This repository contains the code and configurations for an autonomous navigation system developed using several technologies including Aruco markers, Webots simulator, Yolov5, and a real drone controlled via the tellopy. The system allows for both simulation and real-world testing, focusing on indoor autonomous navigation.
This project provides an system for autonomous navigation and mapping, leveraging various technologies like ARUCO markers, Webots simulation, and deep learning object detection through Yolov5. The system is designed to perform autonomous indoor navigation using drones and can be deployed both in a simulated environment (Webots) and real-world scenarios.
The main goal is to develop a system that can navigate autonomously while mapping its environment. Some of the key technologies used are:
- ARUCO Markers for localization.
- Webots Simulator to replicate real-world environments using Tellopy API.
- Tellopy to control the drone in real-time.
- Yolov5 for object detection and obstacle avoidance.
Several technical challenges had to be addressed:
- Ensuring the integration of ARUCO markers with object detection.
- Achieving accurate indoor navigation with real-time drone control.
- Simulating realistic environments in Webots that replicate real-world conditions.
Before the system can be deployed, several configurations must be set up, including ARUCO tag generation, environment preparation, and network integration.
If you would like to see a detailed step-by-step guide (in Spanish) on how to set up the system, please refer to the following PDF document: Step by Step Guide PDF (Spanish).
Initial setup includes configuring the ARUCO markers, setting up the Webots environment, and preparing the Tellopy API for controlling the drone.
During the setup, error measurements are conducted to ensure that the ARUCO markers and the object detection systems perform with acceptable accuracy.
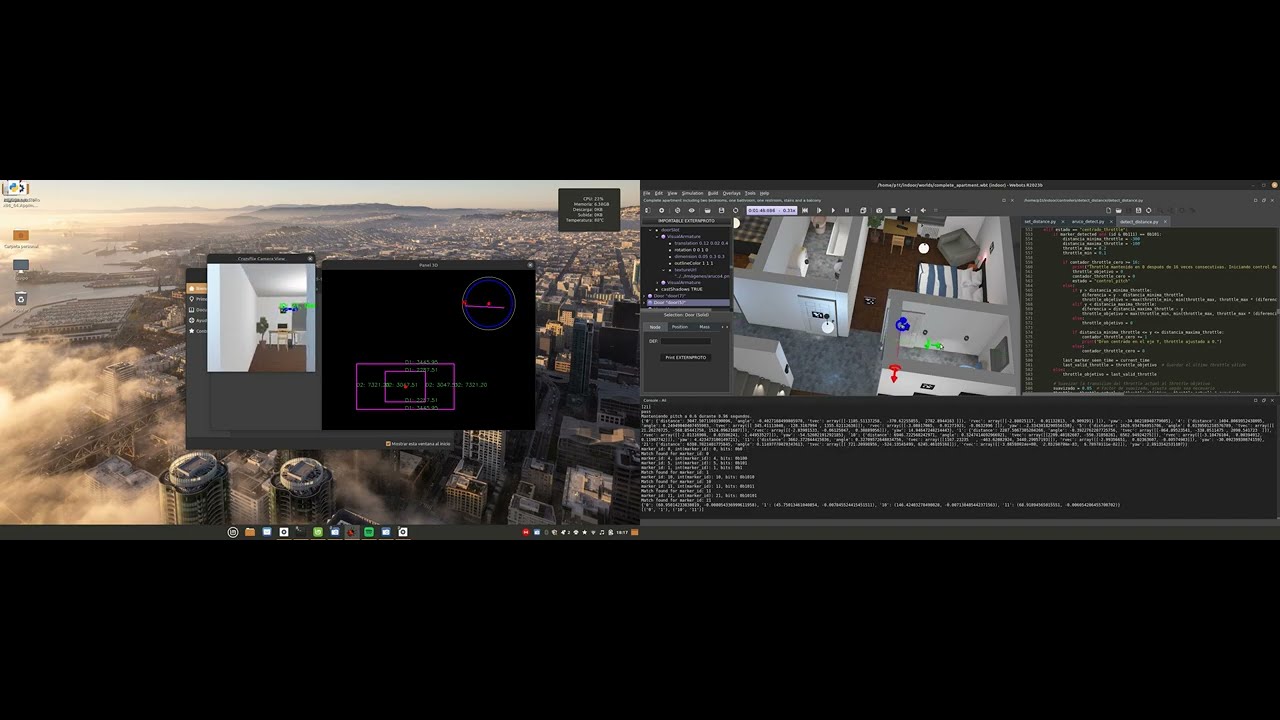
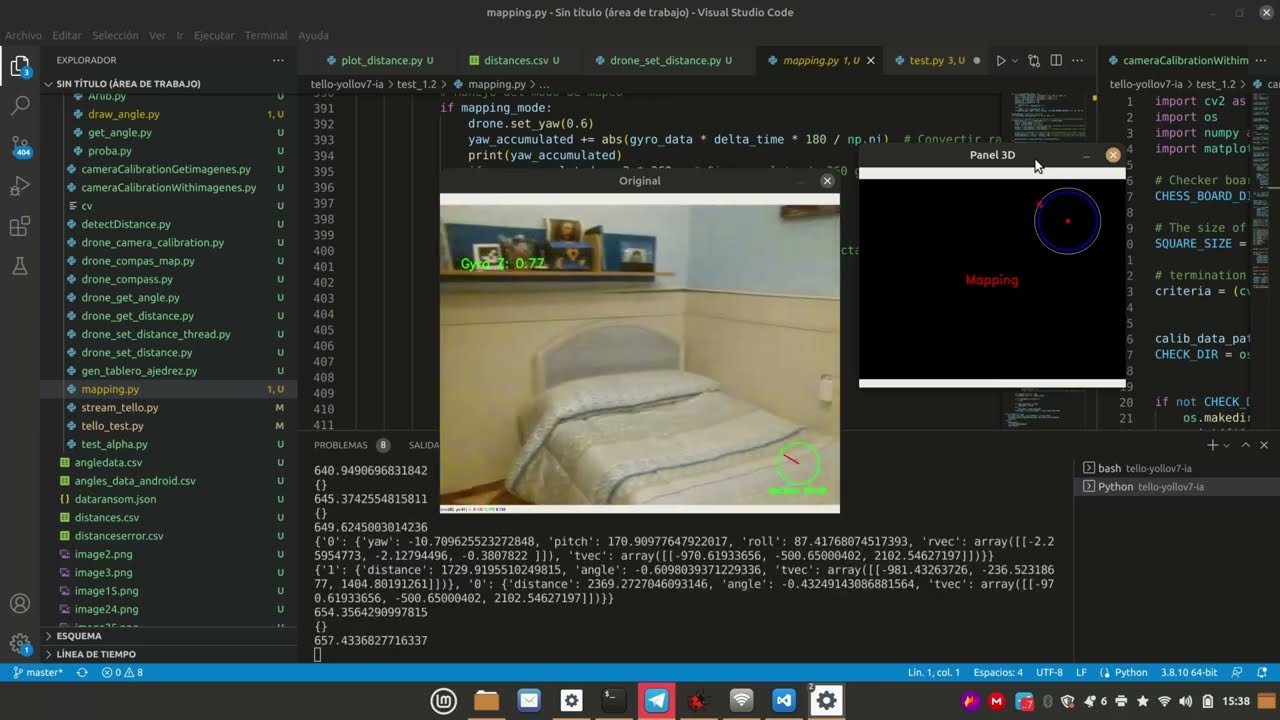
ARUCO markers are used to provide positional data for the drone. The configuration involves generating and placing ARUCO tags in the environment, followed by calibrating the system to detect these tags in real-time.
To replicate real-world conditions, a simulated environment was created in Webots. The drone’s movements and interactions are tested under various scenarios to ensure robustness before transitioning to real-world testing.
A custom API was implemented to mimic the control of a real drone in the Webots simulator, ensuring that commands issued in the simulation are similar to those executed on a physical drone using the Tellopy API.
The system integrates ARUCO marker detection with Yolov5 object detection. This allows the drone to not only navigate based on positional data but also recognize and avoid obstacles detected by Yolov5.
The ARUCO tags are parameterized to provide accurate location data, which is essential for precise navigation within indoor environments.
A GUI was developed to allow users to interact with the system, providing real-time feedback and control over the drone’s navigation.
Navigation control involves real-time adjustments of the drone’s movement based on ARUCO marker detection and object avoidance powered by Yolov5.
The system follows a structured control flow that integrates inputs from ARUCO, Yolov5, and the drone’s onboard sensors to make navigation decisions autonomously.
A Telegram-based alert system was developed to send real-time notifications to the user. Alerts are triggered based on specific events during navigation, such as obstacle detection or route completion.
- Aruco/: Contains code for generating and detecting ARUCO markers.
- Camera Calibration/: Scripts and tools for calibrating the drone's camera for accurate ARUCO detection.
- Real Drone/: Code and configurations for controlling the real drone using the Tellopy.
- Simulation/webots/: Simulation scripts and environment setups for Webots.
- Yolov5/: Object detection scripts and models using the Yolov5 framework.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.