-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Home
Deep linking is a techniques in which the user directly redirect to the specific pages of the application by click on the deeplink url.
There are two types deeplinking
-
Normal deeplinking - Direct deep linking occurs when a user already has your app installed on their device. When this is the case, the deep link will redirect the user to the screen specified in the link.
-
Deferred deeplinking - Deferred deep linking occurs when a user does not have your app installed on their device. When this is the case, the deep link will first send the user to the device app store to install the app. Once the user has installed and opened the app, the SDK will redirect them to the screen specified in the link.
Please check below the Deeplinking scenario
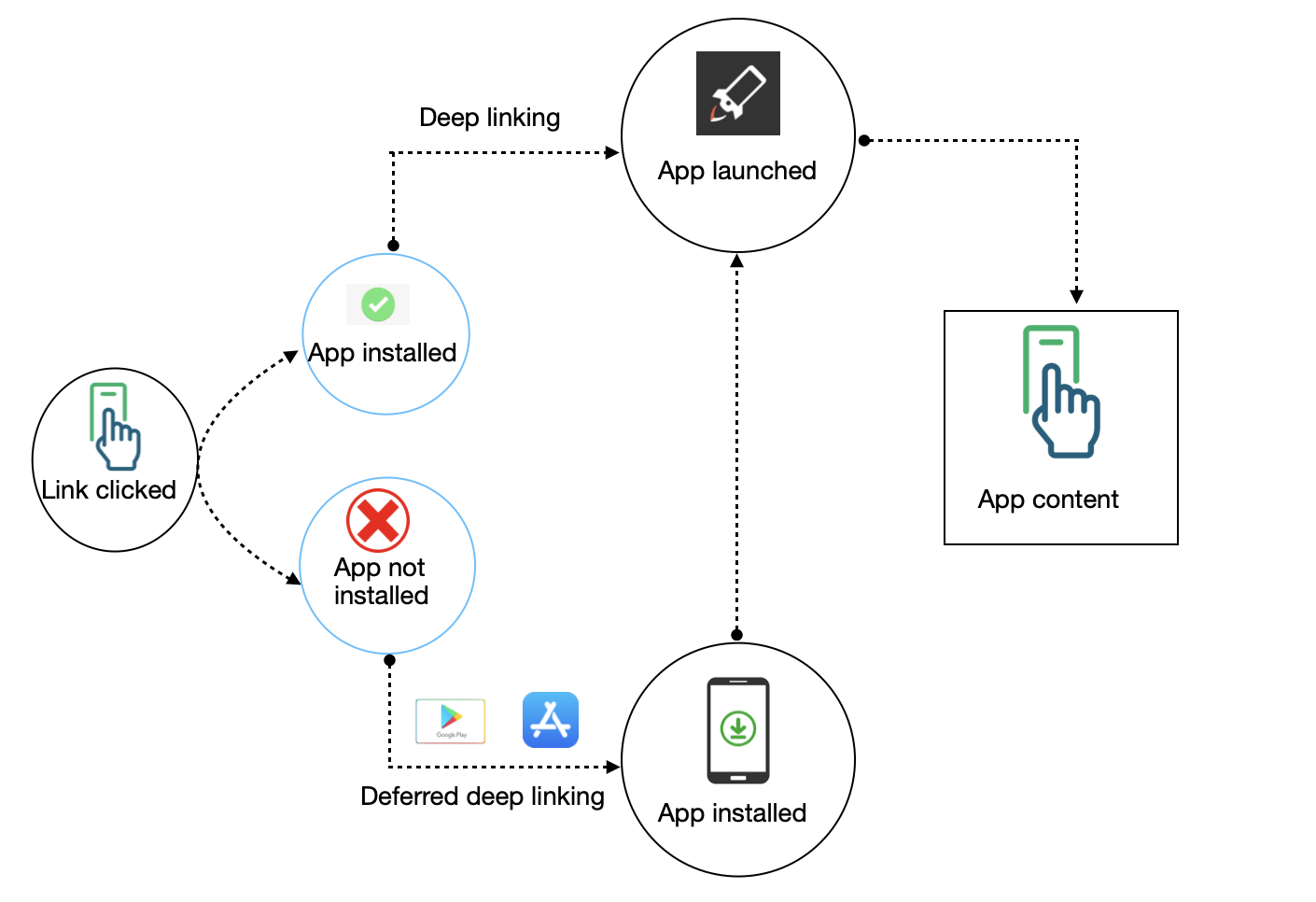
If a user already has your app on their device, it will open when they interact with a tracker containing a deep link. You can then parse the deep link information for further use. To do this, you need to choose a desired unique scheme name.
You can set up a specific activity to launch when a user interacts with a deep link. To do this:
- Assign the unique scheme name to the activity in your AndroidManifest.xml file.
- Add the intent-filter section to the activity definition.
- Assign an android:scheme property value with your preferred scheme name.
For example, you could set up an activity called FirstActivity to open like this:
<activity
android:name=".Activity.FirstProduct"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:host="trackier.u9ilnk.me"
android:pathPrefix="/product"
android:scheme="https" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
To open your app when a user clicks on a tracker URL, add its scheme name to the Trackier tracker as a deep_link parameter. A tracker URL without any extra information might look like this:
https://trackier.u9ilnk.me/product?dlv=FirstProduct&quantity=10&pid=sms
After follow the above example, your app will open when a user interacts with a trackier URL and it will launch the FirstProduct activity as per our example. You will receive information about the deep_link parameter content inside the FirstProduct class.
The SDK will deliver deep link information within the Intent object of your activity. It uses either the activity's onCreate or onNewIntent methods to do this. Once you have launched your app and triggered one of these methods, you can access the deep link content. You can then use this information in other places in your app.
You can extract deep link content from either of these methods like this:
Using the onCreate method:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.product_first);
Intent intent = getIntent();
Uri data = intent.getData();
// data.toString() -> This is your deep_link parameter value.
}
Using the onNewIntent method:
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent);
Uri data = intent.getData();
// data.toString() -> This is your deep_link parameter value.
}
Deferred deep linking happened, when a user does not have your app installed on their device. When the user clicks a trackier URL, the URL will redirect them to the Play Store to download and install your app. When the user opens the app for the first time, the SDK will read the deep_link content.
The Trackier SDK opens the deferred deep link by default. just need to add some code in application class just after initilazation of Trackier SDk
Below are the example of the code :-
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Intent;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import com.trackier.sdk.DeepLink;
import com.trackier.sdk.DeepLinkListener;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
DeepLinkListener deepLinkListener=new DeepLinkListener() {
@Override
public void onDeepLinking(@NonNull DeepLink deepLink) {
if(deepLink.getDeepLinkValue().equalsIgnoreCase("DeepLinkActivity")){ //This activity/class name should be same as mmp unlink dlv.
Intent intent= new Intent(MainApplication.this, MainActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
final String TR_DEV_KEY = "XXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-80e3-5938fadff"; //Please pass your Development key here.
/*While Initializing the Sdk, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
TrackierSDKConfig sdkConfig = new TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_DEV_KEY, "development");
sdkConfig.setDeepLinkListener(deepLinkListener);
sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); // Pass true value to disable organic tracking.
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig);
}
}