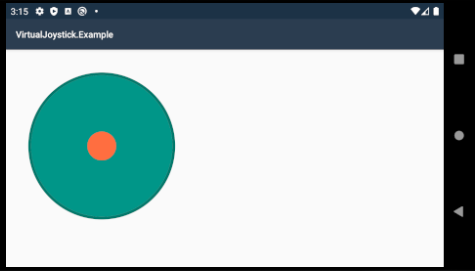
This library provides a very simple and ready-to-use custom view which emulates a joystick for Xamarin.Android.
This repository is just a transfer of the library (https://github.com/controlwear/virtual-joystick-android) from Java to Xamarin.Android(C#). aka .aar -> .dll
just add .dll in your project.
In .axml:
<io.github.controlwear.virtual.joystick.android.JoystickView
android:id="@+id/joystickView"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
app:JV_buttonColor="#FF6E40"
app:JV_buttonSizeRatio="15%"
app:JV_borderColor="#00796B"
app:JV_backgroundColor="#009688"
app:JV_borderWidth="4dp"
app:JV_fixedCenter="false"/>In activity, example in OnCreate():
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.activity_main);
var joystick = FindViewById<JoystickView>(Resource.Id.joystickView);
joystick.Move += JoystickOnMove;
}
private void JoystickOnMove(object sender, JoystickView.MoveEventArgs e)
{
Log.Info("JoystickView",
$"Angle: {e.P0}; " +
$"Power: {e.P1}");
}Initially, the library provides only the angle and power values. But using the code from here, you can translate into coordinates(x,y)
Values may be inaccurate!
Let's do it as an extension method:
JoystickExtensions.cs:
public static class JoystickExtensions
{
public static Point GetPoint(this JoystickView.MoveEventArgs e)
{
var angle = e.P0;
var power = e.P1;
var radians = angle.ToRadians();
var x = Math.Cos(radians);
var y = Math.Sin(radians);
var length = Math.Sqrt( (x*x) + (y*y) );
x /= length;
y /= length;
x *= power;
y *= power;
return new Point((int) x,(int) y);
}
}then, in listener:
private void JoystickOnMove(object sender, JoystickView.MoveEventArgs e)
{
var point = e.GetPoint();
Log.Info("JoystickView",
$"X: {point.X}; " +
$"Y: {point.Y}");
}