Fast CPython extensions to Python standard library with focus on performance.
This library provides CPython native extensions to mimic some of the well known built-in types. The implementation relies on enforced protocol - all the objects and abstract data types are implemented in C/C++ to provide highly effective manipulation.
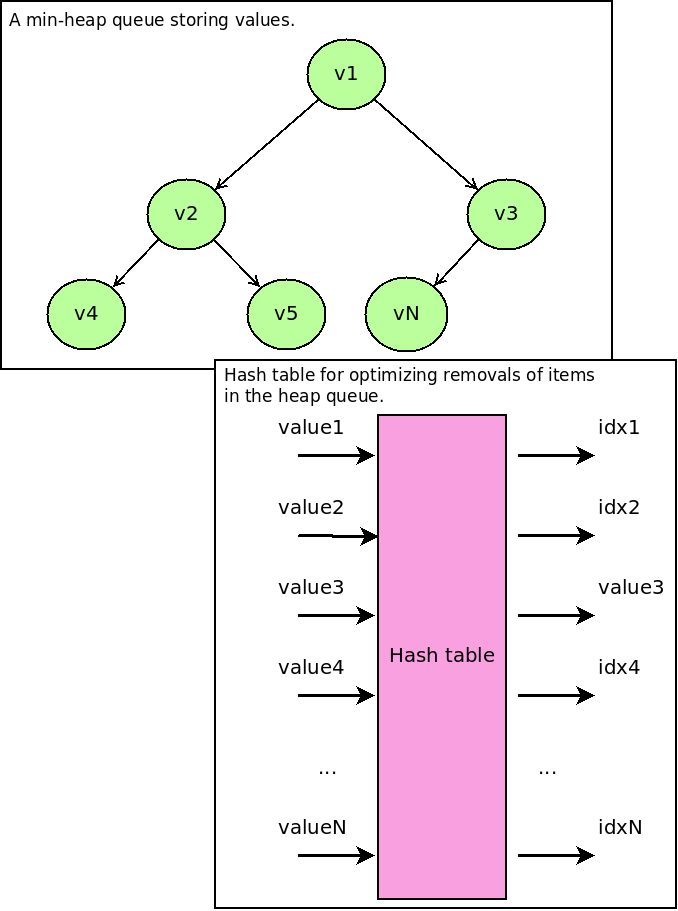
The extended heap queue acts as a min-heap queue from the standard Python library. It uses a hash table for storing information about indexes (where values sit in the min-heap queue) to optimize removals from the heap to O(log(N)) in comparision to the original O(N+N*log(N)).
The design of this library allows you to use sources in your C++ project as
well. The eheapq.hpp file defines the extended heap queue and edict.hpp the
extended dictionary. Python files then act as a bindings to their respective
Python interfaces. Mind the API design for the templated classes - it was meant to
be used with pointers to objects (so avoid possible copy constructors).
To build extensions, install the following packages (Fedora):
dnf install -y python3-devel g++ gccNow you can build extensions:
python3 setup.py buildIf you would like to produce binaries with debug information:
CFLAGS='-Wall -O0 -ggdb' python3 setup.py buildCheck sections below for more info on testing the C/C++ parts of extensions.
When building extension for a more recent Python releases (e.g. Python 3.8) build the extension inside the container image so that it provides required libraries with the required symbols:
`console
cd fext/
podman run --rm --workdir /io --entrypoint bash -it --volume `pwd`:/io:Z quay.io/pypa/manylinux2014_x86_64
yum install -y rh-python38-python-setuptools-wheel rh-python38-python rh-python38-python-devel rh-python38-python-wheel
scl enable rh-python38 bash
python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
auditwheel repair dist/*
twine upload dist/*
`
You can find Makefile in the Git repo. This repo defines targets to
perform leak checks and reference count checks. Note they use different Python
interpreters (with/without debug information) so make sure you do not mix
virtual environments when running the tests.
make checkFirst, prepare your environment:
dnf install -y make
make depsTo develop or adjust sources, simply change sources and verify your change is accepted by the test suite:
make check
The check target will run the actual test suite (see also make test).
Besides it, the test suite will be executed two more times to check test suite
and its behaviour with respect to Python object reference counting
(python3-debug dependency will be automatically installed with the provided
make deps). This part of the test suite can be executed using make
check-refcount. The last part of the test suite runs valgrind against the
test suite - you can explicitly trigger this part by calling make
check-leaks.
Mind make check-refcount and make check-leaks will take some time given the
checks and processing that is done on the background. To verify your changes
more iterativelly, make test should do the trick (don't forget to do make
check after that though).
To clean up your environment, perform:
make cleanThe release can be done from a containerized environment:
podman run --rm --workdir /io --entrypoint bash -it --volume `pwd`:/io:Z quay.io/pypa/manylinux2014_x86_64 -c "yum install -y make && make all"To check what's happening, let's run a containerized environment - this can be helpful when you are testing or developing the extension:
podman run --rm --workdir /io --entrypoint bash -it --volume `pwd`:/io:Z quay.io/pypa/manylinux2014_x86_64The following commands (run in the container stated above) will install all the necessary tools:
yum install -y make
make depsOnce tests pass, clean the environment:
make cleanNow we should be ready to produce bdist_wheel and sdist distribution
for PyPI:
python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
python3 setup.py sdistFinally, upload artifacts to PyPI:
auditwheel repair fext/*.whl
twine upload wheelhouse/*.whlAlternativelly you can let make all happen.
The project is hosted on PyPI. You can
install it via pip or Pipenv:
pipenv install fext
# pip3 install fextIf there is no release conforming your system, a build process is triggered
during the installation - requires python3-devel and gcc/g++.
These data structures were designed for Thoth's adviser - for data kept in resolver's internal state as well as in the reinforcement learning part.