system).
Create an instance of the class TerminalMenu and pass the menu entries as a list of strings to the constructor. Call
the show method to output the menu and wait for keyboard input:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu
def main():
options = ["entry 1", "entry 2", "entry 3"]
terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(options)
menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show()
print(f"You have selected {options[menu_entry_index]}!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()You will get an output like:
You can now select a menu entry with the arrow keys or j/k (vim motions) and accept your choice by hitting enter or
cancel the menu with escape, q or <Ctrl>-C. show returns the selected menu entry index or None if the menu was
canceled.
You can pass an optional title to the TerminalMenu constructor which will be placed above the menu. title can be a
simple string, a multiline string (with \n newlines) or a list of strings. The same applies to the status_bar
parameter, which places a status bar below the menu. Moreover, you can use a callable as status_bar parameter which
takes the currently selected entry and returns a status bar string.
You can pass styling arguments to the TerminalMenu constructor. Each style is a tuple of keyword strings. Currently
the following keywords are accepted:
bg_blackbg_bluebg_cyanbg_graybg_greenbg_purplebg_redbg_yellowfg_blackfg_bluefg_cyanfg_grayfg_greenfg_purplefg_redfg_yellowbolditalicsstandoutunderline
You can alter the following styles:
-
menu_cursor_style: The style of the shown cursor. The default style is("fg_red", "bold"). -
menu_highlight_style: The style of the selected menu entry. The default style is("standout",). -
search_highlight_style: The style of matched search strings. The default style is("fg_black", "bg_yellow", "bold"). -
shortcut_key_highlight_style: The style of shortcut keys. The default style is("fg_blue",). -
shortcut_brackets_highlight_style: The style of brackets enclosing shortcut keys. The default style is("fg_gray",). -
status_bar_style: The style of the status bar below the menu. The default style is("fg_yellow", "bg_black"). -
multi_select_cursor_style: The style of the cursor which pins a selected entry in a multi-selection. The default style is("fg_yellow", "bold"). This style excludes brackets (see below). -
multi_select_cursor_brackets_style: The style of brackets in themulti_select_cursor(([{<)]}>). The default style is("fg_gray",).
By setting menu_cursor you can define another cursor or disable it (None). The default cursor is "> ".
The parameter multi_select_cursor customizes the multi-select cursor (the default is "[*] ").
simple_term_menu has a built-in search feature to filter shown menu entries. The default key to activate search mode
is / (like in Vim, less and other terminal programs). If you prefer another search key, pass a search_key parameter
to the TerminalMenu constructor. None can be passed to activate the search on every letter key. Obviously, j and
k cannot be used for cursor motions in that mode. Use <Ctrl-j> and <Ctrl-k> instead.
The search mode supports Python regex syntax. Visit the Python re documentation for more details.
String parts of the menu entries which match the given search pattern are highlighted. Use the search_highlight_style
parameter to adjust the highlight style to your liking.
By default, the search is case insensitive. Set search_case_sensitive to True if you prefer a case sensitive search
line.
Pass show_search_hint=True to the TerminalMenu constructor to activate a search hint in the search line (like
(Press "/" to search)).
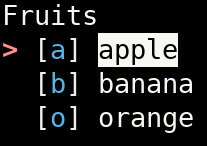
You can define shortcuts for selected menu entries by prepending a single character enclosed in square brackets (like
[a]). Pass shortcut_key_highlight_style and/or shortcut_brackets_highlight_style to the TerminalMenu constructor
to change the default highlight style of the shortcuts.
By default, the show method returns when a shortcut key is pressed. If you only want the selection to jump the
shortcut target, pass exit_on_shortcut=False to the TerminalMenu constructor.
If you configured the search to be activated on every letter key, the shortcut feature will be disabled.
Pass show_shortcut_hints=True to the TerminalMenu constructor to display shortcut hints in the status bar (useful
for very long menus which need scrolling). Additionally pass show_shortcut_hints_in_status_bar=False if you prefer
shortcut hints in the menu title.
Create a menu of some fruits and use the first letter as shortcut key:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu
def main():
fruits = ["[a] apple", "[b] banana", "[o] orange"]
terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(fruits, title="Fruits")
menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()The default key to accept a menu item is enter. Pass the accept_keys parameter with a tuple of keys (as strings) to
the TerminalMenu constructor to use a different set of accept keys. Custom accept keys can be plain ascii letters or
ascii letters with a modifier key (prepend ctrl- or alt- to an ascii letter). Use the chosen_accept_key property
of the TerminalMenu instance to query which accept key was pressed by the user.
Be aware that not all combinations of modifier and ascii keys will work depending on your terminal emulator and
graphical user interface. In addition, some combinations generate other existing keys (e.g. ctrl-m is enter /
carriage return).
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu
def main():
terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(["entry 1", "entry 2", "entry 3"], accept_keys=("enter", "alt-d", "ctrl-i"))
menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show()
print(terminal_menu.chosen_accept_key)
if __name__ == "__main__":
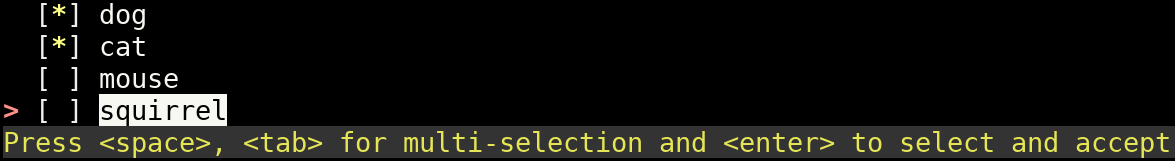
main()Pass multi_select=True to the TerminalMenu constructor to enable the multi-select mode. Press space or tab on an
arbitrary menu item to add it to your selection. Press enter (or any other configured accept_key) to add the
currently selected entry as the last item to the selection and to return from the show method as usual. In
multi-select mode, the show method returns a sorted tuple of all your selected menu indices instead of a single int.
Use the chosen_menu_entries property to get a tuple of the menu entry strings instead. By setting multi_select_keys
you can define another set of keys to toggle a selected item. By passing show_multi_select_hint=True a multi-select
mode hint is shown in the status bar. If you don't want the accept_key to also select the last highlighted item you
can pass multi_select_select_on_accept=False. If no menu item is explicitly selected, the last highlighted menu item
will still be added to the selection unless you also pass multi_select_empty_ok=True.
An optional list (or any other iterable object) preselected_entries can also be passed to have items already selected
when the menu is displayed. This list can be composed of either integers representing indexes of the menu_entries
list, or strings matching the elements of menu_entries. Integers and strings can be mixed.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu
def main():
terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(
["dog", "cat", "mouse", "squirrel"],
multi_select=True,
show_multi_select_hint=True,
)
menu_entry_indices = terminal_menu.show()
print(menu_entry_indices)
print(terminal_menu.chosen_menu_entries)
if __name__ == "__main__":
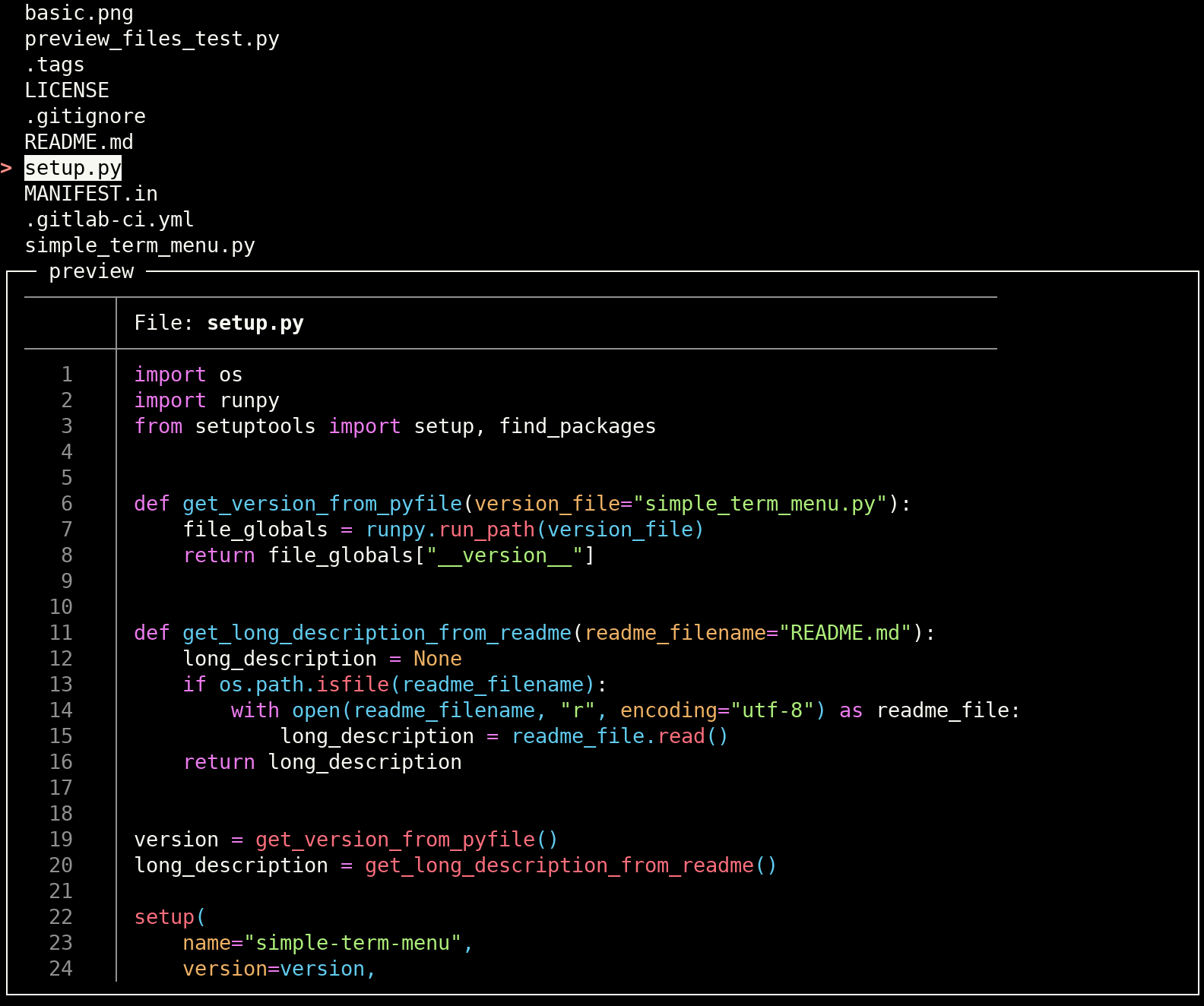
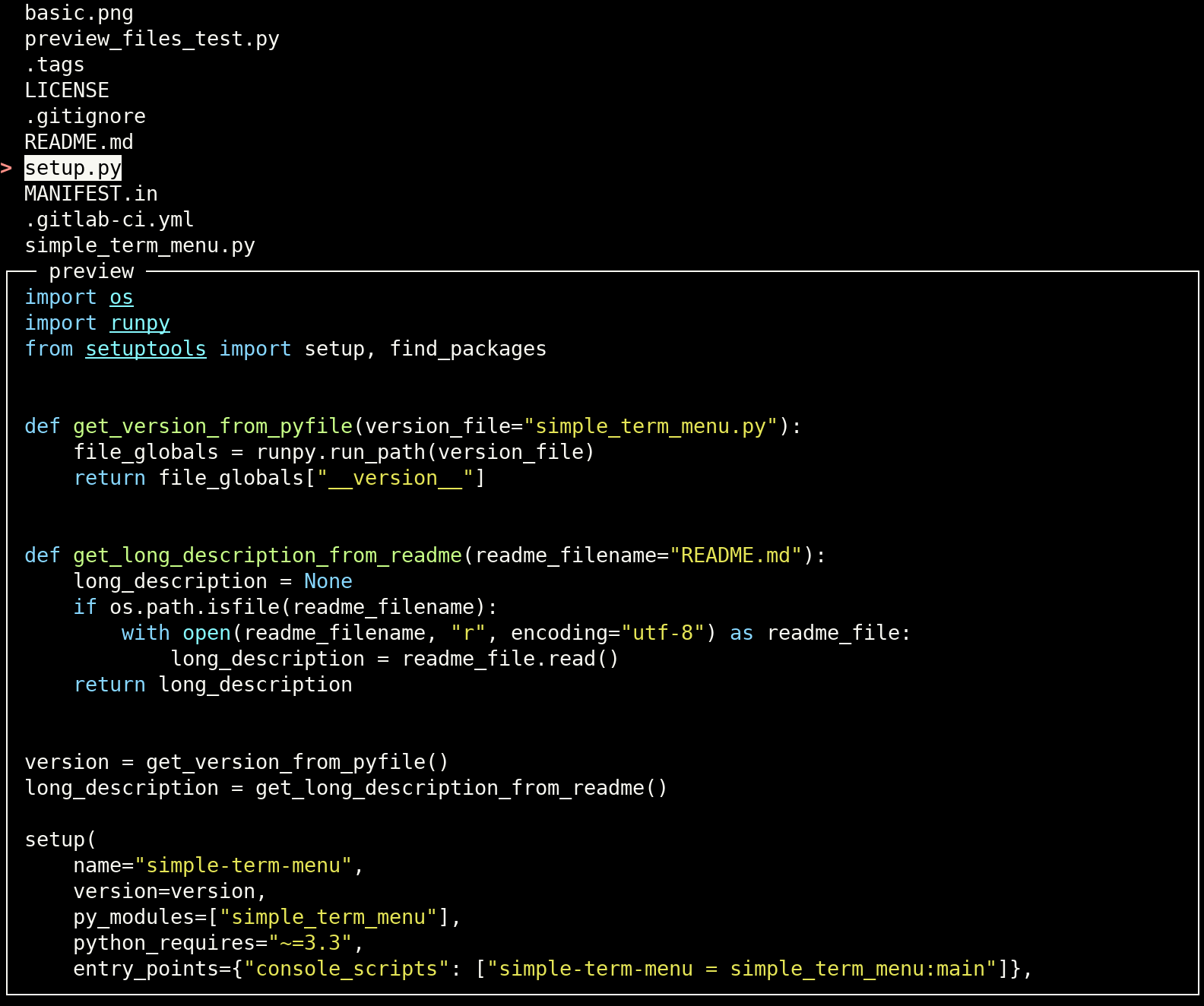
main()simple-term-menu can show a preview for each menu entry. Pass a preview_command to the TerminalMenu constructor to
activate this optional feature. preview_command either takes a command string which will be executed as a subprocess
or a Python callable which converts a given menu entry string into the preview output. If a command string is given, the
pattern {} is replaced with the current menu entry string. If a menu entry has an additional data component (separated
by |), it is passed instead to the preview command. \| can be used for a literal |. If you simply append a |
(without a data component), the preview window will be disabled for this entry.
The additional keyword argument preview_size can be used to control the height of the preview window. It is given as
fraction of the complete terminal height (default: 0.25). The width cannot be set, it is always the complete width of
the terminal window.
Pass preview_title with a string of your choice to customize the preview window title (default: "preview") or
preview_border=False to deactivate the border around the preview window (also deactivates the title string).
Preview commands are allowed to generate ANSI escape color codes.
-
Create a menu for all files in the current directory and preview their contents with the
batcommand:#!/usr/bin/env python3 import os from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu def list_files(directory="."): return (file for file in os.listdir(directory) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(directory, file))) def main(): terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(list_files(), preview_command="bat --color=always {}", preview_size=0.75) menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
-
Another file preview example using the Pygments api:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 import os from pygments import formatters, highlight, lexers from pygments.util import ClassNotFound from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu def highlight_file(filepath): with open(filepath, "r") as f: file_content = f.read() try: lexer = lexers.get_lexer_for_filename(filepath, stripnl=False, stripall=False) except ClassNotFound: lexer = lexers.get_lexer_by_name("text", stripnl=False, stripall=False) formatter = formatters.TerminalFormatter(bg="dark") # dark or light highlighted_file_content = highlight(file_content, lexer, formatter) return highlighted_file_content def list_files(directory="."): return (file for file in os.listdir(directory) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(directory, file))) def main(): terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(list_files(), preview_command=highlight_file, preview_size=0.75) menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
-
Preview the active pane of each running tmux session (the session ids are appended to the menu entries with the
|separator):#!/usr/bin/env python3 import subprocess from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu def list_tmux_sessions(): tmux_command_output = subprocess.check_output( ["tmux", "list-sessions", "-F#{session_id}:#{session_name}"], universal_newlines=True ) tmux_sessions = [] for line in tmux_command_output.split("\n"): line = line.strip() if not line: continue session_id, session_name = tuple(line.split(":")) tmux_sessions.append((session_name, session_id)) return tmux_sessions def main(): terminal_menu = TerminalMenu( ("|".join(session) for session in list_tmux_sessions()), preview_command="tmux capture-pane -e -p -t {}", preview_size=0.75, ) menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Use the constructor parameter skip_empty_entries or the flag --skip-empty-entries to interpret an empty string value
in the menu entries as an empty menu entry (will be skipped when iterating over the entries). A None value is always
considered as an empty menu entry independently from the skip_empty_entries parameter.
from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu
def main(): # Or use `None` instead of `""`:
options = ["entry 1", "entry 2", "", "add", "edit"] # ["entry 1", "entry 2", None, "add", "edit"]
terminal_menu = TerminalMenu(options, skip_empty_entries=True) # TerminalMenu(options)
menu_entry_index = terminal_menu.show()
print(f"You have selected {options[menu_entry_index]}!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Use the constructor parameters
show_search_hint_textandshow_multi_select_hint_text
to modify the corresponding texts. Use the placeholder {key} for the search key in show_search_hint_text and both
{accept_keys} and {multi_select_keys} in show_multi_select_hint_text if appropriately.
Furthermore, the TerminalMenu constructor takes these additional parameters to change the menu behavior:
cycle_cursor: A bool value which indicates if the menu cursor cycles when the end of the menu is reached. Defaults toTrue.clear_screen: A bool value which indicates if the screen will be cleared before the menu is shown. Defaults toFalse.clear_menu_on_exit: A bool value which indicates if the menu will be cleared after theshowmethod. Defaults toTrue.cursor_index: The initially selected item index.status_bar_below_preview: Position the status bar below the preview window (default positioning is above).
simple-term-menu can be used as a terminal program in shell scripts. The exit code of the script is the 1-based index
of the selected menu entry. The exit code 0 reports the cancel action. The following command line arguments are
supported:
usage: simple-term-menu [-h] [-s] [-X] [-l] [--cursor CURSOR]
[-i CURSOR_INDEX] [--cursor-style CURSOR_STYLE] [-C]
[-E] [--highlight-style HIGHLIGHT_STYLE] [-m]
[--multi-select-cursor MULTI_SELECT_CURSOR]
[--multi-select-cursor-brackets-style MULTI_SELECT_CURSOR_BRACKETS_STYLE]
[--multi-select-cursor-style MULTI_SELECT_CURSOR_STYLE]
[--multi-select-keys MULTI_SELECT_KEYS]
[--multi-select-no-select-on-accept]
[--multi-select-empty-ok] [-p PREVIEW_COMMAND]
[--no-preview-border] [--preview-size PREVIEW_SIZE]
[--preview-title PREVIEW_TITLE]
[--search-highlight-style SEARCH_HIGHLIGHT_STYLE]
[--search-key SEARCH_KEY]
[--shortcut-brackets-highlight-style SHORTCUT_BRACKETS_HIGHLIGHT_STYLE]
[--shortcut-key-highlight-style SHORTCUT_KEY_HIGHLIGHT_STYLE]
[--show-multi-select-hint]
[--show-multi-select-hint-text SHOW_MULTI_SELECT_HINT_TEXT]
[--show-search-hint]
[--show-search-hint-text SHOW_SEARCH_HINT_TEXT]
[--show-shortcut-hints]
[--show-shortcut-hints-in-title]
[--skip-empty-entries] [-b STATUS_BAR] [-d]
[--status-bar-style STATUS_BAR_STYLE] [--stdout]
[-t TITLE] [-V]
[-r PRESELECTED_ENTRIES | -R PRESELECTED_INDICES]
[entries ...]
simple-term-menu creates simple interactive menus in the terminal and returns the selected entry as exit code.
positional arguments:
entries the menu entries to show
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s, --case-sensitive searches are case sensitive
-X, --no-clear-menu-on-exit
do not clear the menu on exit
-l, --clear-screen clear the screen before the menu is shown
--cursor CURSOR menu cursor (default: "> ")
-i CURSOR_INDEX, --cursor-index CURSOR_INDEX
initially selected item index
--cursor-style CURSOR_STYLE
style for the menu cursor as comma separated list
(default: "fg_red,bold")
-C, --no-cycle do not cycle the menu selection
-E, --no-exit-on-shortcut
do not exit on shortcut keys
--highlight-style HIGHLIGHT_STYLE
style for the selected menu entry as comma separated
list (default: "standout")
-m, --multi-select Allow the selection of multiple entries (implies
`--stdout`)
--multi-select-cursor MULTI_SELECT_CURSOR
multi-select menu cursor (default: "[*] ")
--multi-select-cursor-brackets-style MULTI_SELECT_CURSOR_BRACKETS_STYLE
style for brackets of the multi-select menu cursor as
comma separated list (default: "fg_gray")
--multi-select-cursor-style MULTI_SELECT_CURSOR_STYLE
style for the multi-select menu cursor as comma
separated list (default: "fg_yellow,bold")
--multi-select-keys MULTI_SELECT_KEYS
key for toggling a selected item in a multi-selection
(default: " ,tab",
--multi-select-no-select-on-accept
do not select the currently highlighted menu item when
the accept key is pressed (it is still selected if no
other item was selected before)
--multi-select-empty-ok
when used together with --multi-select-no-select-on-
accept allows returning no selection at all
-p PREVIEW_COMMAND, --preview PREVIEW_COMMAND
Command to generate a preview for the selected menu
entry. "{}" can be used as placeholder for the menu
text. If the menu entry has a data component
(separated by "|"), this is used instead.
--no-preview-border do not draw a border around the preview window
--preview-size PREVIEW_SIZE
maximum height of the preview window in fractions of
the terminal height (default: "0.25")
--preview-title PREVIEW_TITLE
title of the preview window (default: "preview")
--search-highlight-style SEARCH_HIGHLIGHT_STYLE
style of matched search patterns (default:
"fg_black,bg_yellow,bold")
--search-key SEARCH_KEY
key to start a search (default: "/", "none" is treated
a special value which activates the search on any
letter key)
--shortcut-brackets-highlight-style SHORTCUT_BRACKETS_HIGHLIGHT_STYLE
style of brackets enclosing shortcut keys (default:
"fg_gray")
--shortcut-key-highlight-style SHORTCUT_KEY_HIGHLIGHT_STYLE
style of shortcut keys (default: "fg_blue")
--show-multi-select-hint
show a multi-select hint in the status bar
--show-multi-select-hint-text SHOW_MULTI_SELECT_HINT_TEXT
Custom text which will be shown as multi-select hint.
Use the placeholders {multi_select_keys} and
{accept_keys} if appropriately.
--show-search-hint show a search hint in the search line
--show-search-hint-text SHOW_SEARCH_HINT_TEXT
Custom text which will be shown as search hint. Use
the placeholders {key} for the search key if
appropriately.
--show-shortcut-hints
show shortcut hints in the status bar
--show-shortcut-hints-in-title
show shortcut hints in the menu title
--skip-empty-entries Interpret an empty string in menu entries as an empty
menu entry
-b STATUS_BAR, --status-bar STATUS_BAR
status bar text
-d, --status-bar-below-preview
show the status bar below the preview window if any
--status-bar-style STATUS_BAR_STYLE
style of the status bar lines (default:
"fg_yellow,bg_black")
--stdout Print the selected menu index or indices to stdout (in
addition to the exit status). Multiple indices are
separated by ";".
-t TITLE, --title TITLE
menu title
-V, --version print the version number and exit
-r PRESELECTED_ENTRIES, --preselected_entries PRESELECTED_ENTRIES
Comma separated list of strings matching menu items to
start pre-selected in a multi-select menu.
-R PRESELECTED_INDICES, --preselected_indices PRESELECTED_INDICES
Comma separated list of numeric indexes of menu items
to start pre-selected in a multi-select menu.
Instead of using the Python api as in the previous examples, a file menu with bat preview can
also be created from the command line:
simple-term-menu -p "bat --color=always {}" \
--preview-size 0.75 \
$(find . -maxdepth 1 -type f | awk '{ print substr($0, 3) }')A more advanced example with sub menus (thanks to pageauc):
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Demonstration example for GitHub Project at
https://github.com/IngoMeyer441/simple-term-menu
This code only works in python3. Install per
sudo pip3 install simple-term-menu
"""
import time
from simple_term_menu import TerminalMenu
def main():
main_menu_title = " Main Menu\n"
main_menu_items = ["Edit Menu", "Second Item", "Third Item", "Quit"]
main_menu_cursor = "> "
main_menu_cursor_style = ("fg_red", "bold")
main_menu_style = ("bg_red", "fg_yellow")
main_menu_exit = False
main_menu = TerminalMenu(
menu_entries=main_menu_items,
title=main_menu_title,
menu_cursor=main_menu_cursor,
menu_cursor_style=main_menu_cursor_style,
menu_highlight_style=main_menu_style,
cycle_cursor=True,
clear_screen=True,
)
edit_menu_title = " Edit Menu\n"
edit_menu_items = ["Edit Config", "Save Settings", "Back to Main Menu"]
edit_menu_back = False
edit_menu = TerminalMenu(
edit_menu_items,
title=edit_menu_title,
menu_cursor=main_menu_cursor,
menu_cursor_style=main_menu_cursor_style,
menu_highlight_style=main_menu_style,
cycle_cursor=True,
clear_screen=True,
)
while not main_menu_exit:
main_sel = main_menu.show()
if main_sel == 0:
while not edit_menu_back:
edit_sel = edit_menu.show()
if edit_sel == 0:
print("Edit Config Selected")
time.sleep(5)
elif edit_sel == 1:
print("Save Selected")
time.sleep(5)
elif edit_sel == 2:
edit_menu_back = True
print("Back Selected")
edit_menu_back = False
elif main_sel == 1:
print("option 2 selected")
time.sleep(5)
elif main_sel == 2:
print("option 3 selected")
time.sleep(5)
elif main_sel == 3:
main_menu_exit = True
print("Quit Selected")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()bullet: Creates bullet-lists with multi-selection support.
Please open an issue on GitHub if you experience bugs or miss features. Please consider to send a pull request if you can spend time on fixing the issue yourself. This project uses pre-commit to ensure code quality and a consistent code style. Run
make git-hooks-installto install all linters as Git hooks in your local clone of simple-term-menu.