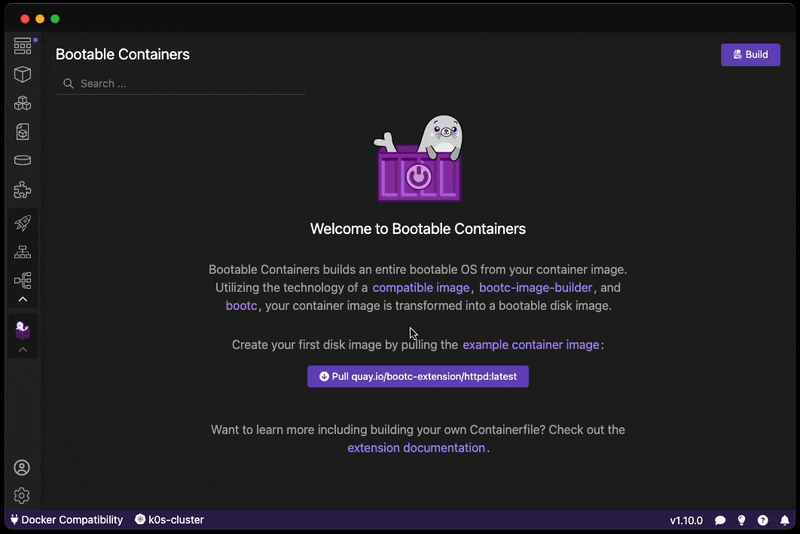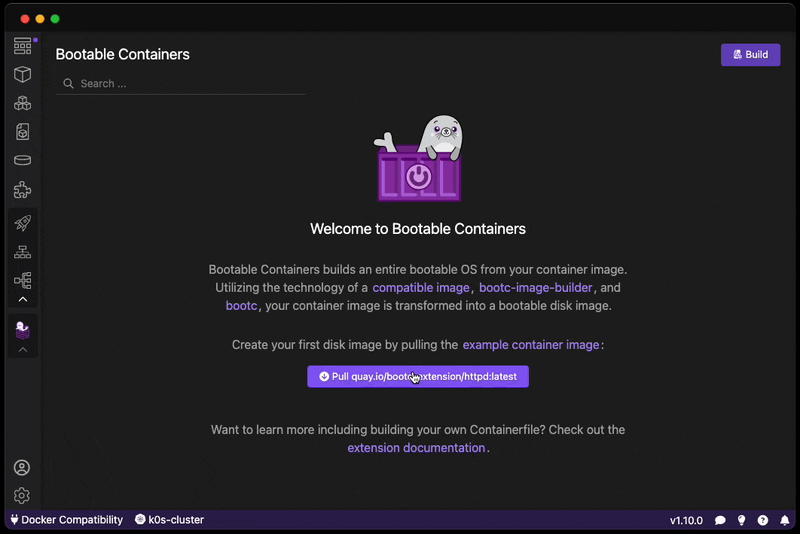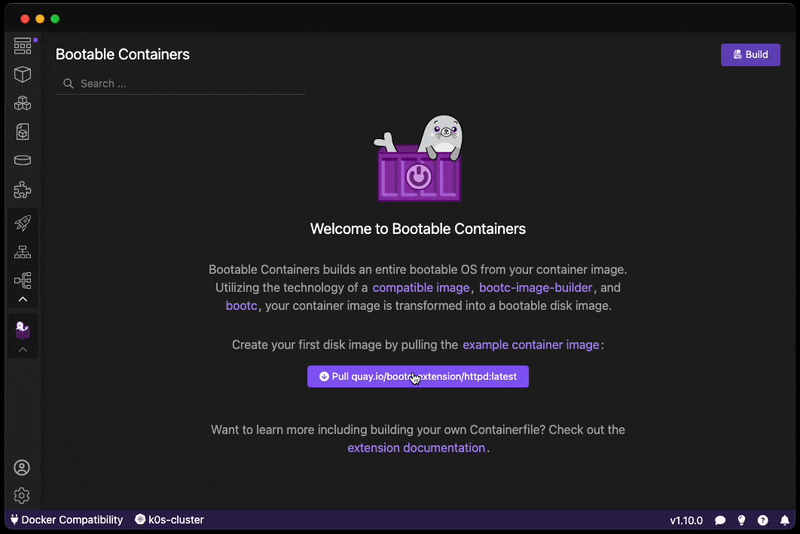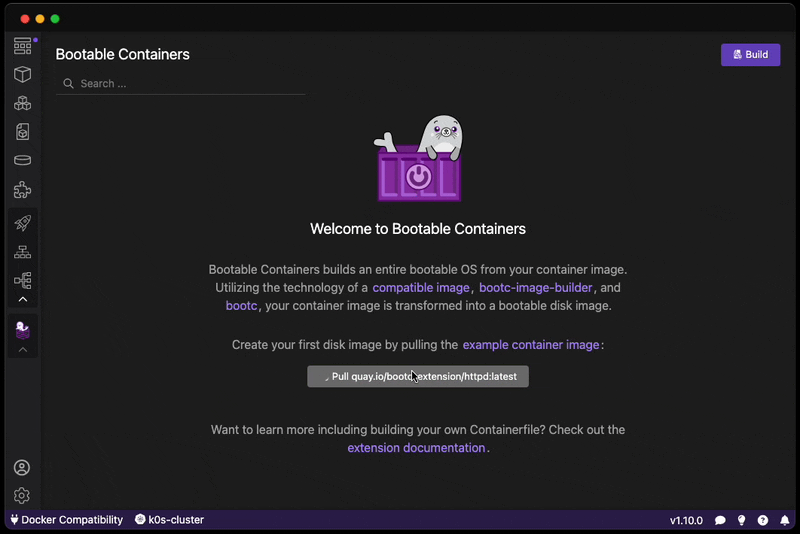
Want to create a bootable operating system from a Containerfile? Download this extension!
Easily go from container to VM / ISO-on-a-USB / RAW image!
- Technology
- Bootable Container Images
- Read Before Using
- Example Images
- Use Case
- Requirements
- Installation
- Usage
- Preferences
- Known Issues
- Contributing
The Bootable Container (bootc) extension uses bootc-image-builder in order to build bootable container disk images.
Once a machine is created from the disk image, it can apply transactional updates "in place" from newly pushed container images (without creating a new disk image). For more information, see bootc.
There are many projects at work at creating "bootc" images. Below is a non-exhaustive list of compatible images which are known to work with bootc-image-builder.
CentOS:
- Containerfile:
FROM quay.io/centos-bootc/centos-bootc:stream9 - Repo:
quay.io/centos-bootc/centos-bootc:stream9 - Example Images: gitlab.com/fedora/bootc/examples
- Documentation: fedoraproject.org
- Notes: N/A
Fedora:
- Containerfile:
FROM quay.io/fedora/fedora-bootc:40 - Repo:
quay.io/fedora/fedora-bootc:40 - Example Images: gitlab.com/fedora/bootc/examples
- Documentation: fedoraproject.org
- Notes: Must select "XFS", "EXT4" or "BTRFS" for the root filesystem when building in the GUI. Read more here.
RHEL:
- Containerfile:
FROM registry.redhat.io/rhel9/rhel-bootc:9.4 - Repo:
registry.redhat.io/rhel9/rhel-bootc:9.4 - Documentation: Red Hat Customer Portal
The images can then be added to your Containerfile:
FROM quay.io/centos-bootc/centos-bootc:stream9If you want to learn more about bootable containers, please refer to the Fedora Getting Started Guide where you can find a number of videos, demos, best practices and detailed information.
Some concepts to grasp before using.
You are "creating" an OS straight from a Containerfile, isn't that awesome?
FIRST realize that you are creating an OS with all your applications, developer tools, even games that you want.
SECONDLY ask yourself what applications you want to have running (perhaps on boot too!).
Want a quick straight-to-the-point Hello World Containerfile?
FROM quay.io/centos-bootc/centos-bootc:stream9
# Change your root password for a "test login" that
# allows to log in on a virtual/physical console
# NOTE: While some base images may set `PermitRootLogin prohibit-password`
# for OpenSSH, not all will.
# This is VERY dangerous and only meant for Hello World purposes.
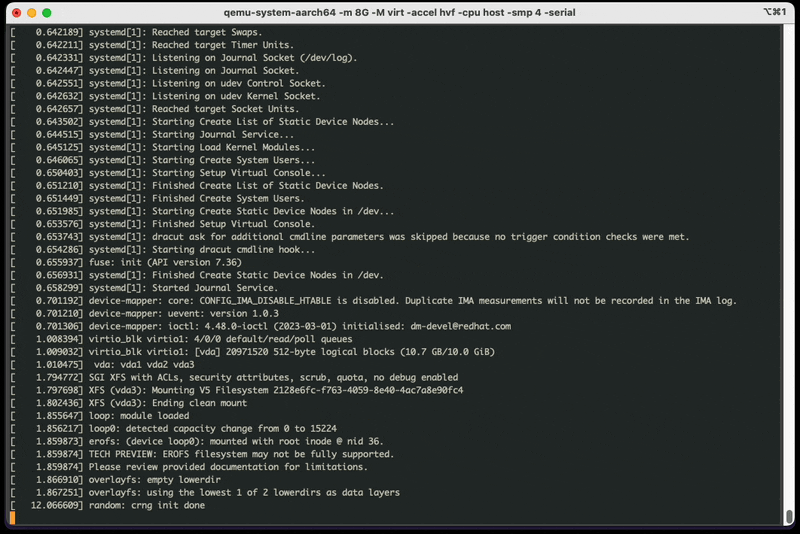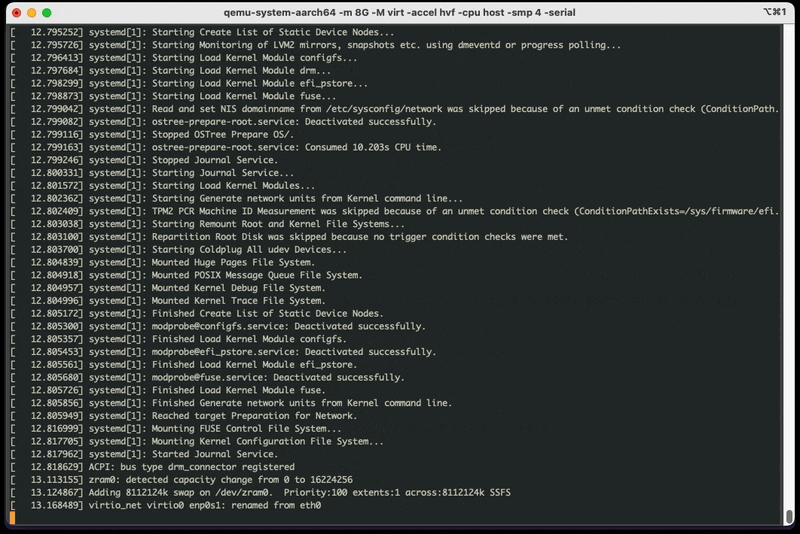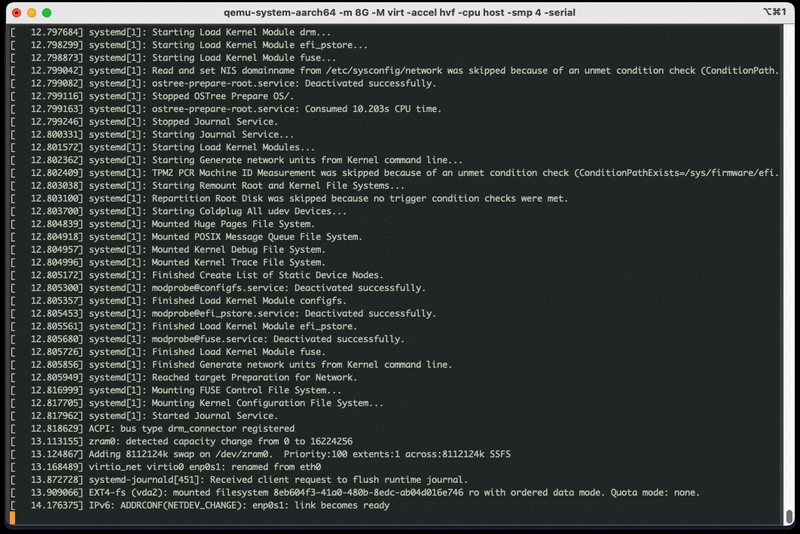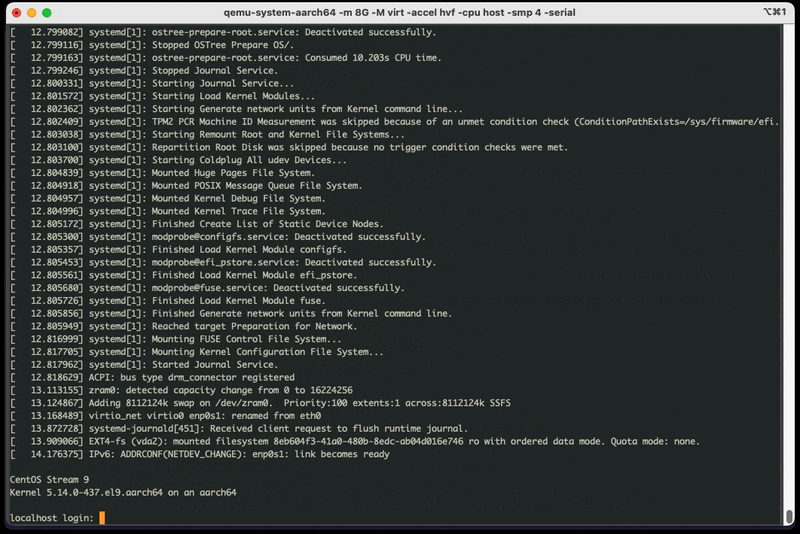
RUN echo "root:root" | chpasswdAfter creating your image you can now login and explore your bootable OS.
Want to view more example images Such as httpd and nvidia?
All of our maintained example images are on the gitlab.com/fedora/bootc/examples repo.
You can also pull our example image based on the httpd example:
After building, read our Virtual Machine Guide on how to launch your image and access your HTTP server.
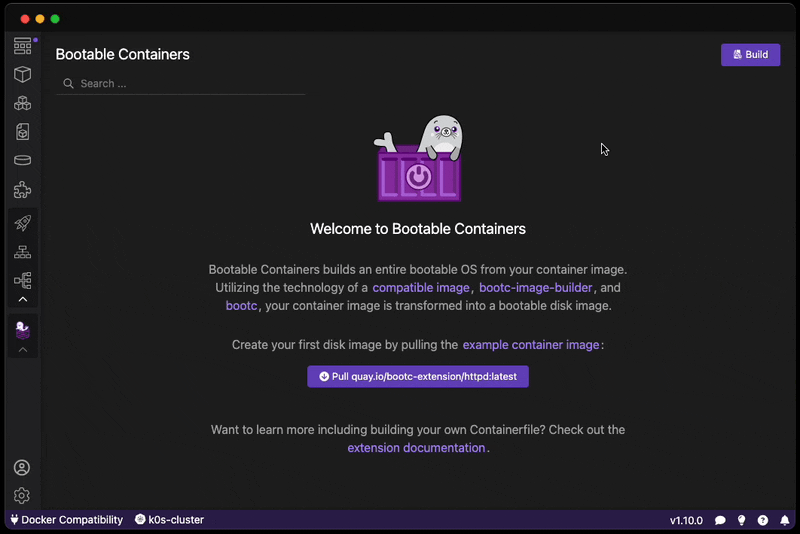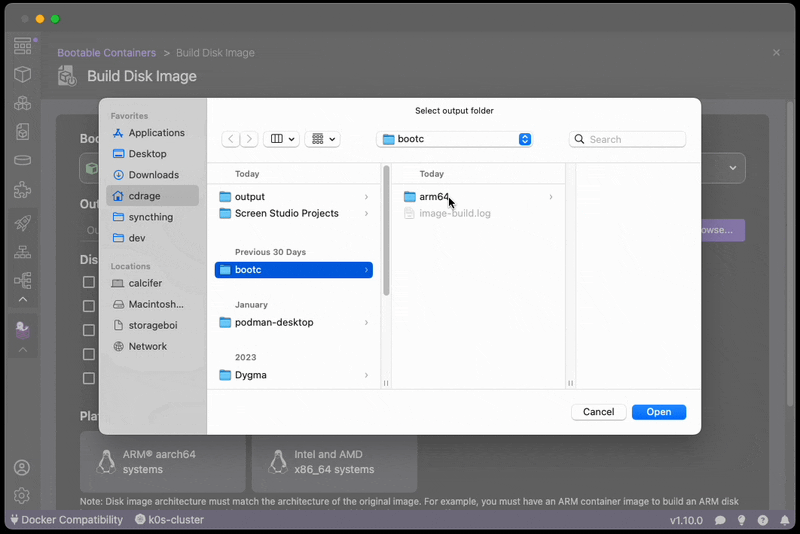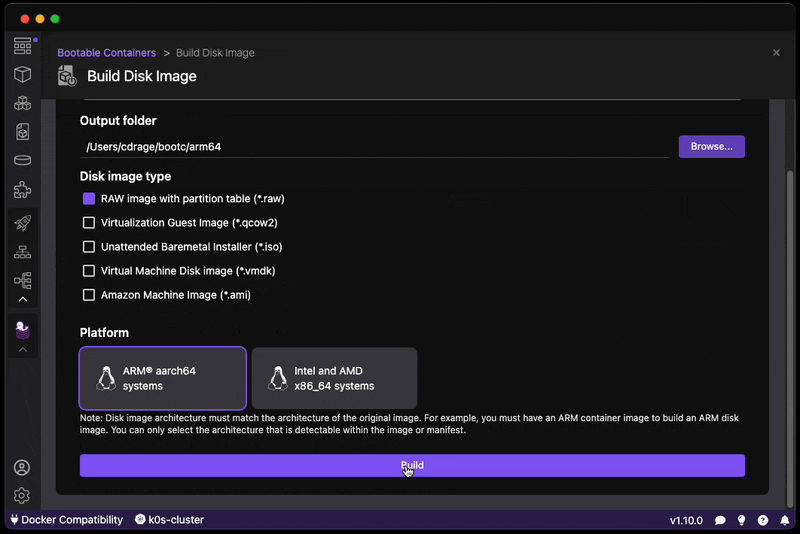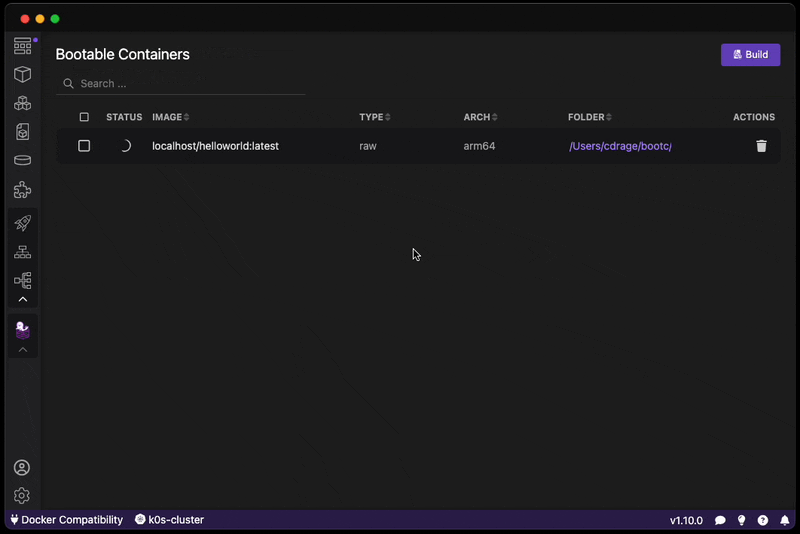
Go from a bootc compatible derived container build to a disk image format:
qcow2: QEMU Disk Imagesami: Amazon Machine Imagesraw: RAW disk image an MBR or GPT partition tableanaconda-iso: Unattended installation method (USB sticks / install-on-boot)vmdk: Usable in vSpherevhd: Virtual Hard Disk
The list above is what is supported by the underlying bootc-image-builder technology. The list can be found here.
OS:
Compatible on Windows, macOS & Linux
Software:
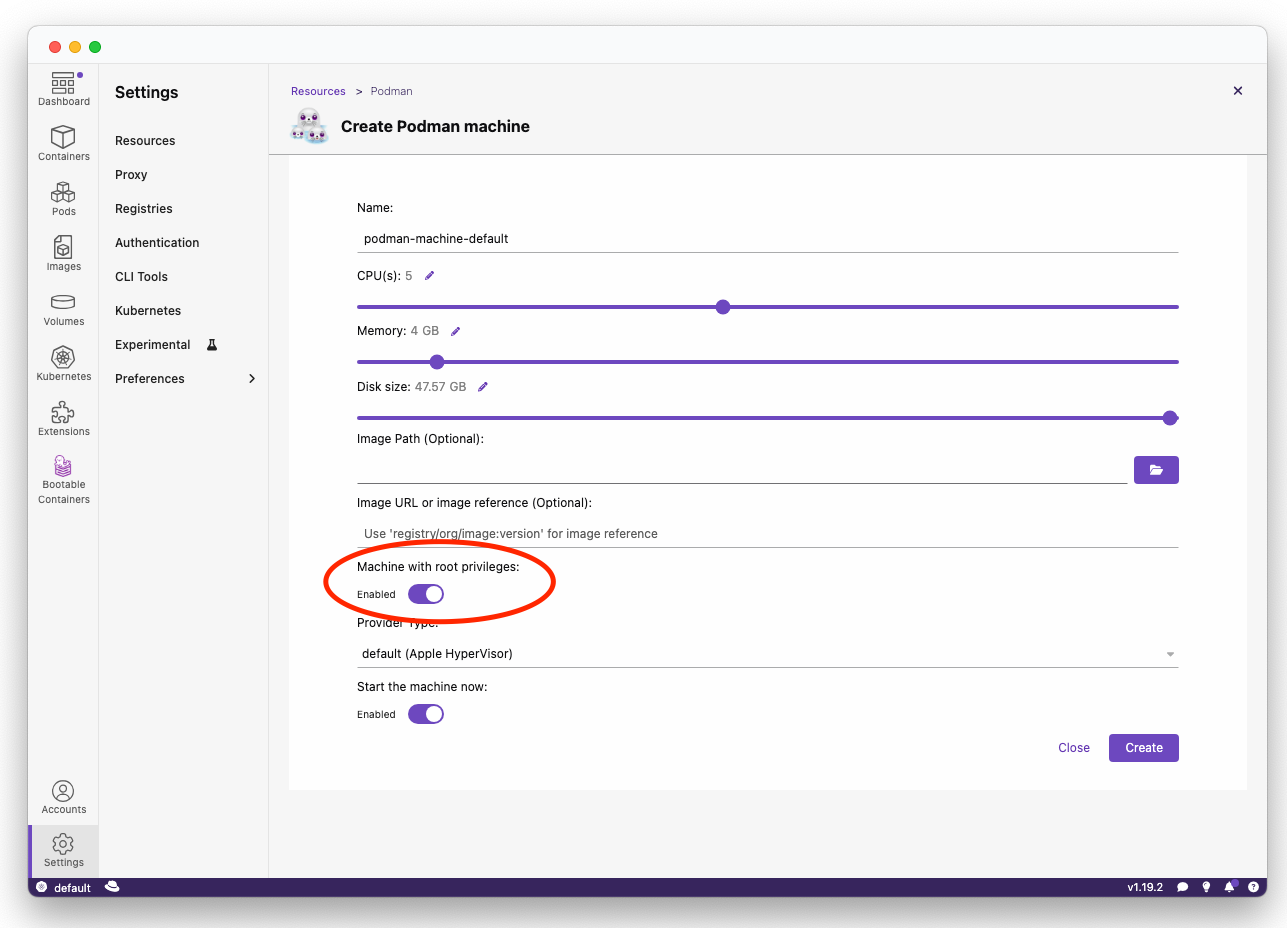
Podman Machine is required for macOS and Windows in order to run Podman as well as utilize filesystem privileges to build a disk image.
Podman Machine requirements:
- Rootful mode enabled
- At least 6GB of RAM allocated in order to build the disk image
Rootful mode can be enabled through the CLI to an already deployed VM:
podman machine stop
podman machine set --rootful
podman machine startOr set when initially creating a Podman Machine via Podman Desktop:
During the build process, you will be asked to enter your credentials so that the bootc extension may run a sudo podman run underlying CLI command.
Podman Desktop is ran as the logged-in user. However, bootc-image-builder requires escalated / sudo privileges to run a rootful container.
You can find more information about what specific commands are being ran from the console logs of Podman Desktop.
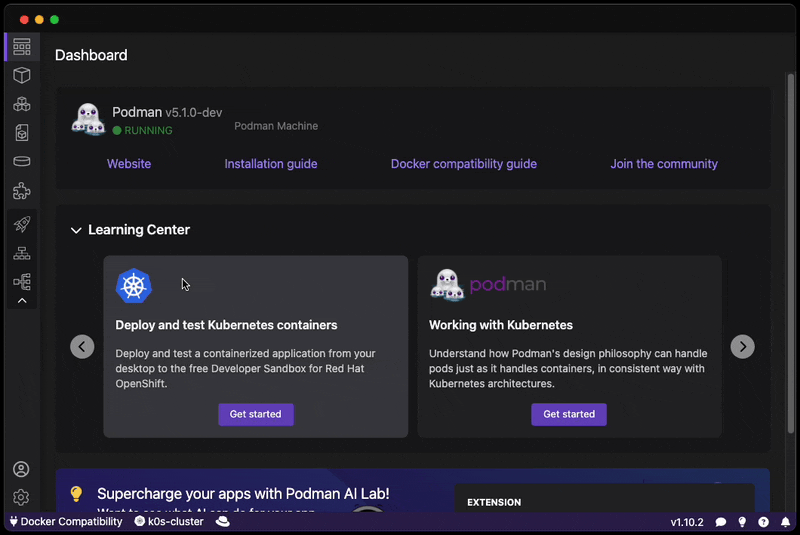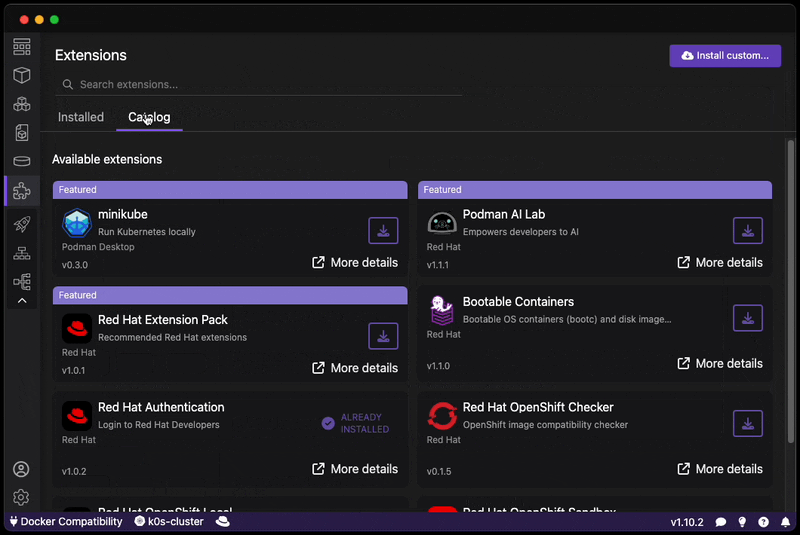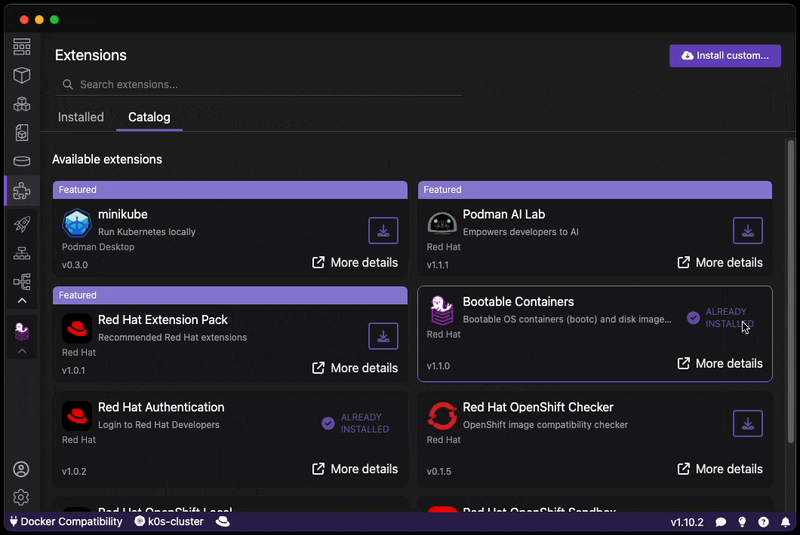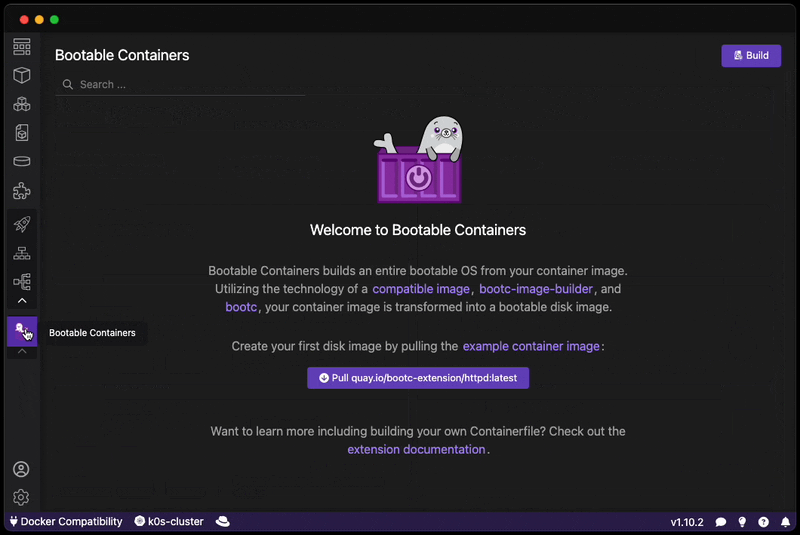
This extension can be installed through the Extensions section of Podman Desktop within the Catalog tab:
- Go to Extensions in the navbar.
- Click on the Catalog tab.
- Install the extension.
A version of the extension using the latest commit changes can be installed via the Install custom... button with the following link:
ghcr.io/containers/podman-desktop-extension-bootc:nightly
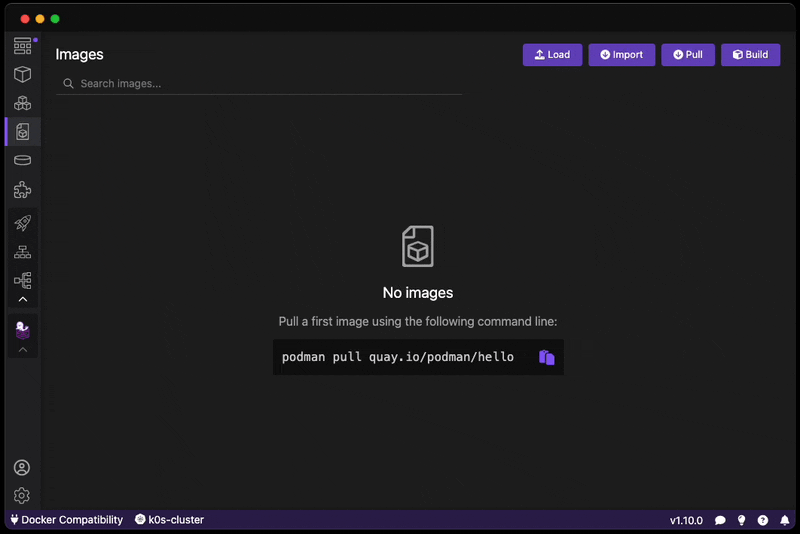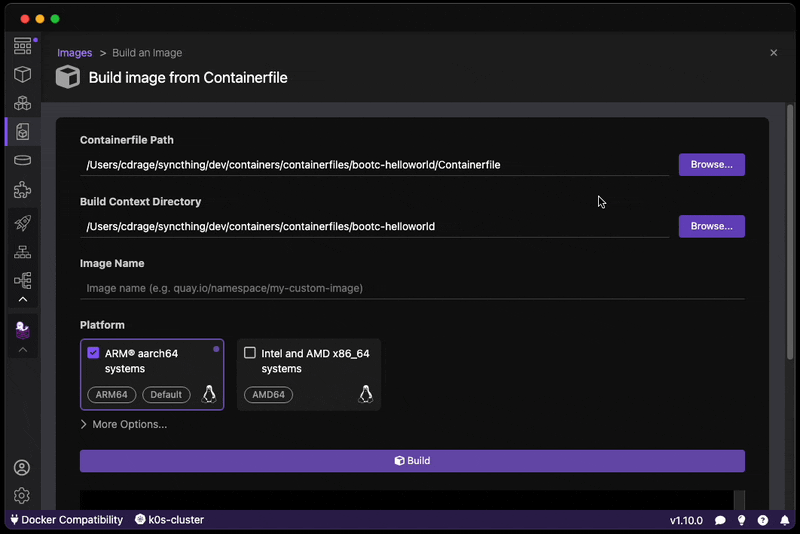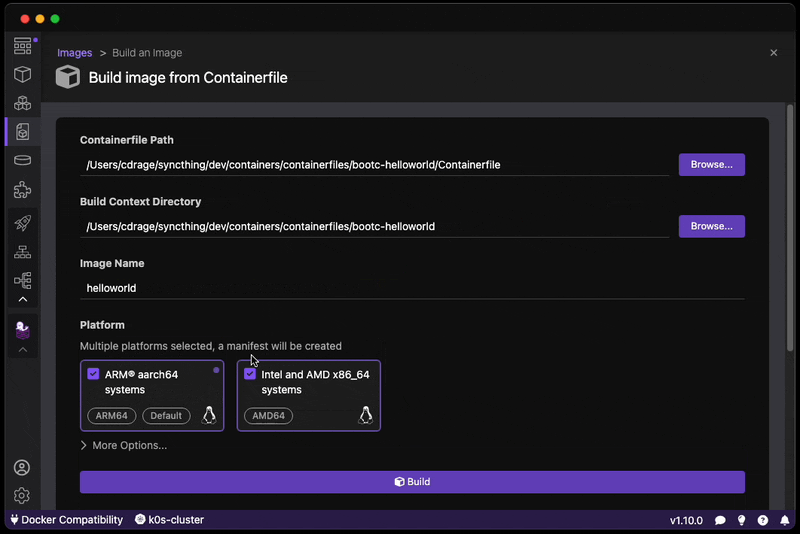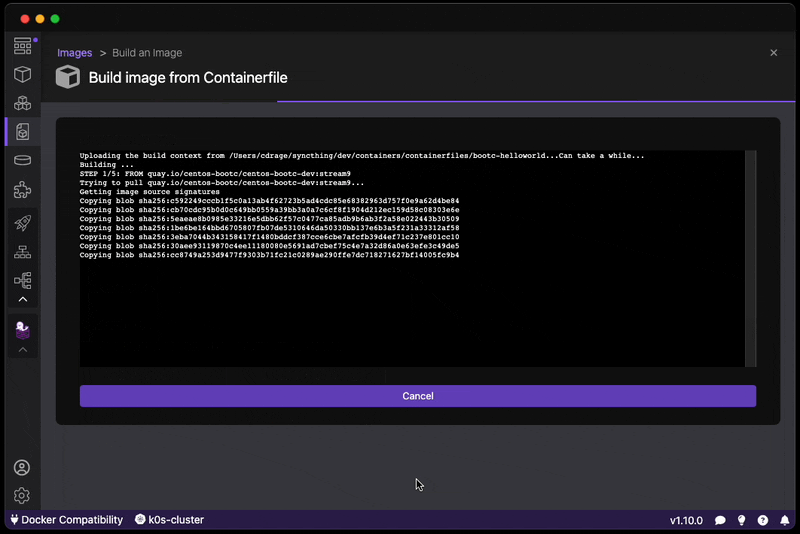
- Build your bootc-enabled Containerfile:
In the example below, we are going to change the root password for testing purposes when accessing the OS.
FROM quay.io/centos-bootc/centos-bootc:stream9
# Change the root password
# CAUTION: This is NOT recommended and is used only for testing / hello world purposes
RUN echo "root:root" | chpasswd- Build the disk image:
Build the disk image, this takes approximatley 2-5 minutes depending on the performance of your machine.
- Launching the VM:
See our Virtual Machine Guide on how to launch the image!
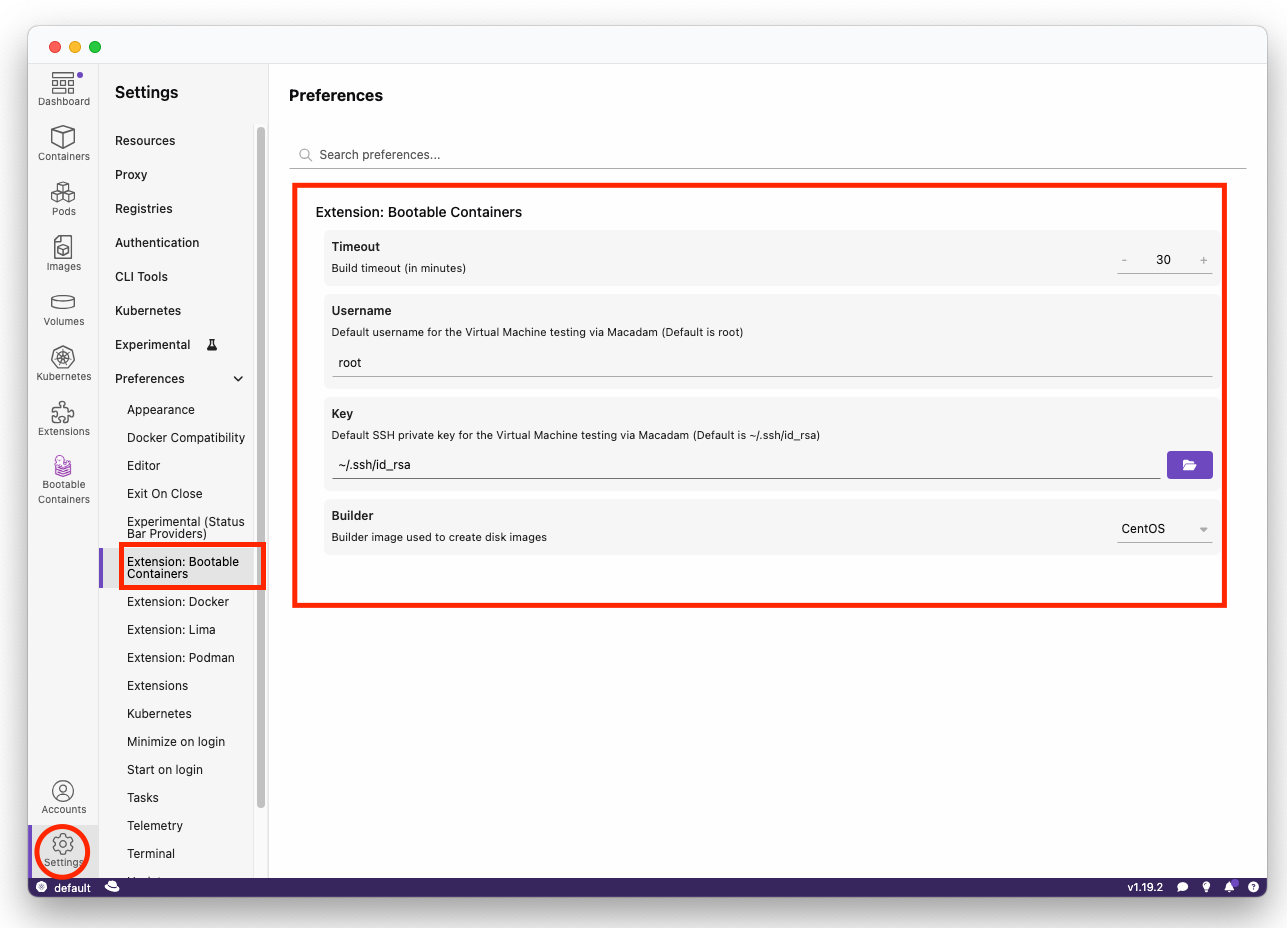
Preferences such as the default bootc-builder-image as well as timeouts can be adjusted within the Preferences section of Podman Desktop.
Unable to build cross-arch images on macOS and Windows:
This is a known issue when attempting to build cross-architecture images using Podman Machine on macOS and Windows. For example, building an x86 image on macOS with Apple Silicon (ARM).
The issue stems from a missing openat2 system call in QEMU, which has now been patched upstream. While waiting for the patch to be incorporated into Podman Machine, Fedora packages have been created to address the issue.
Your Podman Machine might not have the required QEMU patch to build cross-architecture images.
macOS only:
- Delete your current Podman Machine via Settings > Resources > Podman.
- Disable Rosetta under Settings > Preferences > Extension: Podman > Rosetta.
- Create a new Podman Machine.
Windows and macOS:
- Start your Podman Machine.
- SSH into the Podman Machine:
podman machine ssh- Override the QEMU binaries:
If your host machine is x86 (AMD64), run:
rpm-ostree override replace https://download.copr.fedorainfracloud.org/results/michaelvogt/qemu-user-with-openat2/fedora-40-x86_64/08033635-qemu/qemu-user-8.2.6-3.mvo1.fc40.x86_64.rpm
rpm-ostree override replace https://download.copr.fedorainfracloud.org/results/michaelvogt/qemu-user-with-openat2/fedora-40-x86_64/08033635-qemu/qemu-user-static-aarch64-8.2.6-3.mvo1.fc40.x86_64.rpmIf your host machine is ARM (ARM64), run:
rpm-ostree override replace https://download.copr.fedorainfracloud.org/results/michaelvogt/qemu-user-with-openat2/fedora-40-aarch64/08033635-qemu/qemu-user-8.2.6-3.mvo1.fc40.aarch64.rpm
rpm-ostree override replace https://download.copr.fedorainfracloud.org/results/michaelvogt/qemu-user-with-openat2/fedora-40-aarch64/08033635-qemu/qemu-user-static-x86-8.2.6-3.mvo1.fc40.aarch64.rpm- Restart your Podman Machine:
podman machine stop
podman machine startTo undo the fix, either delete and re-create the Podman Machine, or:
podman machine ssh
rpm-ostree override reset --allWant to help develop and contribute to the bootc extension? View our CONTRIBUTING document.