Paper : https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3339326
Optimization is the process of the action of making the best or most effective use of a situation or resource. In this scenario optimization is used to solve the issue of the high time requirement of the algorithm, software and hardware optimization was performed on the program to a point where it was able to in real-time on the hardware board used. Here, we discuss the entire procedure of the process implemented.
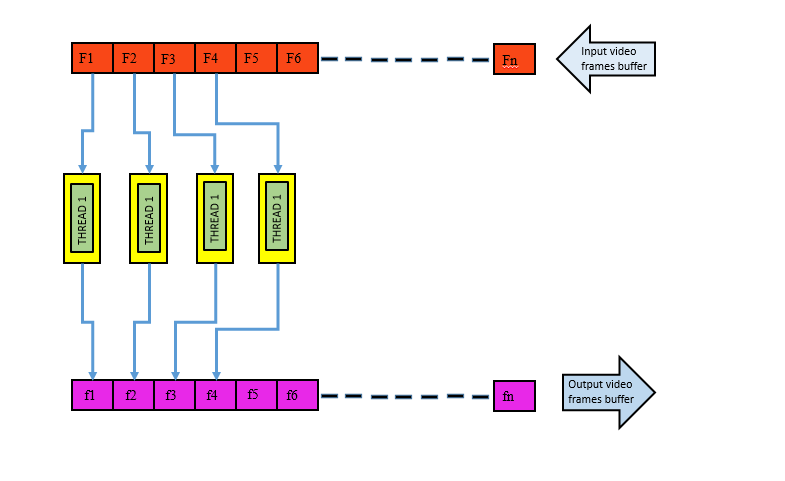
The best way to run a process faster is to divide the main process into multiple threads that can run in parallel with respect to each other. This way we can make maximum utilization of the CPU, thereby decreasing the processing time. It’s also important to take into consideration the number of threads that can be handled efficiently by the operating system. Two threads were found to be the optimum number of threads that could produce the transformation with the least processing time. With more than two threads the communication time between the threads slows the process down. The memory model architecture is depicted in the below figure. The above memory model was developed for video processing application. First, the individual frames of the video are pushed into the input buffer one at a time. The first thread takes the first frame followed by the second thread that takes the next thread and the same pattern follows till the end of the video. In this manner the task is divided among the threads which are executed concurrently. After the threads are done with their job, the processed frames are stored in an output queue from where they are accessed to be shown on the output display.
Multi threading is a very efficient way of implementing parallelism into the code.Generally categorized into,
- Thread
- PThread
- WinThread
After threading each thread can be run on different core to achieve 100% CPU utilization
In my code I have used following type of memory model where each thread independently process each frame reducing problems like deadlock.
The most time-consuming process of the Retinex algorithm is the computation of the log functions. Also, the log functions need to be calculated for the R, G and B spectral components of the frames separately. In spite of running multiple threads together, computing the log functions for each frames’ RGB components is still a laborious task for the processor. To overcome this, the log values were calculated at the beginning of the program for the required range and stored in the memory as a lookup table. Instead of calling the log function, the pre-defined values are accessed directly. Accessing a memory happens faster than computing a set of equations, which therefore increases the performance speed of the algorithm. With this adjustment the speed of the algorithm doubled compared to when multi- threading was done with regular log computation.
GPUs are generally used for accelerating programs by providing high throughput. Thus, highly parallelizable tasks can be run on GPU efficiently. For e.g., Gaming, Artificial Neural Networks etc.
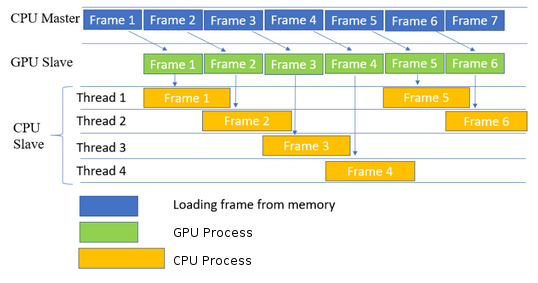
Heterogeneous computing refers to systems that use more than one kind of processor or cores. These systems gain performance or energy efficiency not just by adding the same type of processors, but by adding dissimilar coprocessors, usually incorporating specialized processing capabilities to handle particular tasks. Using GPUs alone to process a complex computational problem is one part of improving performance drastically. However, to get close to the theoretical peak performance of the system, the CPU has to be utilized in a useful way, too, instead of it having only act as a supervisor for the GPU. Combining the different paradigms and programming models of CPUs and GPUs to work together at the same problem must be the ultimate goal. When ever we deploy a process on Heterogenous or parallel manner we need to keep a thread or ideally main program to be master to control other slave device and thread. Master will be looking into ,
- Process execution status
- Availability of data
- Presence of redundant wait time
Consider the diagram given below this is one of the simple heterogeneous computation method.
note : please refer the research papers for explanation of algorithms
The Above algorithms are implemented on various embedded hardware boards and the result obtained is as below
1. Single Scale Retinex
-without optimzation on UDOOx86 Ultra
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 126.10s | 4 |
| 900 | 227.32s | 4 |
-with optimzation on UDOOx86 Ultra
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 14.56s | 34 |
| 900 | 26.46s | 34 |
-without optimzation on Jetson Tk1
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 156.10s | 3 |
| 900 | 283.32s | 3 |
-with optimzation on Jetson Tk1
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 17.73s | 28 |
| 900 | 32.02s | 28 |
2. Multi Scale Retinex
-without optimzation on UDOOx86 Ultra
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 243.10s | 2 |
| 900 | 464.32s | 2 |
-with optimzation on UDOOx86 Ultra
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 18.02s | 28 |
| 900 | 31.96s | 28 |
-without optimzation on Jetson Tk1
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 256.10s | 2 |
| 900 | 483.32s | 2 |
-with optimzation on Jetson Tk1
| Frames | Duration | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | 20.23s | 25 |
| 900 | 35.98s | 25 |
Majumdar, Jharna & C, Adarsh & Singh, Harshpreet & C, Rahul. (2019). Real-time performance analysis of retinex algorithm on embedded boards for robotics application. ICAICR '19: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Advanced Informatics for Computing Research. 1-8. 10.1145/3339311.3339326.