| Documentation | Installation | Website | Tutorial | Research | Github |
-
[8/14/2024]: New Version is Available: We are releasing LibAUC 1.4.0. We offer new optimizers/losses/models and have improved some existing optimizers. For more details, please check the latest release note.
-
[04/07/2024]: Bugs fixed: We fixed a bug in datasets/folder.py by returning a return_index to support SogCLR/iSogCLR for contrastive learning. Fixed incorrect communication with all_gather in GCLoss_v1 and set gamma to original value when u is not 0. None of these were in our experimental code of the paper.
-
[02/11/2024]: A Bug fixed: We fixed a bug in the calculation of AUCM loss and MultiLabelAUCM loss (the margin parameter is missed in the original calculation which might cause the loss to be negative). However, it does not affect the learning as the updates are not affected by this. Both the source code and pip install are updated.
-
[06/10/2023]: LibAUC 1.3.0 is now available! In this update, we have made improvements and introduced new features. We also release a new documentation website at https://docs.libauc.org/. Please see the release notes for details.
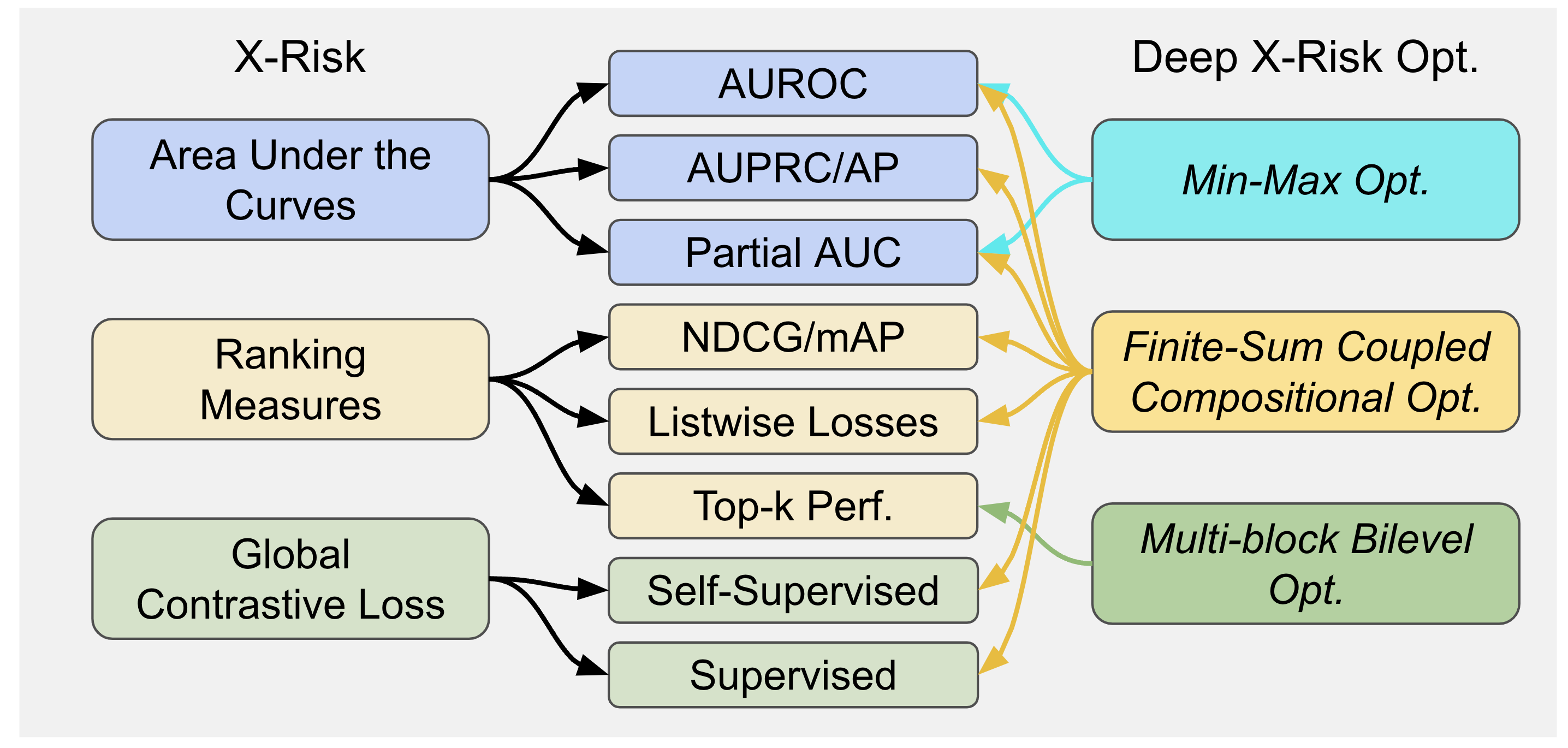
LibAUC offers an easier way to directly optimize commonly-used performance measures and losses with user-friendly API. LibAUC has broad applications in AI for tackling many challenges, such as Classification of Imbalanced Data (CID), Learning to Rank (LTR), and Contrastive Learning of Representation (CLR). LibAUC provides a unified framework to abstract the optimization of many compositional loss functions, including surrogate losses for AUROC, AUPRC/AP, and partial AUROC that are suitable for CID, surrogate losses for NDCG, top-K NDCG, and listwise losses that are used in LTR, and global contrastive losses for CLR. Here’s an overview:
Installing from pip
$ pip install -U libauc
Installing from source
$ git clone https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC.git
$ cd LibAUC
$ pip install .
>>> #import our loss and optimizer
>>> from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss
>>> from libauc.optimizers import PESG
>>> #pretraining your model through supervised learning or self-supervised learning
>>> #load a pretrained encoder and random initialize the last linear layer
>>> #define loss & optimizer
>>> Loss = AUCMLoss()
>>> optimizer = PESG()
...
>>> #training
>>> model.train()
>>> for data, targets in trainloader:
>>> data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
logits = model(data)
preds = torch.sigmoid(logits)
loss = Loss(preds, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
...
>>> #update internal parameters
>>> optimizer.update_regularizer()- Optimizing AUCMLoss: [example]
- Optimizing APLoss: [example]
- Optimizing CompositionalAUCLoss: [example]
- Optimizing pAUCLoss: [example]
- Optimizing MIDAMLoss: [example]
- Optimizing NDCGLoss: [example]
- Optimizing GCLoss (Unimodal): [example]
- Optimizing GCLoss (Bimodal): [example]
Other Applications
- Constructing benchmark imbalanced datasets for CIFAR10, CIFAR100, CATvsDOG, STL10
- Using LibAUC with PyTorch learning rate scheduler
- Optimizing AUROC loss on Chest X-Ray dataset (CheXpert)
- Optimizing AUROC loss on Skin Cancer dataset (Melanoma)
- Optimizing multi-label AUROC loss on Chest X-Ray dataset (CheXpert)
- Optimizing AUROC loss on Tabular dataset (Credit Fraud)
- Optimizing AUROC loss for Federated Learning
- Optimizing GCLoss (Bimodal with Cosine Gamma)
If you find LibAUC useful in your work, please cite the following papers:
@inproceedings{yuan2023libauc,
title={LibAUC: A Deep Learning Library for X-Risk Optimization},
author={Zhuoning Yuan and Dixian Zhu and Zi-Hao Qiu and Gang Li and Xuanhui Wang and Tianbao Yang},
booktitle={29th SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining},
year={2023}
}
@article{yang2022algorithmic,
title={Algorithmic Foundations of Empirical X-Risk Minimization},
author={Yang, Tianbao},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.00439},
year={2022}
}
For any technical questions, please open a new issue in the Github. If you have any other questions, please contact us via [email protected] or [email protected].