Blazing fast, simple and modular header-only logging library with zero allocation for C and C++, implemented in C90. Allow logging into various output formats such as Key-Value and JSON.
Logax is designed with speed and modularity in mind,. It requires no heap-allocated memory. Each components can be excluded by defining an exclusion macro, to adjust to an environment or increase compile/runtime speed.
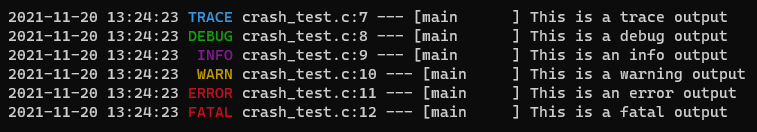
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "This is a trace output");
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_DEBUG, "%s", "This is a debug output");
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_INFO, "%s", "This is an info output");
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_WARN, "%s", "This is a warning output");
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_ERROR, "%s", "This is an error output");
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_FATAL, "%s", "This is a fatal output");
}Output
The log output can be formatted as text, key/value or json. Where the output is not required or the platform does not have any output stream (e.g. Arduino, stm32) a callback can be registered that will process the log event.
- Features
- Standards Compliance and Portability
- Installation
- Documentation
- Usage
- Modularity
- How it works
- Contributing
- References
- License
- Single header only, just download logax.h and you are good to go.
- Speed. logax was developed with speed and zero performance intrusion in mind.
- Modular, excluded un-used features from your test, modularity.
- Zero allocation, No memory allocation.
- Levelled logging to customize and differentiate the outputs.
- Support for callbacks and hooks.
- Very portable, compatible with ANSI C and C++98 without any trade off in functionalities.
- Output log in text, key-value and JSON encoding formats.
- Pretty logging for all supported output formats.
- Simple method to achieve options in the logging system using bitwise operations.
- Detail documentation with examples and API references.
The project is compliant with the original C language specification ISO/IEC 9899:1990 and the first POSIX specification IEEE Std 1003.1-1988 which ensures the project compatibility in various environments.
Even though the project is designed for C, but also works with C++ as it is compatible with C++98 Standard (ISO/IEC 14882:1998), C++03 Standard (ISO/IEC 14882:2003) and C++11 Standard (ISO/IEC 14882:2011).
The project can be used with any C or C++ compiler. There are optional macros and options that can be used to attain the desired output in the case of undesired results.
If you install the library file logax.h using any of the commands below, it can be included in your test like <exotic/logax.h>.
Install the library using powershell. It auto detect your installed C and C++ compilers include directory and install liblogax into the include folder. Execute the command in powershell as admin.
& $([scriptblock]::Create((New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://exoticlibraries.github.io/magic/install.ps1"))) liblogaxUse the remote installation script to install liblogax with bash. If the command is executes with super user priviledge (sudo) it will be installed in the folder /usr/include else it will be installed in the folder /usr/local/include. Or you can specify where to install it using the option --installfolder=./
bash <(curl -s https://exoticlibraries.github.io/magic/install.sh) liblogaxYou can simply download the header file logax.h from the repo into your project source folder and include it in your project. Download the file from here. Then you can include it in your test relatively like #include "logax.h".
The documentation provides several examples, tutorials, and detailed guides for using the library. While reference provides a low-level overview of all the implemented APIs in the library.
Some of the documentation pages are listed below:
- Logging without LogaxLogger
- Logging with LogaxLogger
- Modularity
- Logging levels
- Output Formats
- Callback and Hook
- Options
- How it works
it allows the log to be reported to custom function with optional printing to output stream. The default maximum number of callback that can be registered is 5.
The library can be used to output log without need to setup the LogaxLogger struct, this will require the platform to have output stream or can write to file. If the macro LOGAX_NO_LOGGER is defined before including the logax.h header file, the LogaxLogger struct and all related functions will not be compiled. The following functions provides the API to write to output stream in the supported formats
- logax_write_text_format_to_stream
- logax_write_key_value_format_to_stream
- logax_write_json_format_to_stream
logax_write_text_format_to_stream write the output in plain text format, the first parameter is the stream, followed by the options, the options is the combinations of any of the LOGAX_OPTION_, LOGAX_LEVEL_ and LOGAX_FORMATTER_* macros.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}
// output
// 2021-11-21 06:34:07 TRACE crash_test.c:13 Logging the test for TRACElogax_write_key_value_format_to_stream write the output in a key-value format coloring is ignored in this format, the first parameter is the stream, followed by the options, the options is the combinations of any of the LOGAX_OPTION_, LOGAX_LEVEL_ and LOGAX_FORMATTER_* macros.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_key_value_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}
// output
// date="2021-11-21" time="06:41:34" level="TRACE" file="crash_test.c" line_number=8 function="main" message="This is a trace output"logax_write_json_format_to_stream write the output in a json format, the first parameter is the stream, followed by the options, the options is the combinations of any of the LOGAX_OPTION_, LOGAX_LEVEL_ and LOGAX_FORMATTER_* macros.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_json_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}
// output
// {"date":"2021-11-21","time":"06:42:25","level":"TRACE","file":"crash_test.c","line_number":8,"function":"main","message":"This is a trace output"},In a situation where callback is needed, no FILE* ability on the platform or the flags/options want to be shared across the log, the LogaxLogger struct can be used. No memory allocation is required when initialized.
To iinitialized the LogaxLogger the function logax_init_logger can be used, it not necessary to call the logax_init_logger function, all it does is set the LogaxLogger flags to default value, output_stream to stdout and fill the empty callbacks with NULL, these can be self-managed.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
LogaxLogger logax_logger;
logax_init_logger(&logax_logger);
}For each of the logging level in logax a function is provider that accepts LogaxLogger struct as parameter:
- logax_logger_trace
- logax_logger_debug
- logax_logger_info
- logax_logger_warn
- logax_logger_error
- logax_logger_fatal
Each of the function above invoke the corresponding logax_write_*_format_to_stream respectively, the default formatter when LogaxLogger is initialized with the function logax_init_logger is LOGAX_FORMATTER_TEXT, the output format can be changed using the function logax_set_formatter.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
LogaxLogger logax_logger;
logax_init_logger(&logax_logger);
logax_set_formatter(&logax_logger, LOGAX_FORMATTER_TEXT);
logax_logger_trace(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for TRACE");
logax_logger_debug(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for DEBUG");
logax_logger_info(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for INFO");
logax_logger_warn(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for WARN");
logax_logger_error(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for ERROR");
logax_logger_fatal(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for FATAL");
}LogaxLogger supports callback (or hook), the callbacks are invoked when a new log is sent. The callback can be used to create a custom output format or used to changed out the log is processed (e.g. blink bulb on andruino e.t.c). The output stream can be completely disabled by defining the macro LOGAX_NO_OUTPUT_STREAM or setting the option to QUIET using the function logax_set_quiet, in this case if callbacks are registered they will be invoked with the log event.
The callback function signature is
typedef void (*logax_callback)(const char *date, const char *time, const int level, const char *file, const size_t line_number, const char *function_name, const char *fmt, ...);The example below shows how to register a callback which is invoked when there is a new log
#include <exotic/logax.h>
void on_new_log_callback(const char *date, const char *time, const int level, const char *file, const size_t line_number, const char *function_name, const char *fmt, ...) {
va_list args;
printf("<logevent>");
printf("\n <date>%s</date>", date);
printf("\n <time>%s</time>", time);
printf("\n <level>%s</level>", GET_LEVEL_STRING(level));
printf("\n <file>%s</file>", file);
printf("\n <line_number>%d</line_number>", line_number);
printf("\n <function_name>%s</function_name>", function_name);
printf("\n <message>");
va_start(args, fmt);vfprintf(stdout, fmt, args);va_end(args);
printf("</message>\n</logevent>\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
LogaxLogger logax_logger;
logax_init_logger(&logax_logger);
logax_set_quiet(&logax_logger, 1);
logax_logger_add_callback(&logax_logger, on_new_log_callback);
logax_logger_trace(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for TRACE");
logax_logger_debug(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for DEBUG");
logax_logger_info(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for INFO");
logax_logger_warn(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for WARN");
logax_logger_error(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for ERROR");
logax_logger_fatal(&logax_logger, "%s", "Logging the test for FATAL");
}This gives the following outputs the in XML format as defined in the on_new_log_callback function:
<logevent>
<date>2021-11-21</date>
<time>07:26:02</time>
<level>TRACE</level>
<file>C:\Users\azeez\Documents\OPEN_SOURCE\EXOTIC_LIBRARIES\liblogax\test\crash_test.c</file>
<line_number>25</line_number>
<function_name>main</function_name>
<message>Logging the test for TRACE</message>
</logevent>
<logevent>
<date>2021-11-21</date>
<time>07:26:02</time>
<level>DEBUG</level>
<file>C:\Users\azeez\Documents\OPEN_SOURCE\EXOTIC_LIBRARIES\liblogax\test\crash_test.c</file>
<line_number>26</line_number>
<function_name>main</function_name>
<message>Logging the test for DEBUG</message>
</logevent>
...liblogax currently support only three output format, which are text, key-value and json. To set the output format of a LogaxLogger struct use the function logax_set_formatter. The following are the format options:
- LOGAX_FORMATTER_TEXT
- LOGAX_FORMATTER_KEY_VALUE
- LOGAX_FORMATTER_JSON
Output as text using logax_write_text_format_to_stream
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_text_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}2021-11-21 08:41:19 TRACE crash_test.c:6 --- [main ] Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877
Output as text using the LOGAX_FORMATTER_TEXT option with LogaxLogger.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
LogaxLogger logax_logger;
logax_init_logger(&logax_logger);
logax_set_formatter(&logax_logger, LOGAX_FORMATTER_TEXT);
logax_logger_trace(&logax_logger, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}2021-11-21 08:38:38 TRACE crash_test.c:10 Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877
Output as key value using logax_write_key_value_format_to_stream
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_key_value_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}date="2021-11-21" time="08:43:59" level="TRACE" file="crash_test.c" line_number=6 function="main" message="Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877"
Output as key value using the LOGAX_FORMATTER_KEY_VALUE option with LogaxLogger.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
LogaxLogger logax_logger;
logax_init_logger(&logax_logger);
logax_set_formatter(&logax_logger, LOGAX_FORMATTER_KEY_VALUE);
logax_logger_trace(&logax_logger, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}date="2021-11-21" time="08:46:00" level="TRACE" file="crash_test.c" line_number=10 message="Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877"
Output as json using logax_write_json_format_to_stream
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
logax_write_json_format_to_stream(stdout, LOGAX_OPTION_ALL | LOGAX_LEVEL_TRACE, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}{"date":"2021-11-21","time":"08:44:58","level":"TRACE","file":"crash_test.c","line_number":6,"function":"main","message":"Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877"},Output as json using the LOGAX_FORMATTER_JSON option with LogaxLogger.
#include <exotic/logax.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
LogaxLogger logax_logger;
logax_init_logger(&logax_logger);
logax_set_formatter(&logax_logger, LOGAX_FORMATTER_JSON);
logax_logger_trace(&logax_logger, "%s", "Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877");
}{"date":"2021-11-21","time":"08:45:36","level":"TRACE","file":"crash_test.c","line_number":10,"message":"Enemy approaching from X=108,Y=877"},
liblogax is big on modularity, each component of the library can be excluded at compile time. The following macros if defined will exclude some component from the library:
- LOGAX_USE_OLD_CONSOLE_MODE
- LOGAX_NO_OUTPUT_STREAM
- LOGAX_LOGGER_NO_OUTPUT_STREAM
- LOGAX_LOGGER_NO_CALLBACK
- LOGAX_NO_COLORING
- LOGAX_NO_TIME
If this macro is define the library will use the Windows API to color the log outputs, this macro is only effective on Windows system. This macro is most useful for old windows platform which the console cannot process the ANSI Color Codes.
#define LOGAX_USE_OLD_CONSOLE_MODE
#include <exotic/logax.h>
//...
Note that there might slight different in the color variation between using Windows Console attributes and ANSI Color codes
If this macro is defined the library will not be compiled with the writing to stream feature, both explicit write to streams function logax_write_*_format_to_stream and LogaxLogger loggers will not write to stream, but the callback will still be invoked is any is registered.
#define LOGAX_NO_OUTPUT_STREAM
#include <exotic/logax.h>
//...If this macro is defined the LogaxLogger struct will not be compiled with the writing to stream capability, but the explicit writing to stream functions logax_write_*_format_to_stream will be have the write to stream capability.
#define LOGAX_LOGGER_NO_OUTPUT_STREAM
#include <exotic/logax.h>
//...Define this macro to exclude the callback and hook feature of the library, this does not affect the writing to output stream. You can still write the statement to register hook if needed but it ll have no effect unless this macro is removed.
#define LOGAX_LOGGER_NO_CALLBACK
#include <exotic/logax.h>
//...If this macro is define the library will not be compiled with pretty print capability. The flag LOGAX_OPTION_COLORED will also not be available for use to customize the output.
#define LOGAX_NO_COLORING
#include <exotic/logax.h>
//...On a system that does not have floating point capability or the time headers are not available this macro can be defined to exclude adding data and time capability to the logging. Defining this macro will make the following macros unavailable LOGAX_OPTION_DATE, LOGAX_OPTION_TIME, LOGAX_OPTION_DATE_TIME.
#define LOGAX_NO_TIME
#include <exotic/logax.h>
//...These three internal functions are responsible for the actual logging to output stream,
- logax_write_text_format_to_stream
- logax_write_key_value_format_to_stream
- logax_write_json_format_to_stream
The functions accept variadic parameters, the first 3 parameters are compulsory and the followed X parameters are for the vfprintf function for formatting. The first parameter is the output stream FILE *, the second parameters is the flags to customize the outputs, the third parameter is the fmt to processes the variadic values.
LogaxLogger struct allows logging properties and output stream to be shared across function calls, it internally uses the 3 functions above to output the log. The special feature of LogaxLogger is the callback. On new log entry all the registered callbacks are invoked with the log event.
See the pages at how it works for more explanation.
If you have any issue or you want to request a feature you can open a request here anytime and if you made some changes that should be added to the main project send in a pull request.
- ANSI C
- Exotic Libraries
- Author
- Login icon by Icons8
MIT License Copyright (c) 2021, Adewale Azeez