-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 12
Configuring PBench
Create a JSON file for each stage of a benchmark.
Always begin the file with a description.
Set the catalog and schema using catalog and schema.
Use queries and query_files to define the SQL queries to run in a stage.
Use next to define the order of stage files in a benchmark.
For more information, see Parameters.
Use the next parameter in a stage file to define the order of stage files in a benchmark.
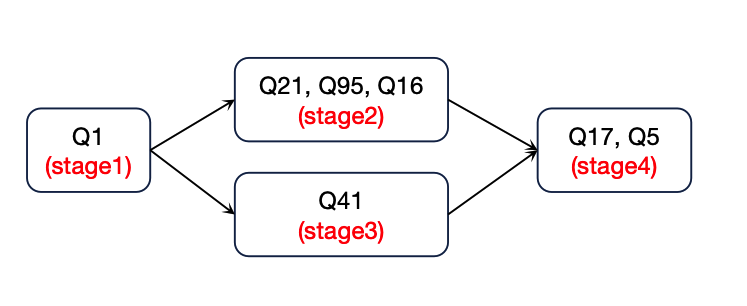
For example, consider the four files stage1.json, stage2.json, stage3.json, and stage4.json:
-
stage1.jsonhas the following entry fornext:"next": [ "stage2.json", "stage3.json" ]
stage2andstage3are started in parallel whenstage1completes.stage2andstage3inherit parameters fromstage1. See Inherited Parameters in Stage Files. -
stage2.jsonandstage3.jsonhave the following entry fornext:"next": [ "stage4.json" ]
stage4inherits its parameters from the stage that starts it:- if
stage3completes beforestage2, thenstage3passes inheritable parameters tostage4 - if
stage2completes beforestage3, thenstage2passes inheritable parameters tostage4
See Inherited Parameters in Stage Files.
When both
stage2andstage3are finished, stage4` is started. - if
-
stage4.jsonis the last stage of the benchmark run and has nonextparameter entry.
A child stage inherits some parameters from its parent stage if those parameters are not explicitly set in the child file. If a child stage has multiple parents, the child stage inherits those parameters from the first of the parent stages that finishes, which starts the child stage.
The parameters that a child stage inherits from a parent stage are:
abort_on_errorcatalogcold_runssave_column_metadatasave_jsonsave_outputschemasession_paramstimezonewarm_runs
New values for catalog, schema, session_params, and timezone assigned in a stage are not applied unless a stage also sets start_on_new_client = true.
For more information, see Parameters.
A query file is a file containing one or more - usually several - SQL queries that are called by the query_files parameter of a stage file. For a query file example, see query_01.sql.
Save the connection information for InfluxDB and MySQL databases in configuration files, then use those configuration files with pbench run with the --influx and --mysql command options.
NOTE:
An example configuration template for InfluxDB namedinfluxdb.template.jsoncan be found in the PBench repository. Copyinfluxdb.template.jsonto the directory local to PBench and edit it as appropriate.
Create a file named influxdb.json similar to the following example and edited as appropriate in the directory local to PBench.
Use --influx influxdb.json with pbench run to call the new file.
{
"url": "https://example.com)",
"org": "myorg",
"bucket": "benchmark",
"token": "*******=="
}NOTE:
An example configuration template for MySQL namedmysql.template.jsoncan be found in the PBench repository. Copymysql.template.jsonto the directory local to PBench and edit it as appropriate.
Create a file named mysql.json similar to the following example and edited as appropriate in the directory local to PBench.
Use --mysql mysql.json with pbench run to call the new file.
{
"username": "presto",
"password": "*******",
"server": "localhost",
"database": "test"
}For more information, see Running PBench.