-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 332
User Behavior Analysis in Practice 9:Enumerated Dimension and Tag Dimension
We have a user events table T. Below is its structure and part of its data:
| Time | UserID | EventType | OS | Browser | … | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022/6/1 10:20 | 1072755 | Search | Android | IE | … | true | false | false | true | false | … |
| 2022/6/1 12:12 | 1078030 | Browse | IOS | Safari | … | false | false | true | true | true | … |
| 2022/6/1 12:36 | 1005093 | Submit | Android | Chrome | … | true | true | true | false | false | … |
| 2022/6/1 13:21 | 1048655 | Login | Windows | Chrome | … | false | false | true | true | true | … |
| 2022/6/1 14:46 | 1037824 | Logout | Android | Edge | … | false | false | false | true | true | … |
| 2022/6/1 15:19 | 1049626 | AddtoCart | Windows | Edge | … | true | true | false | true | false | … |
| 2022/6/1 16:00 | 1009296 | Submit | IOS | Firefox | … | false | true | false | false | true | … |
| 2022/6/1 16:39 | 1070713 | Browse | IOS | Sogou | … | true | true | true | false | false | … |
| 2022/6/1 17:40 | 1090884 | Search | Windows | IE | … | true | false | true | true | false | … |
Fields in table T:
| Field name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Time | Datetime | Time stamp of an event, accurate to milliseconds |
| UserID | String | User ID |
| EventType | String | Event type |
| OS | String | Operating system, whose value is Android, IOS, Windows, …… or Unknown |
| Browser | String | Browser, whose value is IE, Safari, Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Sogou, …… or Unknown |
| … | String | Other fields that have enumerated values |
| f1 | Boolean | Whether it is an offsite event or not; value is true or false |
| f2 | Boolean | Whether it is a usual device or not; value is true or false |
| f3 | Boolean | Whether it is a usual browser or not; value is true or false |
| f4 | Boolean | Whether it is a cell phone or not; value is true or false |
| f5 | Boolean | Whether it is the first operation; value is true or false |
| … | Boolean | Other fields that have boolean values |
Computing task:
Find the number of occurrences of each type of event performed by users who are not newcomers on a local Android or IOS system using Safari, Edge or Chrome within a specified time period, and count the distinct users under same conditions.
Find more about enumerated dimensions and tag dimensions in What is the Key to Make the Multi-tag User Profile Analysis Run Faster? and Multidimensional Analysis Backend Practice 7: Boolean Dimension and Binary Dimension.
According to the value lists of OS and Browser fields, convert values of corresponding fields in events table T into their ordinal numbers in the lists.
Put every 16 binary fields (f1,…) whose values are true/false in events table T into one group, and store 16 values as bits in an integer field. An integer field stores 16 values of the original fields. Note: SPL optimizes the 16-bit integer and can achieve a fast retrieval. Generally, a 16-bit integer is enough. If there are more than 16 binary dimensions, use more integer fields to store them.
After two conversions, events table T now has the following structure:
| Field name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Time | Datetime | Time stamp of an event, accurate to milliseconds |
| UserID | String | User ID |
| EventType | String | Event type |
| OS | Integer | Operating system, whose values are ordinal numbers in the enumerated sequence |
| Browser | Integer | Browser, whose values are ordinal numbers in the enumerated sequence |
| … | … | … |
| b1 | Integer | An integer field that stores binary fields using bits |
| b2 | Integer | An integer field that stores binary fields using bits |
| … | … | … |
Use SPL ordinal-number-based reference and bitwise operations to perform aggregations.
| A | |
|---|---|
| 10 | =connect("demo").cursor@x("select * from T order by Time") |
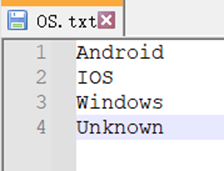
| 11 | =file("OS.txt").import@i() |
| 12 | =file("Browser.txt").import@i() |
| 13 | =A10.new(Time,UserID,EventType,A11.pos(OS):OS,A12.pos(Browser):Browser,……,bits@n(f1,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6,f7,f8,f9,f10,f11,f12,f13,f14,f15,f16):b1,bits@n(f17,…..,f32):b2,……) |
| 14 | =file("T.ctx").create(#Time,UserID,EventType,OS,Browser,……,b1,b2,……) |
| 15 | =A14.append(A13) |
| 16 | >A14.close() |
A10 Import the fact table and sort it by Time.
A11 Import the list of all possible values for OS field.
A12 Import the list of all possible values for Browser field.
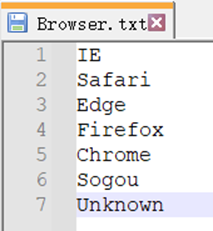
Replace OS field values with the corresponding ordinal numbers in A11, and transform Browser field values to the corresponding ordinal numbers in A12. If the value list is ordered, we can use @b option in pos function and use binary search to locate the targe ordinal number more quickly.
Store every 16 binary fields whose values are true or false into an integer field by bit, 1 represents true and 0 represents false. bits@n means converting true/false into 1/0.
A14 Create composite table file structure.
A15 Append records of A13 to A14’s composite table file.
When there are a lot of enumerated fields, we can name the value list file after the corresponding field name so that expression can be generated automatically. For example:
| A | |
|---|---|
| 6 | [OS,Browser] |
| 7 | =A6.(file(~/".txt").import@i()) |
| 8 | =A6.("A7("/#/").pos("/~/"):"/~).concat@c() |
A6 Define a sequence of enumerated field names.
A7 Import lists of enumerated field values and return the following result:
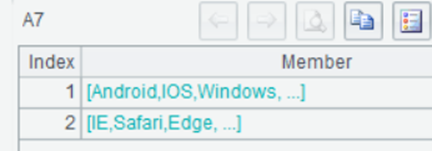
A8 Generate an expression that converts enumerated values into corresponding ordinal number in the enumerated sequence. The result is as follows:
A7(1).pos(OS):OS,A7(2).pos(Browser):Browser
Insert A8’s expression into A13’s expression in step 1 in the form of a macro replacement symbol ${A8}, and the code becomes this:
=A10.new(Time,UserID,EventType, ${A8}, bits@n(f1,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6,f7,f8,f9,f10,f11,f12,f13,f14,f15,f16):b1, bits@n(f17,…..,f32):b2,……)
When there are many binary fields and their names are similar, such as fn, we can automatically generate a bits expression according to them:
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | >n=50 |
| 2 | =n\16 |
| 3 | =A2.((a=(#-1)*16,"bits@n("+16.("f"/(~+a)).concat@c()+"):b"/#)) |
| 4 | ="bits@n("+to(A2*16+1,n).("f"/~).concat@c()+"):b"/(A2+1) |
| 5 | =(A3 |
A1 The number of binary fields.
A2 Find how many integers are needed to store the binary fields.
A3 Automatically piece together a bits@n expression.
A4 Take the rest of the fields whose number is less than 16 as the last integer field and generate expression for it.
Here’s A5’s result:
bits@n(f1,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6,f7,f8,f9,f10,f11,f12,f13,f14,f15,f16):b1,bits@n(f17,f18,f19,f20,f21,f22,f23,f24,f25,f26,f27,f28,f29,f30,f31,f32):b2,bits@n(f33,f34,f35,f36,f37,f38,f39,f40,f41,f42,f43,f44,f45,f46,f47,f48):b3,bits@n(f49,f50):b4
Insert A5’s expression into A13’s expression in step 1 in the form of a macro replacement symbol ${A5}, and the code becomes this:
=A10.new(Time,UserID,EventType, ${A8}, ${A5})
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | >n=50 |
| 2 | =n\16 |
| 3 | =A2.((a=(#-1)*16,"bits@n("+16.("f"/(~+a)).concat@c()+"):b"/#)) |
| 4 | ="bits@n("+to(A2*16+1,n).("f"/~).concat@c()+"):b"/(A2+1) |
| 5 | =(A3 |
| 6 | [OS,Browser] |
| 7 | =A6.(file(~/".txt").import@i()) |
| 8 | =A6.("A7("/#/").pos("/~/"):"/~).concat@c() |
| 9 | =connect("demo").cursor@x("select * from T order by Time") |
| 10 | =A9.new(Time,UserID,EventType, ${A8}, ${A5}) |
| 11 | =file("T.ctx").create(#Time,UserID,EventType,OS,Browser,……,b1,b2,……) |
| 12 | =A11.append(A10) |
| 13 | >A11.close() |
The filtering condition that “users who are not newcomers use Safari/Edge/Chrome on a local Android/IOS system” corresponds to f1 field whose value is 0, f5 field whose value is 0, OS field whose values are Android/IOS and Browser field whose values are Safari/Edge/Chrome.
| A | |
|---|---|
| 12 | =bits(0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) |
| 13 | =bits(1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) |
| 14 | =file("OS.txt").import@i() |
| 15 | =A14.(["Android","IOS"].contain@b(~)) |
| 16 | =file("Browser.txt").import@i() |
| 17 | =A16.(["Chrome","Edge","Safari"].contain@b(~)) |
| 18 | >start=date("2022-03-15","yyyy-MM-dd"),end=date("2022-06-16","yyyy-MM-dd") |
| 19 | =file("T.ctx").open().cursor(UserID, EventType;Time>=start && Time<=end && A15(OS) && A17(Browser) && and(b1,A13)==A12).groups(EventType; count(1):Num, icount(UserID):iNum) |
A12 Set the 4th bit as 1 and all the other bits as 0 according to the filtering condition.
A13 Set the 1st, the 4th and the 5th bits that meet the condition as 1 and all the other bits as 0 according to the filtering condition.
A14 Import the sequence of all possible values for OS field.
A15 According to the filtering condition, generate a sequence of same length as A14’s sequence and having members whose values are whether they meet the filtering condition.
A16 Import the sequence of all possible values for Browser field.
A17 According to the filtering condition, generate a sequence of same length as A16’s sequence and having members whose values are whether they meet the filtering condition.
Filter data in table T’s cursor and perform grouping & aggregation. The bitwise operation and(b1,A13)==A12 in A19 means a filtering condition that the 4th bit is 1 and the 1st and the 5th bit are 0.
Execution result:
| EventType | Num | iNum |
|---|---|---|
| AddtoCart | 945674 | 85476 |
| Browse | 1778901 | 178791 |
| Login | 2033000 | 193400 |
| Logout | 2033000 | 193400 |
| Search | 1547931 | 127539 |
| Submit | 467345 | 43375 |
SPL can automatically generate filtering expressions when there are a lot of enumerated dimensions to be filtered:
| A | |
|---|---|
| 12 | ="{OS:[Android,IOS],Browser:[Chrome,Edge,Safari]}" |
| 13 | =json(A12) |
| 14 | =A13.fname() |
| 15 | =A14.(file(~/".txt").import@i().(A13.field(A14.~).contain(~))) |
| 16 | =A14.("A15("/#/")("/~/")") |
| 17 | =A16.concat("&&") |
A12 Define a JSON string made up of names of to-be-filtered enumerated fields and filtering values.
A13 Convert A12’s JSON string into a table sequence.
A14 Get the sequence of field names from A13.
A15 Generate sequences of boolean values to which corresponding enumerated fields are aligned. When the sequence of enumerated values passed from A12 is ordered, we can use @b option with contain function to speed up the computation.
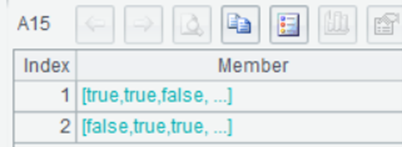
A16 Generate a sequence of filtering expressions.
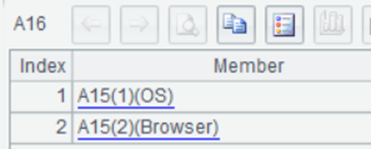
A17 Generate a string of filtering expressions: A15(1)(OS) && A15(2)(Browser)
Insert A17’s expression into A19’s expression in step 5 in the form of a macro replacement symbol ${A17}, and the code becomes this:
=file("T.ctx").open().cursor(UserID, EventType;Time>=start && Time<=end && ${A17} && and(b1,A13)==A12).groups(EventType; count(1):Num, icount(UserID):iNum)
SPL can automatically generate filtering expressions when there are a lot of binary dimensions to be filtered:
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | [1,5,22] |
| 2 | [4,20] |
| 3 | 50 |
| 4 | =[0]*A3 |
| 5 | >A4(A1)=1 |
| 6 | =[0]*A3 |
| 7 | >A6(A1 |
| 8 | =A4.group((#-1)\16) |
| 9 | =A6.group((#-1)\16) |
| 10 | =A8.len().("and(A9("/~/"),b"/~/")==A8("/~/")") |
| 11 | =A10.concat("&&") |
A1 Define a sequence of ordinal numbers of binary fields whose values are required to be true according to the filtering condition.
A2 Define a sequence of ordinal numbers of binary fields whose values are required to be false according to the filtering condition.
A3 The total number of binary fields.
A4 Generate a sequence whose members are 0 and having same length as A3.
A5 Assign 1 to A4’s members whose corresponding values are required to be true.
A6 Generate a sequence whose members are 0 and having same length as A3.
A7 Assign 1 to A6’s members whose corresponding values need to be filtered.
A8 Group A4 by putting every 16 members together.
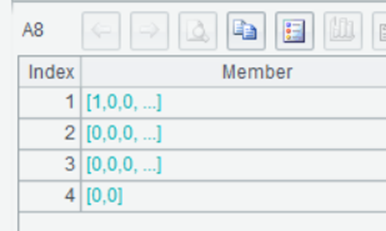
A9 Group A6 by putting every 16 members together.
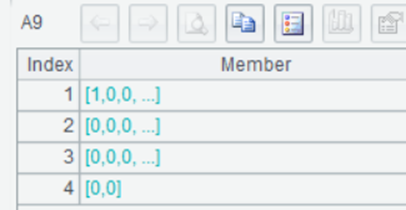
A10 Generate a sequence of filtering expressions.
A11 Concatenate filtering expression into a string.
and(A9(1),b1)==A8(1) && and(A9(2),b2)==A8(2) && and(A9(3),b3)==A8(3) && and(A9(4),b4)==A8(4)
Insert A11’s expression into A19’s expression in step 5 in the form of a macro replacement symbol ${A11}, and the code becomes this:
=file("T.ctx").open().cursor(UserID, EventType;Time>=start && Time<=end && ${A17} && ${A11}).groups(EventType; count(1):Num, icount(UserID):iNum)
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | [1,5,22] |
| 2 | [4,20] |
| 3 | 50 |
| 4 | =[0]*A3 |
| 5 | >A4(A1)=1 |
| 6 | =[0]*A3 |
| 7 | >A6(A1 |
| 8 | =A4.group((#-1)\16) |
| 9 | =A6.group((#-1)\16) |
| 10 | =A8.len().("and(A9("/~/"),b"/~/")==A8("/~/")") |
| 11 | =A10.concat("&&") |
| 12 | ="{OS:[Android,IOS],Browser:[Chrome,Edge,Safari]}" |
| 13 | =json(A12) |
| 14 | =A13.fname() |
| 15 | =A14.(file(~/".txt").import@i().(A13.field(A14.~).contain(~))) |
| 16 | =A14.("A15("/#/")("/~/")") |
| 17 | =A16.concat("&&") |
| 18 | >start=date("2022-03-15","yyyy-MM-dd"),end=date("2022-06-16","yyyy-MM-dd") |
| 19 | =file("T.ctx").open().cursor(UserID, EventType;Time>=start && Time<=end && ${A17} && ${A11}).groups(EventType; count(1):Num, icount(UserID):iNum) |
SPL Resource: SPL Official Website | SPL Blog | Download esProc SPL | SPL Source Code