Kuhn poker implemented in accordance to OpenAI gym interface.
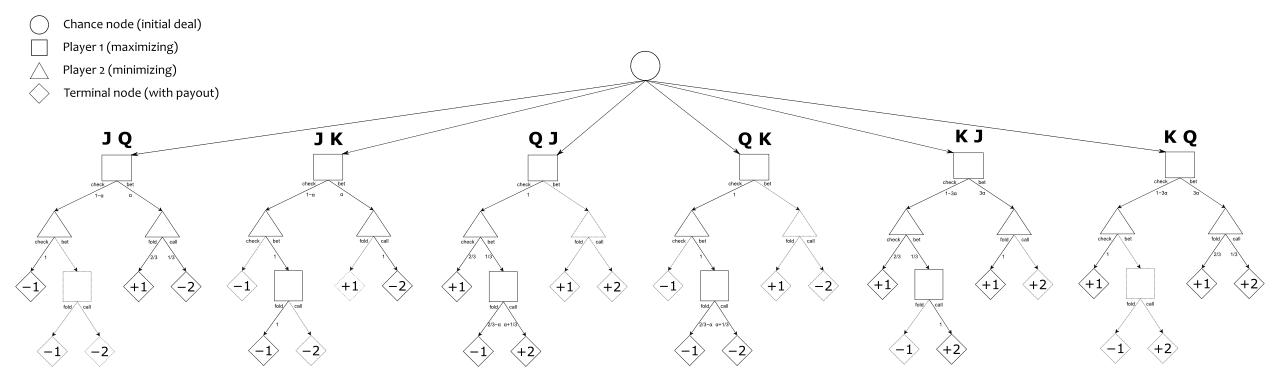
Kuhn poker is an extremely simplified form of poker developed by Harold W. Kuhn as a simple model zero-sum, two-player, imperfect-information, sequential game, amenable to a complete game-theoretic analysis. In Kuhn poker, the deck includes only three playing cards, for example a King, Queen, and Jack. One card is dealt to each player, which may place bets similarly to a standard poker. If both players bet or both players pass, the player with the higher card wins, otherwise, the betting player wins.
Wikipedia Explanation of Kuhn's poker
The action space is discrete, containing two actions: [PASS, BET].
NOTE: original Kuhn's game contains a third move CHECK.
We argue that CHECK dominates PASS dominates PASS,
and hence we eliminate it from the action space. This has the advantage
of ensuring that on every time step there's only 2 possible actions.
The state space represents the internal environment state. It is the concatenation of the following vectors:
Current player. One hot encoding for current player.Player hand. One hot encoding of which card each player has.Betting history. One hot encoding of whether each playerPASSed orBETted.Pot contributions. A vectorp = [p_1, p_2], wherep_1corresponds to the contribution of player 1 to the pot. It includes player'santes.
Example (spaces added for visual clarification):
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2]Description:
- It is player's 1 turn
- Player 1 has card 3 and player 2 has card 2.
- Player one has
PASSed, followed by player 2'sBET. - Player 1 has contributed (1) to the pot and player 2 contributed (2).
Each player recieves an observation which is a strict subset of the state space.
The observation for player i contains:
Player id: One hot encoding of the player's id.Dealt card: One hot encoding of card dealt to playeri.Betting history: Same as above.Pot contributions: Same as above.
Example observation for player 1 from the example state above (spaces added for visual clarification):
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2]Thus, player's do not have access to other player's cards nor the cards which have not been dealt.
Each state transition is associated with a reward vector r = [r_1, r_2],
where r_1 is the scalar float reward associated to player 1. The reward function
works as in standard poker.
gym must be installed. An Kuhn's poker environment can be created via running inside a python interpreter:
>>> import gym
>>> import gym_kuhn_poker
>>> env = gym.make('KuhnPoker-v0', **dict()) # optional secondary argumentThe dict() in the expression above includes keyword arguments for the underlying environment:
number_of_players: Number of players (Default 2).deck_size: Size of the deck from which cards will be drawn, one for each player (Default 3).betting_rounds: Number of times that (Default: 2).ante: Amount of utility that all players must pay at the beginning of an episode (Default 1).
NOTE: Environment has only been tested with default values, feel free to open an issue if they don't work for other values!
This package is available in PyPi as gym-kuhn-poker
pip install gym-kuhn-pokergit clone https://www.github.com/Danielhp95/gym-kuhn-poker
cd gym-kuhn-poker
pip install -e .