This Distributed Application evaluates a RAFT-based DNS cluster along the metrics of performance and safety.
The application consists of application including a multi-node RAFT Distributed DNS Name Server, a Load Balancer capable of performing leader-only querying or general purpose round-robin loadbalancing, and a client application designed to evaluate performance and safety across a variety of scenarios.
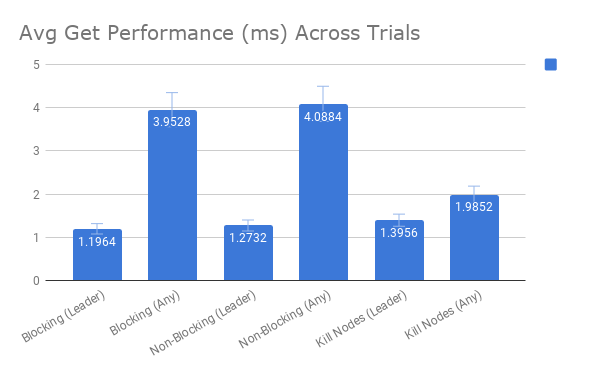
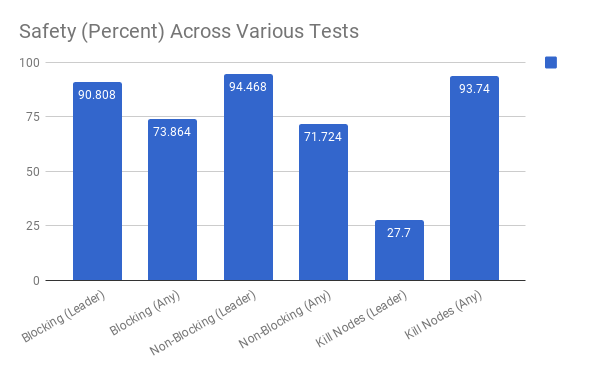
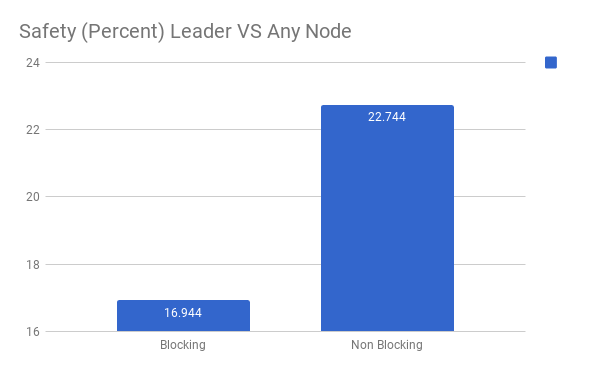
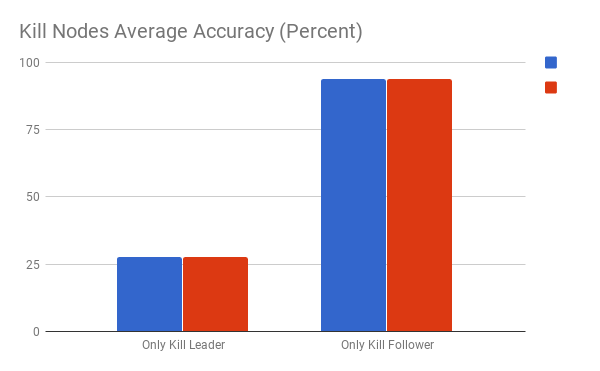
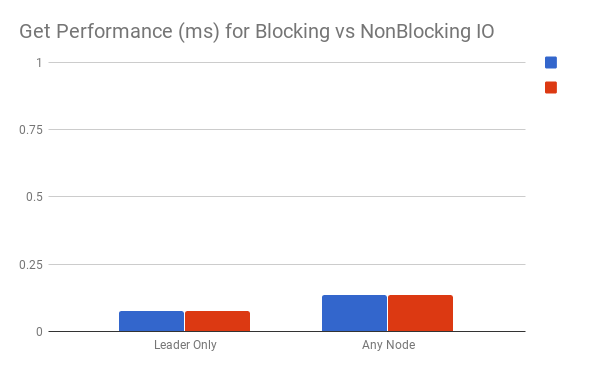
Some of our quantitative results across experiments performed.
For our implementation of RAFT-based DNS, we built atop an existing Open-source solution for a Distributed Key-Store implemented using RAFT called Weave. It is available at the following link.
Our modificaitons included, fixing various errors in the leader-election conditions that the implementaiton used. Additionally, we added the ability to query data from the cluster using socket communication in both a blocking and non-blocking (java NIO library) fashion.
We also added the capacity for a node to "die". We do this by simulating the state and volatile variables that would be set when a actual failure would occur in a RAFT cluster.
To run the experiments we conducted, run the applications in the following order.
The Load Balancer Listens for Leader Election Changes. In the root/client directory, we included a start.sh scrip that runs the following command.
python loadbalancer.py
This causes the Load Balancer to listen on port 5000 for leadership changes as well as connections from the client that send metric tests through the load balancer. The Load Balancer will perform differently, based upon the information encoded in these messsages. This will be explained later in the documentation.
The repo contains a modification of the Open-Source RAFT-Implementation Weave. To run this version of Weave, download Apache maven using the following instructions at https://maven.apache.org/download.cgi.
To build the JAR file for the application run build.sh in the RAFT/ folder or run the following command in the RAFT/ directory:
mvn clean compile assembly:single
This will create a target/ directory with a JAR File. You will then need to modify the nodes.xml file in the RAFT/ directory. The given nodes.xml file, expects all RAFT nodes to run on localhost and will configure a RAFT node to listen on the ports that its id maps to in the nodes.xml file. The nodes.xml also contains "watchers" that are meant to be notified during leader election changes. Modify this depending on what port you run your load balancer at.
<WeaveConfig>
<nodes>
<node id="1">
<ip>localhost</ip>
<client>8080</client>
<heartbeat>8081</heartbeat>
<voting>8082</voting>
</node>
<node id="2">
<ip>localhost</ip>
<client>8090</client>
<heartbeat>8091</heartbeat>
<voting>8092</voting>
</node>
<node id="3">
<ip>localhost</ip>
<client>9000</client>
<heartbeat>9001</heartbeat>
<voting>9002</voting>
</node>
</nodes>
<electionwatchers>
<watcher>
<ip>localhost</ip>
<port>80</port>
</watcher>
</electionwatchers>
</WeaveConfig>
To run the RAFT cluster, open three different terminal windows, or use an orchestration software of choice.
On each terminal, pass in each RAFT node the given paramers. The first parameter is the "id" of the node. This will pull port information from nodes.xml. This second configures the cluster to listen with blocking (1) IO or non-blocking (2) IO. The third paramater is the xml configuration file to pass to each RAFT node.
This is an example of running a 3 node RAFT cluster with the above nodes.xml in blocking IO for querying mode. Each command is issued in a seperate terminal window.
java -jar Weave.jar 1 1 nodes.xml
java -jar Weave.jar 2 1 nodes.xml
java -jar Weave.jar 3 1 nodes.xml
To Build a file to run tests against, run the test generator
python testgen.py
This will create a file cmds.txt. A cmds.txt is a json file, with the following format. It runs set queries and creates get queries, with a higher likelihood of calling domain names that have just been recently set. If pretty printed, it looks like the following.
[
{
"val": "94.8071926072",
"msgid": "0",
"cmd": "set",
"id": "0",
"var": "var11",
"leader": "True"
},
{
"delay": 650
},
{
"var": "var11",
"msgid": "1",
"cmd": "get",
"id": "0",
"leader": "True"
}
...
Then the ./start.sh script can be run to call the following command, To connect to the load balancer running on localhost at port 5000.
python client.py 127.0.0.1 5000
It will then pass the tests one-by one to load balancer who will return the performance of get / set requests and the accuracy of both as well.
To test the RAFT-based DNS, so that follower nodes are queries as well as leader nodes, convert all "leader" keys to "False, in the json stored in cmds.txt.
To do this run: sed -i 's/TRUE/FALSE/g' cmds.txt. The opposite FALSE and TRUE can be switched to convert a any-node querying test to a solely leader querying test.
To have the abily to kill random nodes in the cluster, create a copy of cmds.txt and name it trial[x].txt. Here x is any valid integer. Then run
python kill.py x
This will replace cmds.txt, with three kill commands placed in the test script. This will allow you to test the metrics of performance and safety in an environment where nodes can die.