写代码是单元和分离的艺术。做好单元和分离,管理好抽象和实现,代码就可以测试。
有状态和无状态分离
通常情况下无状态比较好测试,写代码尽可能多的写纯函数(对于固定的输入,有固定的输出)
通过接口隔离耦合
将实现耦合,改为抽象耦合。测试的时候就mock接口
Matcher,用于断言,建议直接使用
gomock来生成代码
参考文章
go官方的mock代码生成工具,可以根据interface生成mock代码
给方法打桩,参考文章
这种打桩方式,通常比较鸡肋,比如变量、函数这类,都需要定义全局变量
和goConvey类似属于BDD测试框架,官方文档
根据struct生成interface,适用解耦既有代码
目录结构
~/c/t/order (master|✔) $ tree
├── application
│ └── db.go
├── clients
│ └── restaurant
│ ├── client.go
│ └── mock_client.go
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── handlers
│ ├── context.go
│ ├── mock_context.go
│ ├── order.go
│ ├── order_test.go
│ └── provider.go // 和service耦合
├── main.go
├── models
│ ├── order.go
│ └── restaurant.go
├── repositories
│ ├── mock_order_repository.go
│ ├── order_repository.go // service interface
│ └── repositories_test.go
└── services
├── mock_order_service.go
├── order_service.go // service interface
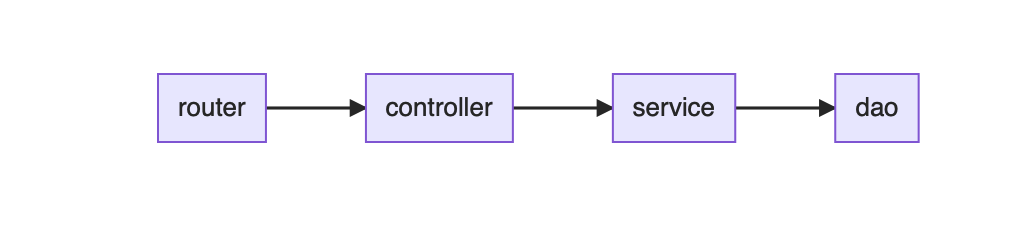
└── services_test.go正常情况下,代码流程如下:
以往的代码都是相互耦合的,即controller和service耦合,service和dao耦合。
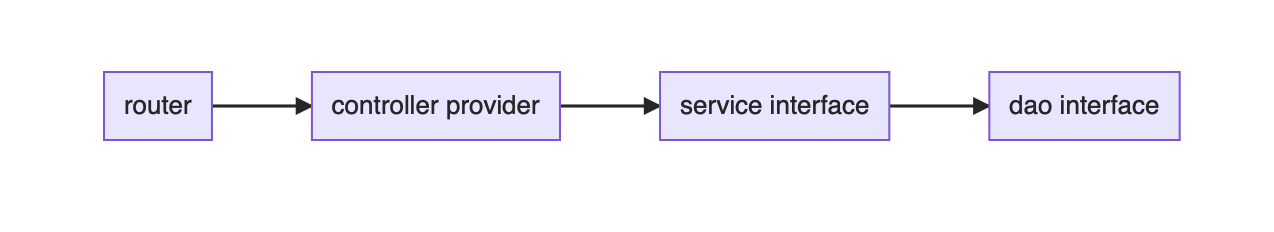
耦合是不可能避免的,但是需要把实现的耦合,转换成接口的耦合。
通过接口耦合,就很容易在test的时候mock实现。
每个被依赖方都需定义接口,比如service部分定义了OrderService接口
type OrderService interface {
FindAllOrderByUserID(userID int) (models.Orders, error)
}在接口的基础上,service根据业务逻辑做了一套实现orderService。
func NewOrderService() *orderService {
return &orderService{}
}
type orderService struct {
db gorm.DB
restaurantClient restaurant.Client
orderRepository repositories.OrderRepository
}
func (s *orderService) SetOrderRepository(r repositories.OrderRepository) {
s.orderRepository = r
}
func (s *orderService) getOrderRepository() repositories.OrderRepository {
if s.orderRepository != nil {
return s.orderRepository
}
s.orderRepository = repositories.NewOrderRepository(application.ResolveDB())
return s.orderRepository
}
func (s *orderService) SetRestaurantClient(c restaurant.Client) {
s.restaurantClient = c
}
func (s *orderService) getRestaurantClient() restaurant.Client {
if s.restaurantClient != nil {
return s.restaurantClient
}
s.restaurantClient = restaurant.NewClient()
return s.restaurantClient
}
func (s orderService) FindAllOrderByUserID(userID int) (models.Orders, error) {
return orders, nil
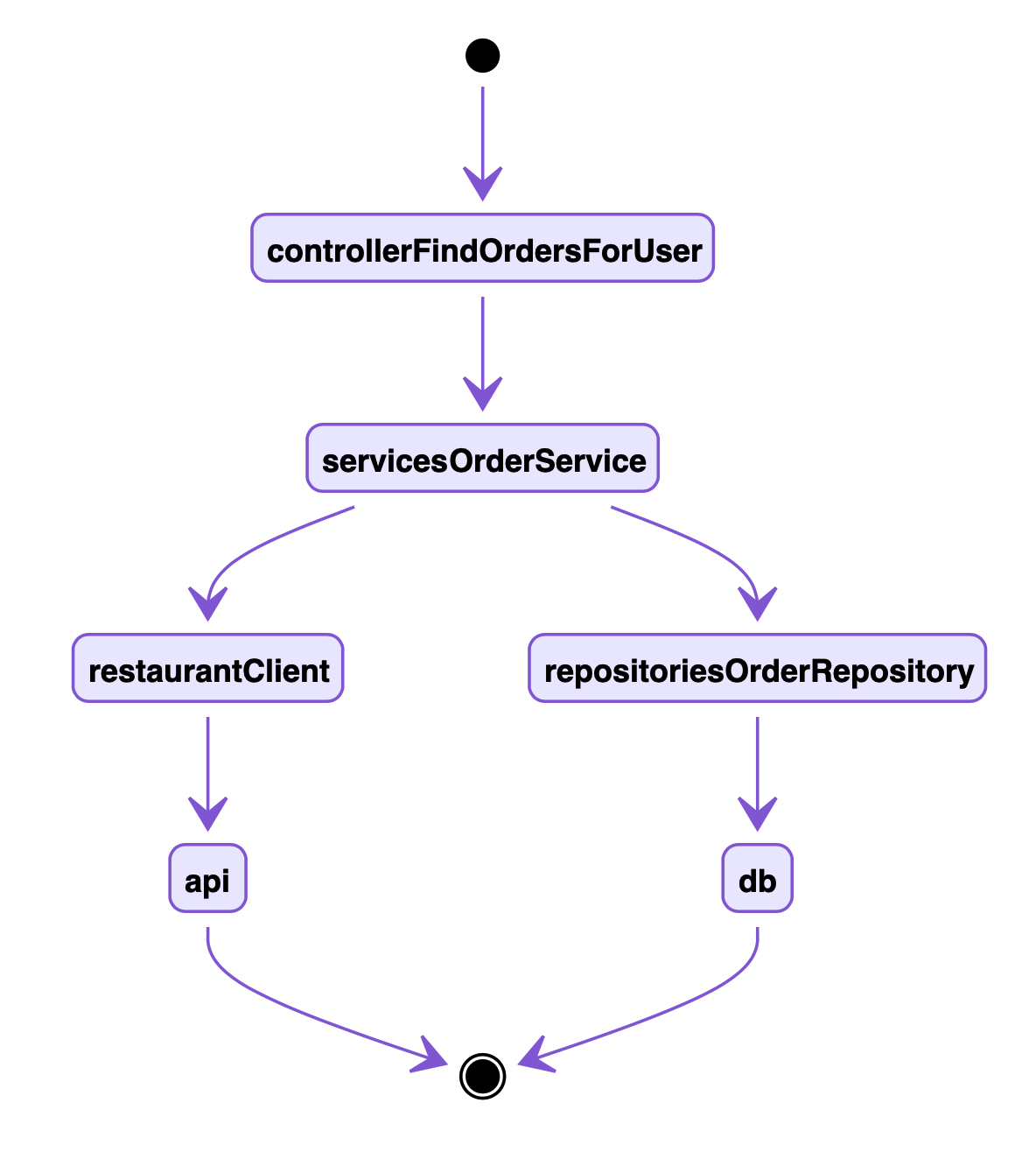
}orderService依赖restaurant.Client和repositories.OrderRepository(都是interface),SetOrderRepository和SetRestaurantClient是提供依赖注入的方式。getOrderRepository和getRestaurantClient是给内部去使用依赖。
先看下依赖关系
在做测试的时候需要先确定单个测试用例的测试范围。
controller里面的findOrdersForUser,只需要mock OrderService来测试,不需要去管service的内部实现(不管是调用啥接口,查询啥数据),只需要关注service可能的返回值情况。
service的单测一般都是比较复杂的,因为业务逻辑会比较多。就我们例子里面FindAllOrderByUserID方法的测试,需要mock restaurant.Client和repositories.OrderRepository的实现,并且要穷举各依赖的各种返回值情况。但是,mock不用关心数据库如何查询,三方接口如何调用,只需要设计好不同的输入和输出就行。
repositories.OrderRepository的单测,需要开启事务做数据测试,记得测试完成之后会滚数据,否者测试用例只能跑一次。当然也可以使用go-testdb库来实现
以测试mysql查询为例子,一共两个用例
- 查询不到数据的情况
- 能查询到数据的情况
func TestRepositories(t *testing.T) {
RegisterFailHandler(Fail)
RunSpecs(t, "Repositories Suite")
}
var _ = Describe("Repositories", func() {
var (
tx *gorm.DB
orderRepo repositories.OrderRepository
orders models.Orders
err error
userID = 5
)
BeforeEach(func() { // 测试前的准备
tx = application.ResolveDB().Begin() // 开启事务,用于测试结束回滚数据
orderRepo = repositories.NewOrderRepository(tx)
})
Describe("FindAllOrdersByUserID", func() {
Describe("with no records in the database", func() { // 测试查询不到数据的情况
It("returns an empty slice of orders", func() {
orders, err = orderRepo.FindAllOrdersByUserID(userID)
Expect(err).To(BeNil())
Expect(len(orders)).To(Equal(0))
})
})
Describe("when a few records exist", func() {
BeforeEach(func() { // 测试数据order1、order2、order3
order1 := &models.Order{
Total: 1000,
CurrencyCode: "GBP",
UserID: userID,
RestaurantID: 8,
PlacedAt: time.Now().Add(-72 * time.Hour),
}
err = tx.Create(order1).Error
Expect(err).To(BeNil())
order2 := &models.Order{
Total: 2500,
CurrencyCode: "GBP",
UserID: userID,
RestaurantID: 9,
PlacedAt: time.Now().Add(-36 * time.Hour),
}
err = tx.Create(order2).Error
Expect(err).To(BeNil())
order3 := &models.Order{
Total: 600,
CurrencyCode: "GBP",
UserID: 7,
RestaurantID: 8,
PlacedAt: time.Now().Add(-24 * time.Hour),
}
err = tx.Create(order3).Error
Expect(err).To(BeNil())
})
It("returns only the records belonging to the user, in order from latest placed_at first", func() {
orders, err = orderRepo.FindAllOrdersByUserID(userID)
Expect(err).To(BeNil())
Expect(len(orders)).To(Equal(2))
Expect(orders[0].RestaurantID).To(Equal(9))
Expect(orders[1].RestaurantID).To(Equal(8))
})
})
})
AfterEach(func() { // 测试完成之后rollback回滚数据
err = tx.Rollback().Error
Expect(err).To(BeNil())
})
})这个例子实际是会做数据库读写的(虽然测试完成之后都回滚了)
正常情况下可以使用数据库事务来进行测试。
使用testdb.SetQueryFunc来stub sql查询
BeforeEach(func() {
testdb.SetQueryFunc(func(query string) (driver.Rows, error) {
columns := []string{"total", "currency_code", "user_id", "restaurant_id"}
result := `
1000,GBP,5,9
2500,GBP,5,8
`
return testdb.RowsFromCSVString(columns, result), nil
})
})