-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Introduction to Front End
- Table of Contents
- INTRODUCTION
- COFFEESCRIPT
- MITHRIL
- MAKING COMPONENTS
- FRONT-END STRUCTURE
- DESIGN
This is an introduction to the front-end of the SuperPhy application. It will cover the combination of software products and programming languages that are currently being used to create the application. Applications typically have two software components: client-side and server-side (also known as front-end and back-end). The front-end tech stack consists of:
- Coffeescript
- Mithril.js
CoffeeScript is basically a shorthand of JavaSciript. In fact, it compiles directly into JavaScript. It's an open-source project that provides a simpler and more readable syntax for JavaScript. Code written in .coffee files are not interpreted at run time, like JavaScript, instead they are compiled into .js files.
Before learning CoffeeScript, I first brushed up on my JavaScript knowledge. It is important to know JS because you need to have a good grasp of it in order for you to successfully understand and debug CS. It's a very concise language which makes it easy to miss what's happening in your code, especially if you don't have a good background knowledge of the underlying language (JS). CS has comparatively less code (no curly braces, semi-colons, e.t.c.) than JS, and it's syntax is closer to natural language than JS. Below is a comparison of the two languages.
JavaScript:
var myFunc;
myFunc = function (myList) {
for(var x in myList) {
console.log(x);
}
};
/*
The syntax for JS is typical to most programming languages
*/And CoffeeScript:
myFunc = (myList) ->
for x of myList
console.log x
return
###
Notice the syntax is simpler
###You should start by working through this JavaScript course on Codecademy, if you don't know JS already. Then go to the various websites listed in the resources page and work through some examples of CS on your own. Don't be afraid to jump in and start working on a feature in your copy of the SuperPhy code, change things and see what happens.
There is also a CoffeeScript tutorial once you are familiar with JS. It should help you with understanding some concepts in CS and Mithril (discussed below).
Creating objects in CS is very similar to JS in syntax and logic. When creating classes, you use the class keyword, and write a function that is invoked upon instantiation (a contructor). When creating an instance of the class, you use the new keyword. When a new instance of a class is created, the constructor of the parent class is invoked (unless you overwrite it).
It's also important to know that there the function in the class named constructor is similar to the __init__ function in Python. Again, similar to python and JS, the keyword this is used in a similar way. Inside a class definition, this refers to the class object. In other words you can set class properties by setting them directly on this.
- The Group Browse pape.
- Table view.
- Map view.
- Tree view.
- The VF & AMR feature.
- Styling on various pages.
Mithril is a front-end MVC JavaScript Framework for building applications. A framework is used to organize code in an easily understandable and maintanable way. It is a comparatively fast and simple JS framework. It's syntax is similar to HTML and CSS (but in JavaScript), which makes it familiar and easy to understand if you know HTML or CSS.
Look at some Mithril code:
m(".panel.panel-default", [
m(".panel-heading", [
m("h3.panel-title", "Panel title")
]),
m(".panel-body", [
"Panel content"
])
])And the equivalent HTML...
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h3 class="panel-title">Panel title</h3>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
Panel content
</div>
</div>

Below you will find more information about the development of the front-end, the file structures on GitHub, and a description and reasoning behind the separation of Model, Component, and Pages.
Each component class should at least have a view method (controllers are optional).
- When creating a class component, make sure the controller does
return @, otherwise the arguments will not be accessible in the view.
The front-end pages are mostly based on the component system of Mithril.js.
Each component class should at least have a view method (controllers are optional). In coffeescript, if the component is a class and it has a controller object with other variables/methods in it, it can be passed to the view if you return @ (equivalent to this in javascript).
class Foo
controller: (args) ->
@someString = args.arg1
@method1= () ->
console.log(args.arg2)
return @
view: (ctrl, args) ->
ctrl.method1() ## Logs "world"
m('.', "Some div")
App =
m.component(Foo, {
arg1: "hello"
arg2: "world"
})In the example above, the object {arg1: "hello", arg2: "world"} is passed in as an argument to Foo, and can be accessed through the args parameter (in both the controller and view). Furthermore, the controller can be accessed in the view through the ctrl parameter.
WARNING: Do not put request methods in a view, as views are redrawn for most user actions like scrolling. Use a config method instead (see Matrix component for example).
mithril
├── bower_components
│ └── mithril-components
├── coffee
│ ├── Components
│ ├── Models
│ └── Pages
│ └── Auth
├── coffee_old
├── css
│ └── font-awesome-4.5.0
├── images
├── js
│ └── d3
└── less
Currently only has the mithril components by eddyystop
Holds all the coffee files for the front-end pages. Folder is split up into more directories:
-
Components: Reusable components of the pages -
Models: Data models -
Pages: Page "skeletons" for the components
All .coffee files are compiled into a one-page Javascript file.
Old Coffeescript code. Most likely not relevant anymore.
Compiled CSS from the less files, in addition to CSS libraries (i.e. Font Awesome and Bootstrap). All of these files are gitignored.
All Less styling files.
TODO: Describe organisation here...
- Genome Explorer
- Group Builder - Map
- Group Builder - Tree
- Group Builder - Metadata Table
- Group Builder - AMR
- Group Builder - VF. See Group Builder - AMR
- Group Builder - Create
- Group Builder - Modify/Merge
- Genome Analysis - Select
- Genome Analysis - Epidemiological Visualisation
- Genome Analysis - Select AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select VF. See Genome Analysis - Select AMR
- Genome Analysis - Gene Distribution
- Genome Analysis - Gene Info
- Genome Analysis - Predictive Genomics
- Genome Analysis - Predictive Genomics Results
GroupModel contains a subset of genomes and associated metadata. There may need to be a cap on the size of a group. GroupModels contains a collection of groups that are active on a page. This class is an interface to the groups and triggers actions for all groups in collection as well as individual group actions. GroupModelPlus extends the parent GroupModel; it also contains gene linkages for group members. GroupModel and GroupModel models are used in pages:
- Genome Explorer
- Group Builder - Map
- Group Builder - Tree
- Group Builder - Metadata Table
- Group Builder - AMR
- Group Builder - VF. See Group Builder - AMR
- Group Builder - Create
- Group Builder - Modify/Merge
- Genome Analysis - Select
- Genome Analysis - Epidemiological Visualisation
- Genome Analysis - Select AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select VF
- Genome Analysis - Gene Info
GroupList lists several selectable groups
GenomeNames model is used in pages:
Contains a summary of visible genomes locations. GenomeLocations model is used in pages:
Contains a summary of genome phylogeny for different tree resolutions. GenomePhylo model is used in pages:
A subset of genome metadata. GenomeMetaPage model is used in pages:
One or more gene features can be linked to each genome. Async requests may be needed if the number of genomes linked is too large. Genes model is used in pages:
- Group Builder - AMR
- Group Builder - VF
- Genome Analysis - Select AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select VF
BuildMenu component is used in pages:
GroupMenu component is used in pages:
GenomeWidget coordinates genome visualisation components (e.g. Map, Tree) with state components (e.g. GenomeList) and controls (e.g. MetadataDisplayControl). SelectionGenomeWidget and DisplayGenomeWidget extend the parent GenomeWidget. It is used in pages:
- Group Builder - Map
- Group Builder - Tree
- Group Builder - Metadata Table
- Group Builder - AMR
- Genome Analysis - Epidemiological Visualisation
- Genome Analysis - Gene Info
Shows distribution of genomes on a geospatial world map. SelectionMap and DisplayMap extend the main parent Map component. It is used in pages:
Shows phylogeny of genomes for different levels/resolutions. SelectionTree and DisplayTree extend the main parent Tree component. It is used in pages:
Shows genome metadata in table format. Using async request to pull down subsets of genome data. SelectionMetaTable and DisplayMetaTable extend the main parent MetaTable component. It is used in pages:
GenomesList shows an active subset of genomes and their metadata properties. Unlike table, GenomesList does only shows a subset of genomes and should not require paging and should fit into memory. SelectionGenomesList and DisplayGenomesList extend the main parent GenomesList component. It is used in pages:
- Group Builder - Map
- Group Builder - Tree
- Group Builder - Metadata Table
- Group Builder - Create
- Group Builder - Modify/Merge
- Group Builder - AMR
- Genome Analysis - Epidemiological Visualisation
MetadataDisplayControl controls what metadata properties are shown in the genome visualisations. It is used in pages:
- Group Builder - Map
- Group Builder - Tree
- Group Builder - Metadata Table
- Group Builder - AMR
- Genome Analysis - Epidemiological Visualisation
- Genome Analysis - Gene Info
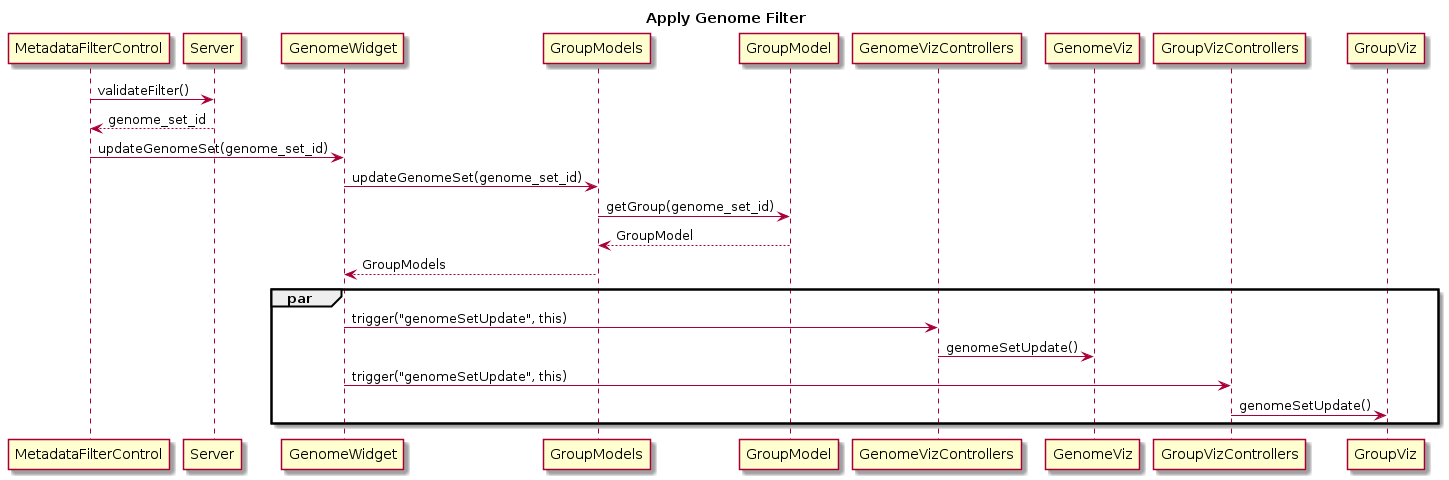
MetadataFilterControl controls what genomes are shown in the genome visualisations, by removing genomes that do not match the specified search criteria. It is used in pages:
- Group Builder - Map
- Group Builder - Tree
- Group Builder - Metadata Table
- Group Builder - AMR
- Genome Analysis - Epidemiological Visualisation
- Genome Analysis - Gene Info
GroupForm is used to add or update new genome groups for a user. NewGenomeForm, UpdateGenomeForm DeleteGenomeForm extend the main parent GroupForm component. It is used in pages:
MergeForm is for combining existing groups using set operations into new groups. It is used in pages:
AnalysisForm is for launching an analysis with a given genome group. It is used in pages:
GeneList displays genes linked to one or more genomes. It has child components GeneCategoryFilter. It is used in pages:
- Group Builder - AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select VF
GeneCategoryFilter can refine a GeneList only displaying certain genes in the model. It is used in pages:
- Group Builder - AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select AMR
- Genome Analysis - Select VF
GeneMatrix displays gene copy number for multiple genes and one or more genomes in matrix format. It has child components GeneCategoryFilter and MetadataFilterControl. It is used in pages:
GeneHistogram displays gene copy number for one gene and one or more genomes in histogram format. It has child components GeneCategoryFilter and MetadataFilterControl. It is used in pages: