-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Power Systems
The battery capacity tells you how much power the battery itself actually stores. A larger capacity will lead to a larger battery and an increased amount of power stored.
The battery voltage is the voltage that should be supplied at the battery's terminals. As a battery cannot always output a constant voltage, the labeled voltage is typically voltage at the lower bound of the battery's cycle.
To get high voltage ratings, batteries are typically comprised of multiple cells wired in series. Depending on the type of battery, this information may or may not be provided. As a very basic example, Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) type batteries (those typically used as the standard AA and AAA type batteries) are usually rated to 1.2V per cell. To achieve a higher voltage output using this technology, multiple of these cells are simply added in series.
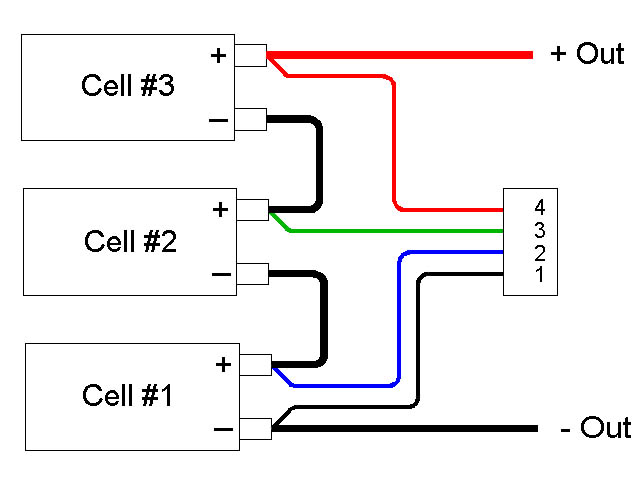
For example, a Lithium Polymer (LiPo) type battery may be labeled as 11.1V (3S). This would tell you that the battery will run flat at 11.1V, and is actually comprised of 3 individual LiPo cells wired, with the S label meaning the cells are wired in series.
The discharge rating of a battery is a critical property to consider when selecting a battery to use, and is highly dependent on your application. The discharge rating is usually given in the form xxC, where x is a multiplier value for the capacity rating.
As an example, a battery with a capacity of 2000mAh and discharge rating of 25C would mean that you could expect the battery to output 50A at peak load without damaging the battery itself. A battery can should be able to output this peak current without much effect, however continuous load or going past this discharge rating will typically cause the output voltage to drop and may cause serious damage to the battery itself.
Note: It is highly recommended to calculate your maximum expected continuous current draw, then add on at least a 25% as a safety barrier to ensure your battery is not damaged (as it is common for hobbyist-grade components to not meet the labeled rating.
Energy density is a measurement of how much energy a battery theoretically contains for how much it weighs. A battery with a high energy density would suggest that it is a "better" option, as it allows you to fit more power into a smaller amount of space, or at a smaller cost in overall weight.
Energy Density is measured in Wh, and can be calculated using the battery voltage, capacity, and mass:
ED = V*C/m

- Home
- Common Terminology
- UAV Setup Guides (2024)
- UAV Setup Guides (2022)
- UAV Setup Guides (2021)
- UAV Setup Guides (--2020)
- General Computing
- On-Board Computers
- ROS
- Sensors & Estimation
- Flight Controllers & Autopilots
- Control in ROS
- Navigation & Localization
- Communications
- Airframes
- Power Systems
- Propulsion
- Imagery & Cameras
- Image Processing
- Web Interfaces
- Simulation