-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
53 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ | ||
| # Read Notes: LSDs for Neuron Segmentation | ||
|
|
||
| Here are linshey's Read Notes for <Sheridan, A., Nguyen, T.M., Deb, D. *et al.* (2023): Local shape descriptors for neuron segmentation[^1]>. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Auxiliary-Task Learning | ||
|
|
||
| A major challenge in neuron segmentation is the paucity of labeled data. Auxiliary-Task Learning (ATL) has emerged as a promising technique to address this challenge, which improves the generalization of target tasks by leveraging the useful signals provided by some related auxiliary tasks (which is label-accessible and simple to train)[^2]. For example, single-image depth estimation can be utilized as ATL for semantic segmentation[^3]. | ||
|
|
||
| Given the target task $\mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{tgt}}$ and the auxiliary task $\mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{aux}}$, then the objective is to optimize[^2]: | ||
| $$ | ||
| \min_{\theta} | ||
| \mathbb{E}_{\mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{tgt}}}\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{tgt}}(\theta)+ | ||
| \lambda\mathbb{E}_{\mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{aux}}}\mathcal{L}_{\mathrm{aux}}(\theta) | ||
| $$ | ||
| The hyper parameter $\theta$ is critical to control the gradient/distribution of $\mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{tgt}}$ and $\mathcal{T}_{\mathrm{aux}}$ in appropriate relationship, and to avoid gradient conflicts and negative transfer[^2]. | ||
|
|
||
| In this article[^1], the auxiliary learning task is to predict Local Shape Descriptors (LSDs), a $\mathbb{R}^{10}$ vector denoting some local object statistics. For every voxel $v$, let $S_v$ be a subset of voxels $\{v'|\mathrm{InTheSameSegment}(v,v')\and |v-v'|<\sigma\}$. The $\mathrm{lsd}(v)\in \mathbb{R}^{10}$ is defined as [the size of $S_v$, the offset between $v$ and the mean coordinates of $S_v$, the covariance of $S_v$]. | ||
|
|
||
| An interesting fact is that the conventional ATL architecture in LSDs paper, MtLSD, in which LSDs and nearest neighbor affinities are output in one pass, does not work well. The best-performance network architecture AcRLSD are auto-context setup in which the LSDs from one U-net are fed into a second U-net to produce the affinities.[^1] | ||
|
|
||
| 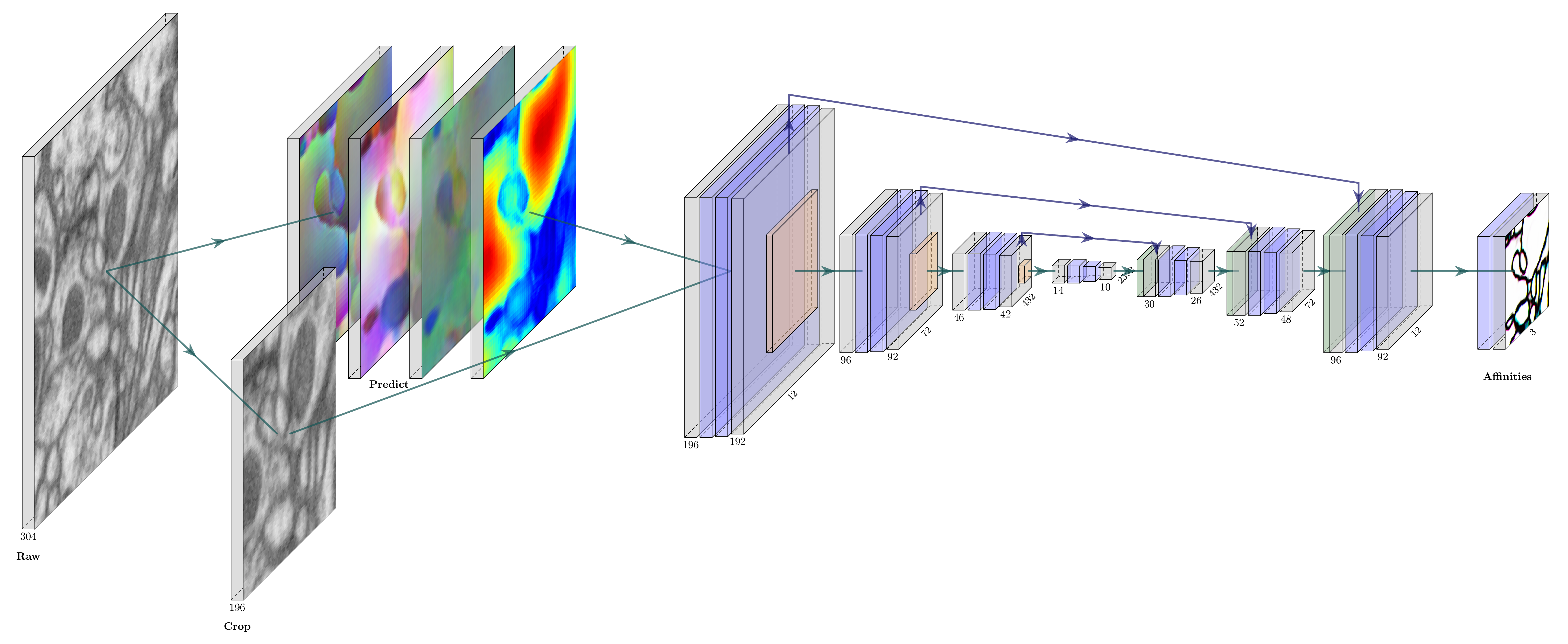](https://localshapedescriptors.github.io/assets/img/lsd.png) | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## 3D U-net | ||
|
|
||
| Intuitively, 3D U-net is quite easy to understand, as you can simply imagine a U-net, in which planar input is replaced by 3D input, and `conv2d` is replaced by `conv3d`. So 3D U-net is a network for volumetric segmentation that learns from sparsely annotated volumetric images and generates dense segmentation.[^3]It is suitable for tasks of sample scarcity due to good generalization performance. The network structure of 3D U-net has nothing special than a up-dimension version of U-net. Here are two figures from 3D U-Net paper.[^4] | ||
|
|
||
| <img src="C:\Users\Lenovo\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20241124165731318.png" width = "500" alt="fig.2" align=center /><img src="C:\Users\Lenovo\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20241124170218020.png" width = "500" alt="fig.2" align=center /> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Post Processing | ||
|
|
||
| How to reconstruct the neurons after receiving affinities from 3D U-net? Funke *et al* (2019)[^5]proposes a solution combining watershed and agglomeration which is also adopted by LSDs.[^1] | ||
|
|
||
| First, extract fragments running a watershed algorithm on the predicted affinities. The fragments are then represented in a region adjacency graph (RAG), where edges are scored to reflect the predicted affinities between adjacent fragments: edges with small scores will be merged before edges with high scores.[^5] (Note: fragment is called supervoxel in LSDs paper). | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| So the reconstruction of neuron is a 2-stage process, prediction of affinities, post processing (such as, watershed + agglomeration). The optimization of the reconstruction process can be categorized by this thinking: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. To optimize the prediction of affinities, such as applying 3D U-net[^6], introducing ATL task for U-net[^1] and Dense Voxel Embeddings[^7]. | ||
| 2. To optimize the training target of prediction network so as to better satisfy the need of post processing, such as utilization of MALIS loss[^5] and min-cut metric[^1]. | ||
| 3. To optimize the the merging of fragments. This part is closely correlated to topology, parallelization and computer graphics. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Refs | ||
|
|
||
| [^1]: Sheridan, A., Nguyen, T.M., Deb, D. *et al.* (2023). Local shape descriptors for neuron segmentation. *Nat Methods* **20**, 295–303 . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01711-z | ||
| [^2]: Jiang, J., Chen, B., Pan, J., Wang, X., Dapeng, L., Jiang, J., & Long, M. (2023). ForkMerge: Mitigating Negative Transfer in Auxiliary-Task Learning. https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12618 | ||
| [^3]: Liebel, L., & Körner, M. (2018). Auxiliary Tasks in Multi-task Learning. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.06334 | ||
| [^4]: Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S. S., Brox, T., & Ronneberger, O. (2016). 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.06650 | ||
| [^5]: Funke, J., Tschopp, F., Grisaitis, W., Sheridan, A., Singh, C., Saalfeld, S., & Turaga, S. C. (2019). Large Scale Image Segmentation with Structured Loss Based Deep Learning for Connectome Reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 41(7), 1669–1680. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2835450 | ||
| [^6]: Lee, K., Zung, J., Li, P., Jain, V., & Seung, H. S. (2017). Superhuman Accuracy on the SNEMI3D Connectomics Challenge. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.00120 | ||
| [^7]: Lee K, Lu R, Luther K, Seung HS. (2021). Learning and Segmenting Dense Voxel Embeddings for 3D Neuron Reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8692755/ |