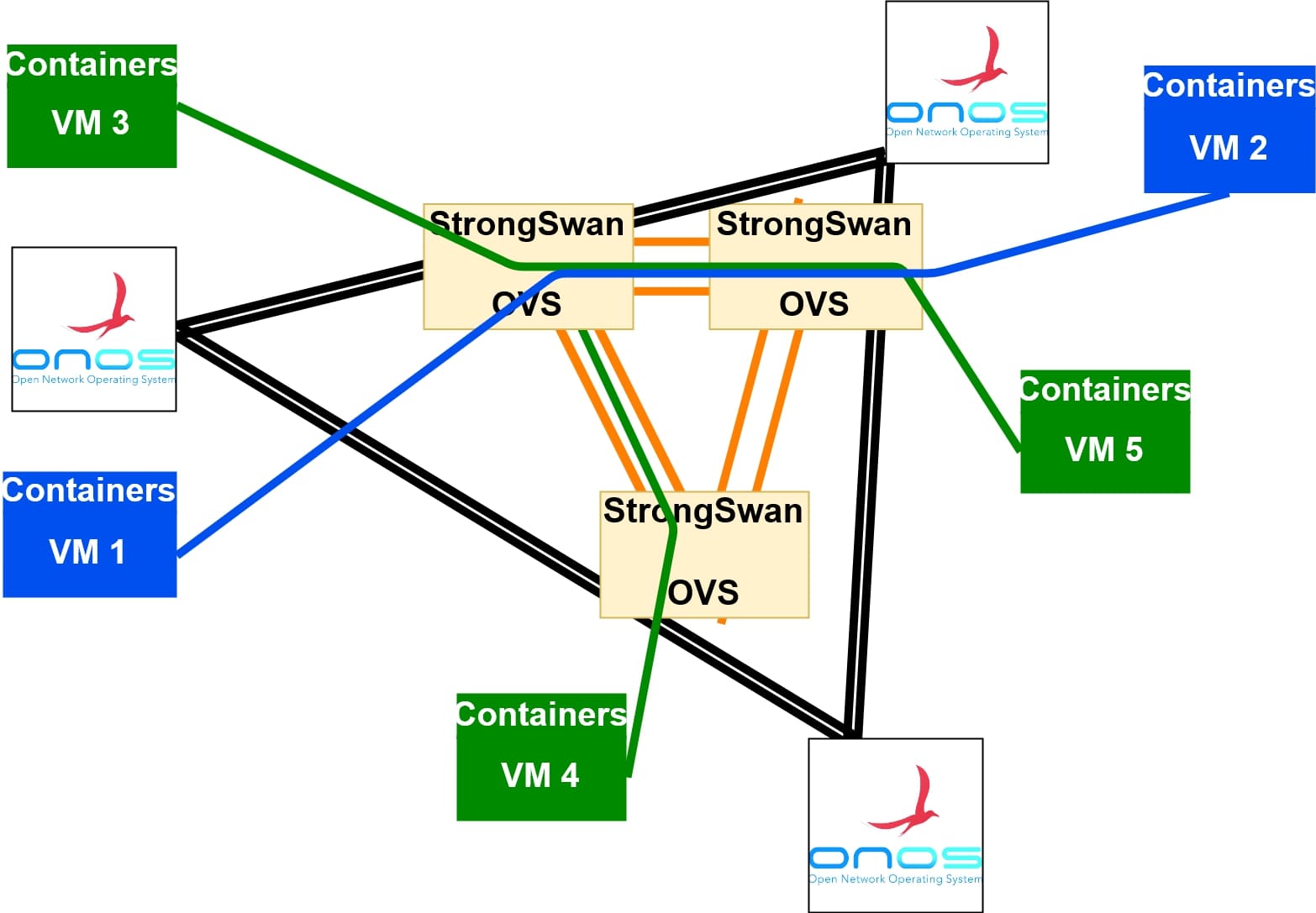
The distributed network architecture uses multiple components:
- ONOS, an SDN controller. We suggest deploying a cluster of Onos instances: one instance for each datacenter.
- Atomix, a framework that provides data consistency between the ONOS instances. We suggest deploying one or more instances of Atomix, outside the data centers.
- Open vSwitch (OvS), an SDN software switch. Its forwarding behavior is controlled by ONOS.
- Strongswan is used to encrypt point to point GRE tunnels with IPsec.
Please keep in mind that there is a limitation in Atomix: it is not possible to dynamically add new nodes to an already deployed cluster. This implies that the creation time of the Atomix nodes must coincide with the creation of the Atomix cluster. Such a cluster is created before the initialization of the Gateway VMs. It is not necessary to instantiate a new shared state VM for each Atomix instance. In fact, since an Atomix instance is containerized, it could be instantiated even in an already existing VM.
There are no particular system requirements for such VM, apart from having a network interface with an IP address. Each Atomix instance needs to be able to communicate with the other Atomix instances using the TCP port 5679.
In each VM where an Atomix node needs to be instantiated, run the script “init atomix_node.sh” with arguments:
- IP address of the local Atomix instance
- IP address of remote Atomix instance 1
- …
- …
- IP address of remote Atomix instance N
For each new data center that joins the network federation, create one gateway VM in that data center with the following system requirements:
- 1 network interface (one public IP address)
- 4 CPU
- 8 GB RAM
- 50 GB disk
- VM Image: Ubuntu 16.04
At VM provisioning (first run), run the script “init_gateway.sh” inside the gateway VM with the public IP address of all the gateways. Arguments:
- public IP address of the local gateway
- public IP of remote gateway 1
- …
- ...
- public IP of the remote gateway N
The “init_gateway.sh” script installs OvS, Strongswan and one containerized instance of the ONOS cluster inside the gateway VM. In OvS two different network bridges are created: the intra-DC bridge and the inter-DC bridge. These two bridges are internally connected by a virtual patch cable (a concept similar to virtual ethernet ). In the inter-DC bridge, OvS opens encrypted GRE+IPsec tunnels to the other gateway VMs, only this bridge is managed by ONOS. 2b - Update configuration of inter-DC tunnels: When a new data center joins the federated network, it is initialized with the “init_gateway.sh” script. Such script connects the gateway VM of that datacenter to the gateway VMs of all the others with GRE tunnels. GRE is an unmanaged tunnel protocol, therefore it is necessary to update the inter-datacenter configuration in all the gateway VMs that are already part of the network federation.
For each gateway VM that needs to be updated run the script “update_interDC_tunnels.sh” inside that VM with the public IP address of all the new gateways. Arguments:
- public IP of remote gateway N+1
- public IP of remote gateway N+2
- ...
In this section, it is described how a host belonging to a data center that is already connected to other data centers (section 2) can join a federated network. Please consider that in the distributed network architecture there are two complementary levels of network federation. In section 2, data centers are interconnected, however, this is not sufficient to create on-demand different federated networks. The network federation for hosts is performed with VLAN technology, in fact, different VLAN ids represent different federated networks.
A host that wants to join a federated network “X” needs to open a GRE tunnel to the gateway VM of its data center with the GRE tunnel key equal to the federated network ID “X” (VLAN id).
The Host VM must be:
- Linux with ip_gre kernel module enabled (this is the default in recent Ubuntu)
In the Host VM run the script: join_network_federation.sh” with arguments:
- public IP address of the local gateway
- VLAN id of the network federation
- the private address for the host in the federated network
- the local address for the host in the data center network
Symmetrically it is necessary, similar to section 2b, to open a GRE tunnel with the correct GRE key from the intra-DC bridge of the gateway VM, to the host VM. OvS is configured in such a way that when terminates a GRE tunnel, it tags the incoming packets with the VLAN id equal to the GRE key. The intra-DC bridge is self-managed by OvS: it performs VLAN MAC learning.
In the local gateway launch “accept_network_federation.sh” with arguments:
- the IP address of the host (assigned by the DC)
- VLAN ID of the network federation
For simplicity login inside the onos web UI (http://localhost:8181/onos/ui) with the following credentials:
- username: onos
- password: rocks
In the web UI, go inside “Applications” and upload our modified “*.oar” application from the “Onos app” folder. Now enable the following applications:
- OpenFlow Base Provider
- Host Location Provider
- Proxy ARP/NDP
- LLDP Link Provider
- Intent Reactive Forwarding (the uploaded application)
If everything is working correctly, ONOS should be able to install reactively network intents for level 2 VLAN flows.