client application loaded with Server Certificates | Server
--------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------
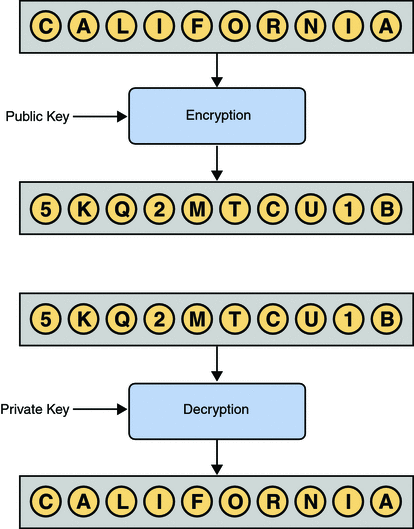
Message ------> [Public Key] -------> Encrypted Message ------|-----> [Private Key]-->Message
| | |
| | |
V | V
TrustStore | Keystore
The trick in a key pair is to
- keep one key secret
(the private key)and - to distribute the other key
(the public key)to everybody.
Anybody can send an encrypted message to the SERVER, that only SERVER will be able to decrypt.
1.2. What is TLS and what are Certificates?
Public Keys, Private Keys, and Certificates
This right person/web server, client has to implicitly trust: client has his/SERVER's certificate loaded in its application/brower (a root Certificate).
Trust Store vs Key Store - creating with keytool
Truststore and Keystore Definitions
Keystore contains private keys, and the certificates with their corresponding public keys.
Essentially, javax.net.ssl.keyStore is meant to contain your private keys and certificates
A Truststore contains certificates from other parties that you expect to communicate with,
or from CAs(Certificate Authorities) that you trust to identify other parties.
Also, javax.net.ssl.trustStore is meant to contain the CA certificates
you're willing to trust when a remote party presents its certificate.
create a keystore -
http://www.backup4all.com/kb/what-is-a-public-private-key-pair-401.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Certificate_authorities