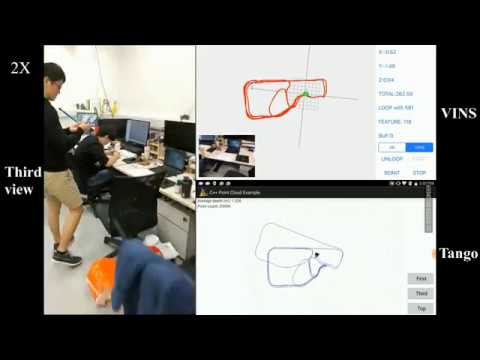
VINS-Mono is a real-time SLAM framework for Monocular Visual-Inertial Systems. It uses an optimization-based sliding window formulation for providing high-accuracy visual-inertial odometry. It features efficient IMU pre-integration with bias correction, automatic estimator initialization, online extrinsic calibration, failure detection and recovery, loop detection, and global pose graph optimization. VINS-Mono is primarily designed for state estimation and feedback control of autonomous drones, but it is also capable of providing accurate localization for AR applications. This code runs on Linux, and is fully integrated with ROS. For iOS mobile implementation, please go to VINS-Mobile.
Authors: Tong Qin, Peiliang Li, Zhenfei Yang, and Shaojie Shen from the HUKST Aerial Robotics Group
Videos:
EuRoC dataset; Indoor and outdoor performance; AR application;
MAV application; Mobile implementation
Related Papers
- VINS-Mono: A Robust and Versatile Monocular Visual-Inertial State Estimator, Tong Qin, Peiliang Li, Zhenfei Yang, Shaojie Shen (Submitted to T-RO) pdf
- Autonomous Aerial Navigation Using Monocular Visual-Inertial Fusion, Yi Lin, Fei Gao, Tong Qin, Wenliang Gao, Tianbo Liu, William Wu, Zhenfei Yang, Shaojie Shen (Submitted to JFR) pdf
If you use VINS-Mono for your academic research, please cite at least one of our related papers.
i. Ubuntu and ROS Ubuntu 14.04 16.04. ROS Indigo, Kinetic. ROS Installation additional ROS pacakge
sudo apt-get install ros-YOUR_DISTRO-tf ros-YOUR_DISTRO-message-filters ros-YOUR_DISTRO-image-transport
ii. Ceres Solver Follow Ceres Installation, remember to make install. (Our testing environment: Ubuntu 14.04, ROS Indigo, OpenCV 2.4.8, Eigen 3.2.0)
Clone the repository and catkin_make:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone [email protected]:HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/VINS-Mono.git
cd ../
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
1.Download EuRoC MAV Dataset. Although it contains stereo cameras, we only use one camera.
2.Open three terminals, launch the vins_estimator , rviz and play the bag file respectively. Take MH_05 as example
roslaunch vins_estimator euroc.launch
roslaunch vins_estimator vins_rviz.launch
rosbag play YOUR_PATH_TO_DATASET/MH_05_difficult.bag
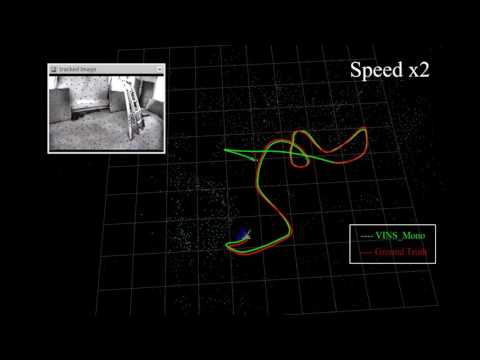
3.(Optional) Visualize ground truth. We write a naive benchmark publisher to help you visualize the ground truth. It uses a naive strategy to align VINS with ground truth. Just for visualization. not for quantitative comparison on academic publications.
roslaunch benchmark_publisher publish.launch sequence_name:=MH_05_difficult
(Green line is VINS result, red line is ground truth).
4.(Optional) You can even run EuRoC without extrinsic parameters between camera and IMU. We will calibrate them online. Replace the first command with:
roslaunch vins_estimator euroc_no_extrinsic_param.launch
No extrinsic parameters in that config file. Waiting a few seconds for initial calibration. Sometimes you cannot feel any difference as the calibration is done quickly.
1.Download the bag file, which is collected from HKUST Robotic Institute. For friends in mainland China, download from bag file.
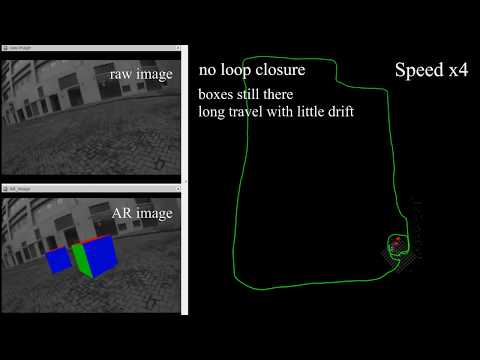
2.Open three terminals, launch the ar_demo, rviz and play the bag file respectively.
roslaunch ar_demo 3dm_bag.launch
roslaunch ar_demo ar_rviz.launch
rosbag play YOUR_PATH_TO_DATASET/ar_box.bag
We put one 0.8m x 0.8m x 0.8m virtual box in front of your view.
Suppose you are familiar with ROS and you can get a camera and an IMU with raw metric measurements in ROS topic, you can follow these steps to set up your device. For beginners, we highly recommend you to first try out VINS-Mobile if you have iOS devices since you don't need to set up anything.
-
Change to your topic name in the config file.
-
Camera calibration. We support the PINHOLE model and the MEI model. You can calibrate your camera with any tools you like. Just write the parameters in the config file in the right format.
-
Camera-Imu extrinsic parameters.
If you have seen the config files for EuRoC and AR demos, you can find that we just use coarse values. If you familiar with transformation, you can figure out the rotation and position by your eyes or via hand measuerments. Then write these values into config as the initial guess. Our estimator will refine extrinsic parameters online. If you don't know anything about the camera-IMU transformation, just ignore the extrinsic parameters and set the estimate_extrinsic to 2, and rotate your device set at the beginning for a few seconds. When the system works successfully, we will save the calibration result. you can use these result as initial values for next time.
- Other parameters setting. Details are included in the config file.
Device Performance: VI-sensor (global shutter camera + synchronized IMU) > (global camera + unsync high frec IMU) > (global camera + low IMU) > (rolling camera + low IMU). Don't start with rolling shutter camera with low IMU (such as DJI M100 + Logitech web camera) at beginning.
We use ceres solver for non-linear optimization and DBoW2 for loop detection, and a generic camera model.
The source code is released under GPLv3 license.
We are still working on improving the code reliability. For any technical issues, please contact Tong QIN [email protected] or Peiliang LI [email protected].
For commercial inquiries, please contact Shaojie SHEN [email protected]